标签:
本文原创, 转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning
在之前一篇博文中<< Android中View绘制流程以及invalidate()等相关方法分析>>,简单的阐述 了Android View
绘制流程的三个步骤,即:
1、 measure过程 --- 测量过程
2、 layout 过程 --- 布局过程
3、 draw 过程 --- 绘制过程
要想对Android 中View这块深入理解,对这三个步骤地学习是必不可少的 。
今天,我着重讲解下如下三个内容:
1、 measure过程
2、WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT属性的原理说明
3、xml布局文件解析成View树的流程分析。
希望对大家能有帮助。- - 分析版本基于Android 2.3 。
1、WRAP_CONTENT、MATCH_PARENT/FILL_PARENT
初入Android殿堂的同学们,对这三个属性一定又爱又恨。爱的是使用起来挺爽地---照葫芦画瓢即可,恨的
却是时常混淆这几个属性地意义,需要三思而后行。在带着大家重温下这几个属性的用法吧(希望我没有啰嗦)。
这三个属性都用来适应视图的水平或垂直大小,一个以视图的内容或尺寸为基础的布局比精确地指定视图范围
更加方便。
① fill_parent
设置一个视图的布局为fill_parent将强制性地使视图扩展至父元素大小。
② match_parent
Android 中match_parent和fill_parent意思一样,但match_parent更贴切,于是从2.2开始两个词都可以
用,但2.3版本后建议使用match_parent。
③ wrap_content
自适应大小,强制性地使视图扩展以便显示其全部内容。以TextView和ImageView控件为例,设置为
wrap_content将完整显示其内部的文本和图像。布局元素将根据内容更改大小。
可不要重复造轮子,以上摘自<<Android fill_parent、wrap_content和match_parent的区别>>。
当然,我们可以设置View的确切宽高,而不是由以上属性指定。
- android:layout_weight="wrap_content"
- android:layout_weight="match_parent"
- android:layout_weight="fill_parent"
- android:layout_weight="100dip"
接下来,我们需要转换下视角,看看ViewGroup.LayoutParams类及其派生类。
2、ViewGroup.LayoutParams类及其派生类
2.1、 ViewGroup.LayoutParams类说明
Android API中如下介绍:
LayoutParams are used by views to tell their parents how they want to be laid out.
意思大概是说: View通过LayoutParams类告诉其父视图它想要地大小(即,长度和宽度)。
因此,每个View都包含一个ViewGroup.LayoutParams类或者其派生类,View类依赖于ViewGroup.LayoutParams。
路径:frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\View.java
- public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback, AccessibilityEventSource {
- ...
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams mLayoutParams;
- ...
- }
2.2、 ViewGroup.LayoutParams源码分析
路径位于:frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\ViewGroup.java
- public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
- ...
- public static class LayoutParams {
-
-
-
-
-
-
- @Deprecated
- public static final int FILL_PARENT = -1;
-
-
-
-
-
- public static final int MATCH_PARENT = -1;
-
-
-
-
-
- public static final int WRAP_CONTENT = -2;
-
-
-
-
-
- public int width;
-
-
-
-
-
- public int height;
-
-
-
- public LayoutAnimationController.AnimationParameters layoutAnimationParameters;
-
-
-
-
-
- public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
- TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout);
- setBaseAttributes(a,
- R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width,
- R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height);
- a.recycle();
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
- this.width = width;
- this.height = height;
- }
-
-
-
-
-
- public LayoutParams(LayoutParams source) {
- this.width = source.width;
- this.height = source.height;
- }
-
-
-
-
- LayoutParams() {
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
- width = a.getLayoutDimension(widthAttr, "layout_width");
- height = a.getLayoutDimension(heightAttr, "layout_height");
- }
- }
我们发现FILL_PARENT/MATCH_PARENT值为 -1 ,WRAP_CONETENT值为-2,是不是有点诧异? 将值
设置为负值的目的是为了区别View的具体值(an exact size) 总是大于0的。
ViewGroup子类可以实现自定义LayoutParams,自定义LayoutParams提供了更好地扩展性,例如LinearLayout
就有LinearLayout. LayoutParams自定义类(见下文)。整个LayoutParams类家族还是挺复杂的。
ViewGroup.LayoutParams及其常用派生类的类图(部分类图)如下:
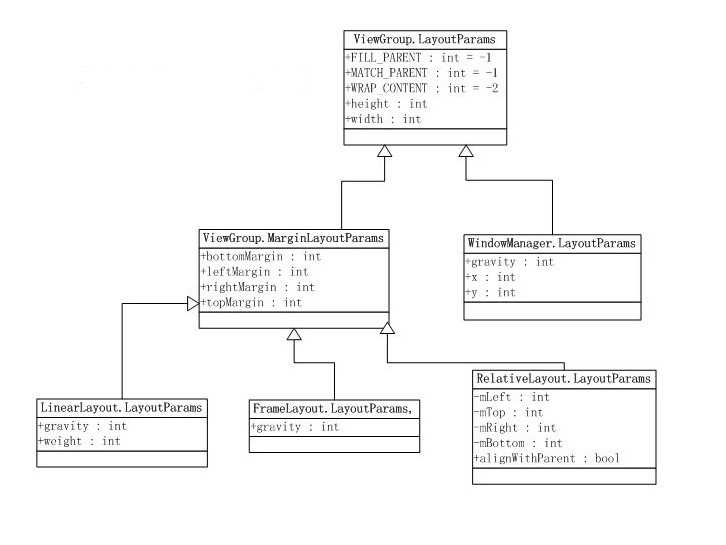
该类图是在太庞大了,大家有兴趣的去看看Android API吧。
前面我们说过,每个View都包含一个ViewGroup.LayoutParams类或者其派生类,下面我们的疑问是Android框架
中时如何为View设置其LayoutParams属性的。
有两种方法会设置View的LayoutParams属性:
1、 直接添加子View时,常见于如下几种方法:ViewGroup.java
-
- void addView(View child, int index)
-
-
- void addView(View child, int width, int height)
-
- void addView(View child, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params)
三个重载方法的区别只是添加View时构造LayoutParams对象的方式不同而已,稍后我们探寻一下它们的源码。
2、 通过xml布局文件指定某个View的属性为:android:layout_heigth=””以及android:layout_weight=”” 时。
总的来说,这两种方式都会设定View的LayoutParams属性值----指定的或者Default值。
方式1流程分析:
直接添加子View时,比较容易理解,我们先来看看这种方式设置LayoutParams的过程:
路径:\frameworks\base\core\java\android\view\ViewGroup.java
- public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
- ...
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public void addView(View child) {
- addView(child, -1);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public void addView(View child, int index) {
- LayoutParams params = child.getLayoutParams();
- if (params == null) {
- params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
- if (params == null) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("generateDefaultLayoutParams() cannot return null");
- }
- }
- addView(child, index, params);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public void addView(View child, int width, int height) {
-
- final LayoutParams params = generateDefaultLayoutParams();
- params.width = width;
- params.height = height;
- addView(child, -1, params);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public void addView(View child, LayoutParams params) {
- addView(child, -1, params);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public void addView(View child, int index, LayoutParams params) {
- ...
-
-
-
- requestLayout();
- invalidate();
- addViewInner(child, index, params, false);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
-
-
- return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
- }
- private void addViewInner(View child, int index, LayoutParams params,
- boolean preventRequestLayout) {
-
- if (!checkLayoutParams(params)) {
- params = generateLayoutParams(params);
- }
-
- if (preventRequestLayout) {
- child.mLayoutParams = params;
- } else {
- child.setLayoutParams(params);
- }
-
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
主要功能就是在添加子View时为其构建了一个LayoutParams对象。但更重要的是,ViewGroup的子类可以重载
上面的几个方法,返回特定的LayoutParams对象,例如:对于LinearLayout而言,则是LinearLayout.LayoutParams
对象。这么做地目的是,能在其他需要它的地方,可以将其强制转换成LinearLayout.LayoutParams对象。
LinearLayout重写函数地实现为:
- public class LinearLayout extends ViewGroup {
- ...
- @Override
- public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
- return new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
- }
- @Override
- protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
-
- if (mOrientation == HORIZONTAL) {
- return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
- } else if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
- return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
- }
- return null;
- }
- @Override
- protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
- return new LayoutParams(p);
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
-
-
-
-
-
-
- @ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(category = "layout")
- public float weight;
-
-
-
-
-
- public int gravity = -1;
-
-
-
- public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(c, attrs);
- TypedArray a =c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout);
- weight = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_weight, 0);
- gravity = a.getInt(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_gravity, -1);
-
- a.recycle();
- }
-
-
-
- public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
- super(width, height);
- weight = 0;
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public LayoutParams(int width, int height, float weight) {
- super(width, height);
- this.weight = weight;
- }
- public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
- super(p);
- }
- public LayoutParams(MarginLayoutParams source) {
- super(source);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
LinearLayout.LayoutParams类继承至ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams类,添加了对android:layout_weight以及
android:layout_gravity这两个属性的获取和保存。而且它的重写函数返回的都是LinearLayout.LayoutParams
类型。这样,我们可以再对子View进行其他操作时,可以将将其强制转换成LinearLayout.LayoutParams对象进行
使用。
例如,LinearLayout进行measure过程,使用了LinearLayout.LayoutParam对象,有如下代码:
- public class LinearLayout extends ViewGroup {
- ...
- @Override
- protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
-
- if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
- measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
- } else {
- measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
- mTotalLength = 0;
- ...
-
- for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
- final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
- ...
-
-
-
- LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
超类ViewGroup.LayoutParams强制转换为了子类LinearLayout.LayoutParams,因为LinearLayout的每个
”直接“子View的LayoutParams属性都是LinearLayout.LayoutParams类型,因此可以安全转换。
PS : Android 2.3源码Launcher2中也实现了自定义的LayoutParams类,在IDLE界面的每个View至少包含如下
信息:所在X方向的单元格索引和高度、所在Y方向的单元格索引和高度等。
路径: packages\apps\Launcher2\src\com\android\launcher2\CellLayout.java
- public class CellLayout extends ViewGroup {
- ...
- public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams {
-
-
-
- public int cellX;
-
-
-
- public int cellY;
-
-
-
- public int cellHSpan;
-
-
-
- public int cellVSpan;
- ...
- public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
- super(c, attrs);
- cellHSpan = 1;
- cellVSpan = 1;
- }
-
- public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
- super(source);
- cellHSpan = 1;
- cellVSpan = 1;
- }
-
- public LayoutParams(int cellX, int cellY, int cellHSpan, int cellVSpan) {
- super(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
- this.cellX = cellX;
- this.cellY = cellY;
- this.cellHSpan = cellHSpan;
- this.cellVSpan = cellVSpan;
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- }
对该自定义CellLayout.LayoutParams类的使用可以参考LinearLayout.LayoutParams类,我也不再赘述了。
方法2流程分析:
使用属性android:layout_heigth=””以及android:layout_weight=”” 时,为某个View设置LayoutParams值。
其实这种赋值方法其实也如同前面那种,只不过它需要一个前期孵化过程---需要利用XML解析将布局文件
解析成一个完整的View树,可别小看它了,所有Xxx.xml的布局文件都需要解析成一个完整的View树。下面,
我们就来仔细走这个过程,重点关注如下两个方面
①、xml布局是如何解析成View树的 ;
②、android:layout_heigth=””和android:layout_weight=””的解析。
PS: 一直以来,我都想当然android:layout_heigth以及android:layout_weight这两个属性的解析过程是在
View.java内部完成的,但当我真正去找寻时,却一直没有在View.java类或者ViewGroup.java类找到。直到一位
网友的一次提问,才发现它们的藏身之地。
3、布局文件解析流程分析
解析布局文件时,使用的类为LayoutInflater。 关于该类的使用请参考如下博客:
<android中LayoutInflater的使用 >>
主要有如下API方法:
public View inflate (XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) public View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup root)
public View inflate (int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot)
这三个类主要迷惑之处在于地三个参数attachToRoot,即是否将该View树添加到root中去。具体可看这篇博客:
<<关于inflate的第3个参数>>
当然还有LayoutInflater的inflate()的其他重载方法,大家可以自行了解下。
我利用下面的例子给大家走走这个流程 :
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
-
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
-
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
-
-
- LayoutInflater layoutInflater = (LayoutInflater)getSystemService();
- View root = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.main, null);
- }
- }
Step 1、获得LayoutInflater的引用。
路径:\frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ContextImpl.java
-
-
-
-
- class ContextImpl extends Context {
- if (WINDOW_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
- return WindowManagerImpl.getDefault();
- } else if (LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
- synchronized (mSync) {
- LayoutInflater inflater = mLayoutInflater;
-
- if (inflater != null) {
- return inflater;
- }
-
- mLayoutInflater = inflater = PolicyManager.makeNewLayoutInflater(getOuterContext());
- return inflater;
- }
- } else if (ACTIVITY_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
- return getActivityManager();
- }...
- }
继续去PolicyManager查询对应函数,看看内部实现。
路径:frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\policy\PolicyManager.java
- public final class PolicyManager {
- private static final String POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME = "com.android.internal.policy.impl.Policy";
- private static final IPolicy sPolicy;
- static {
-
- try {
- Class policyClass = Class.forName(POLICY_IMPL_CLASS_NAME);
- sPolicy = (IPolicy)policyClass.newInstance();
- }
- ...
- }
- ...
- public static LayoutInflater makeNewLayoutInflater(Context context) {
- return sPolicy.makeNewLayoutInflater(context);
- }
- }
-
-
- public class Policy implements IPolicy{
- ...
- public PhoneLayoutInflater makeNewLayoutInflater(Context context) {
-
- return new PhoneLayoutInflater(context);
- }
- }
-
- public class PhoneLayoutInflater extends LayoutInflater {
- ...
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public PhoneLayoutInflater(Context context) {
- super(context);
- }
- ...
- }
LayoutInflater是个抽象类,实际上我们返回的是PhoneLayoutInflater类,但解析过程的操作基本上是在
LayoutInflater中完成地。
Step 2、调用inflate()方法去解析布局文件。- public abstract class LayoutInflater {
- ...
- public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root) {
-
- return inflate(resource, root, root != null);
- }
-
- public View inflate(int resource, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
-
-
- XmlResourceParser parser = getContext().getResources().getLayout(resource);
- try {
- return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
- } finally {
- parser.close();
- }
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public interface XmlResourceParser extends XmlPullParser, AttributeSet {
-
-
-
-
- public void close();
- }
我们获得了一个当前应用程序环境的XmlResourceParser对象,该对象的主要作用就是来解析xml布局文件的。
XmlResourceParser类是个接口类,更多关于XML解析的,大家可以参考下面博客:
<<android之XmlResourceParser类使用实例>>
<<android解析xml文件的方式(其一)>>
<<android解析xml文件的方式(其二)>>
<<android解析xml文件的方式(其三)>>
Step 3 、真正地开始解析工作 。
- public abstract class LayoutInflater {
- ...
-
-
-
-
-
- public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
- synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
- final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
- Context lastContext = (Context)mConstructorArgs[0];
- mConstructorArgs[0] = mContext;
- View result = root;
-
- try {
-
- int type;
- while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG &&
- type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
-
- }
- ...
- final String name = parser.getName();
- if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
- if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
- throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
- + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
- }
-
- rInflate(parser, root, attrs);
- } else {
-
-
- View temp = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
-
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
-
- if (root != null) {
-
-
- params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
- if (!attachToRoot) {
-
-
- temp.setLayoutParams(params);
- }
- }
-
-
- rInflate(parser, temp, attrs);
-
-
-
- if (root != null && attachToRoot) {
- root.addView(temp, params);
- }
-
-
- if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
- result = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- ...
- return result;
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
- View createViewFromTag(String name, AttributeSet attrs) {
-
- if (name.equals("view")) {
- name = attrs.getAttributeValue(null, "class");
- }
- try {
- View view = (mFactory == null) ? null : mFactory.onCreateView(name,
- mContext, attrs);
-
- if (view == null) {
-
- if (-1 == name.indexOf(‘.‘)) {
- view = onCreateView(name, attrs);
- } else {
- view = createView(name, null, attrs);
- }
- }
- return view;
- }
- ...
- }
-
- public final View createView(String name, String prefix, AttributeSet attrs) {
- Constructor constructor = sConstructorMap.get(name);
- Class clazz = null;
-
-
-
-
- try {
- if (constructor == null) {
-
- clazz = mContext.getClassLoader().loadClass(prefix != null ? (prefix + name) : name);
- ...
- constructor = clazz.getConstructor(mConstructorSignature);
- sConstructorMap.put(name, constructor);
- } else {
-
- if (mFilter != null) {
- ...
- }
- }
-
- Object[] args = mConstructorArgs;
- args[1] = attrs;
- return (View) constructor.newInstance(args);
- }
- ...
- }
-
- }
这段代码的作用是获取xml布局文件的root View,做了如下两件事情
1、获取xml布局的View实例,通过createViewFromTag()方法获取,该方法会判断节点名是API 控件
还是自定义控件,继而调用合适的方法去实例化View。
2、判断root以及attachToRoot参数,重新设置root View值以及temp变量的LayoutParams值。
如果仔细看着段代码,不知大家心里有没有疑惑:当root为null时,我们的temp变量的LayoutParams值是为
null的,即它不会被赋值?有个View的LayoutParams值为空,那么,在系统中不会报异常吗?见下面部分
代码:
-
- public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
- synchronized (mConstructorArgs) {
- ...
- try {
-
- ...
- if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
- ...
- } else {
-
-
- View temp = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null;
-
-
- if (root != null) {
-
-
- params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
- if (!attachToRoot) {
-
-
- temp.setLayoutParams(params);
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- }
- ...
- }
- }
关于这个问题的详细答案,我会在后面讲到。这儿我简单说下,任何View树的顶层View被添加至窗口时,
一般调用WindowManager.addView()添加至窗口时,在这个方法中去做进一步处理。即使,LayoutParams
值为空,UI框架每次measure()时都忽略该View的LayoutParams值,而是直接传递MeasureSpec值至View树。
接下来,我们关注另外一个函数,rInflate(),该方法会递归调用每个View下的子节点,以当前View作为根View
形成一个View树。
-
-
-
-
-
- private void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, final AttributeSet attrs)
- throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
-
- final int depth = parser.getDepth();
- int type;
-
- while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG ||
- parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {
-
- if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {
- continue;
- }
- final String name = parser.getName();
-
- if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) {
- parseRequestFocus(parser, parent);
- } else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
- if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
- throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
- }
- parseInclude(parser, parent, attrs);
- } else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
- throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
- } else {
-
- final View view = createViewFromTag(name, attrs);
- final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent;
-
- final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs);
- rInflate(parser, view, attrs);
- viewGroup.addView(view, params);
- }
- }
- parent.onFinishInflate();
- }
值得注意的是,每次addView前都调用了viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs)去构建一个LayoutParams
实例,然后在addView()方法中为其赋值。参见如下代码:ViewGroup.java
- public abstract class ViewGroup extends View implements ViewParent, ViewManager {
- ...
-
- public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
- return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
- }
- public static class LayoutParams {
- ...
- public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
- TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout);
- setBaseAttributes(a,
- R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_width,
- R.styleable.ViewGroup_Layout_layout_height);
- a.recycle();
- }
- protected void setBaseAttributes(TypedArray a, int widthAttr, int heightAttr) {
- width = a.getLayoutDimension(widthAttr, "layout_width");
- height = a.getLayoutDimension(heightAttr, "layout_height");
- }
-
- }
好吧 ~~ 我们还是探寻根底,去TypeArray类的getLayoutDimension()看看。
路径:/frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/res/TypedArray.java
- public class TypedArray {
- ...
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public int getLayoutDimension(int index, String name) {
- index *= AssetManager.STYLE_NUM_ENTRIES;
- final int[] data = mData;
-
- final int type = data[index+AssetManager.STYLE_TYPE];
- if (type >= TypedValue.TYPE_FIRST_INT
- && type <= TypedValue.TYPE_LAST_INT) {
- return data[index+AssetManager.STYLE_DATA];
- } else if (type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) {
- return TypedValue.complexToDimensionPixelSize(
- data[index+AssetManager.STYLE_DATA], mResources.mMetrics);
- }
-
-
- throw new RuntimeException(getPositionDescription()
- + ": You must supply a " + name + " attribute.");
- }
- ...
- }
从上面得知, 我们将View的AttributeSet属性传递给generateLayoutParams()方法,让其构建合适地 LayoutParams对象,并且初始化属性值weight和height。同时我们也得知 布局文件中的View包括自定义View
必须加上属性layout_weight和layout_height,否则会报异常。
Step 3 主要做了如下事情:
首先,获得了了布局文件地root View,即布局文件中最顶层的View。
其次,通过递归调用,我们形成了整个View树以及设置了每个View的LayoutParams对象。
总结:通过对布局文件的解析流程的学习,也就是转换为View树的过程,我们明白了解析过程的个中奥妙,以及
设置ViewLayoutParams对象的过程。但是,我们这儿只是简单的浮光掠影,更深层次的内容希望大家能深入学习。
本来是准备接下去往下写的,但无奈贴出来的代码太多,文章有点长而且自己也有点凌乱了,因此决定做两篇
博客发表吧。下篇内容包括如下方面:
1、MeasureSpec类说明 ;
2、measure过程中如何正确设置每个View的长宽 ;
3、UI框架正确设置顶层View的LayoutParams对象,对Activity而言,顶层View则是DecorView,
其他的皆是普通View了。
Android中measure过程、WRAP_CONTENT详解以及xml布局文件解析流程浅析(上
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ywq-come/p/5927329.html
