标签:
C# 支持两种类型:"值类型"和"引用类型"。值类型包括简单类型(如 char、int 和 float等)、枚举类型和结构类型。引用类型包括类 (Class)类型、接口类型、委托类型和数组类型。
每个变量必须预先声明其类型。如
int a;
int b = 100;
float j = 4.5;
string s1;
用object可以表示所有的类型。
下表列出了预定义类型,并说明如何使用。
|
类型 |
说明 |
示例 |
范围 |
|
object |
所有其他类型的最终基类型 |
object o = null; |
|
|
string |
字符串类型;字符串是 Unicode 字符序列 |
string s = "hello"; |
|
|
sbyte |
8 位有符号整型 |
sbyte val = 12; |
-128 到 127 |
|
short |
16 位有符号整型 |
short val = 12; |
-32,768 到 32,767 |
|
int |
32 位有符号整型 |
int val = 12; |
-2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647 |
|
long |
64 位有符号整型 |
long val1 = 12; long val2 = 34L; |
-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 到 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 |
|
byte |
8 位无符号整型 |
byte val1 = 12; |
0 到 255 |
|
ushort |
16 位无符号整型 |
ushort val1 = 12; |
0 到 65,535 |
|
uint |
32 位无符号整型 |
uint val1 = 12; uint val2 = 34U; |
0 到 4,294,967,295 |
|
ulong |
64 位无符号整型 |
ulong val1 = 12; ulong val2 = 34U; ulong val3 = 56L; ulong val4 = 78UL; |
0 到 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 |
|
float |
单精度浮点型 |
float val = 1.23F;7位 |
±1.5 × 10−45 到 ±3.4 × 1038 |
|
double |
双精度浮点型 |
double val1 = 1.23; double val2 = 4.56D;15-16 |
±5.0 × 10−324 到 ±1.7 × 10308 |
|
bool |
布尔型;bool 值或为真或为假 |
bool val1 = true; bool val2 = false; |
|
|
char |
字符类型;char 值是一个 Unicode 字符 |
char val = ‘h‘; |
|
|
decimal |
精确的小数类型,具有 28 个有效数字 |
decimal val = 1.23M;28-29 |
±1.0 × 10−28 到 ±7.9 × 1028 |
|
DateTime |
简单转换:
float f = 100.1234f;
可以用括号转换:
short s = (short)f
也可以利用Convert方法来转换:
string s1;
s1=Convert.ToString(a);
MessageBox.Show(s1);
常用Convert方法有:
|
C# |
备注 |
|
Convert.ToBoolean |
|
|
Convert.ToByte |
|
|
Convert.ToChar |
|
|
Convert.ToDateTime |
|
|
Convert.ToDecimal |
|
|
Convert.ToDouble |
|
|
Convert.ToInt16 |
|
|
Convert.ToInt32 |
|
|
Convert.ToInt64 |
|
|
Convert.ToSByte |
|
|
Convert.ToSingle |
|
|
Convert.ToString |
|
|
Convert.ToUInt16 |
|
|
Convert.ToUInt32 |
|
|
Convert.ToUInt64 |
常用科学计算方法:
|
C# |
备注 |
|
Math.Abs |
绝对值 |
|
Math.Sqrt |
开方 |
|
Math.Round |
取整,四舍五入 |
|
Math.Floor |
取整,放弃小数 |
|
Math.Cos |
余弦 |
|
Math.Sin |
正弦 |
|
Math.Tan |
正切 |
|
Math.Exp |
返回e的指定次幂 |
|
Math.Log |
对数 |
|
Math.Pow(x,y) |
数字x的y次幂 |
|
Math.Max(x,y) |
返回较大者 |
|
Math.Min(x,y) |
返回较小者 |
一般为字符串,可以定义带数字的枚举型,示例为:
enum Color
{
Red=1,
Blue=2,
Green=3
}
class Shape
{
public int Fill(Color color)
{
int ii;
switch(color)
{
case Color.Red:
ii=10;
break;
case Color.Blue:
ii=11;
break;
case Color.Green:
ii=12;
break;
default:
ii=-1;
break;
}
return ii;
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
int i;
Shape s1=new Shape();
i=s1.Fill((Color)2);
//i=s1.Fill(Color.Blue);
MessageBox.Show(i.ToString());
}
Enum需要放在class外面,才能被其它class的程序调用。
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
数组是一种排列有序的数据结构,包含于数组中的变量被称为数组的元素,它们都有相同的类型。
int [] array1 = new int[5];
int [,,] array3 = new int[10,20,30];
int [] array1 = new int[] {1,2,4};
array1[0]="a1";
注意,如果定义数组为int[5] ,则从0~4。
line0.GetLength(1)
可以从一个已经赋值的数组array2向未赋值的同等数组array1赋值,用
array1=array2;
这时,array1就变成和array2一样的数组了。
集合可以看成是可以随意添加的数组,因此凡是在使用数组的场合,都可以使用集合。而且集合的元素可以是任意对象,操作也比数组灵活的多。
使用集合时,必须注意集合的生命期问题。如果有两个集合L1和L2,使用了
L1=L2;
后,只要L2生命期没有终结,它的以后的变化就可能会影响到L1的数值。因此在赋值后应该及时销毁或者初始化L2,以免发生不可预见的错误。
使用Contains方法。
ArrayList Array1=new ArrayList();
Array1.Add("as");
bool b1=Array1.Contains("as");
MessageBox.Show(b1.ToString());
利用方法来查找,可以返回两个变量。
object Jmax0(ArrayList v11,ref int jj)
{
int i;
object j0=0;
ArrayList y11=new ArrayList(); //各个不同的元素的集合
int [] y12=new int[v11.Count]; //记录各个元素数量的数组
int xmax=0; //最大的一个元素的数量
for (i=0;i<v11.Count;i++)
{
j0=(object)v11[i];
if (y11.Contains(j0))
{
y12[y11.IndexOf(j0)]++;
}
else
{
y11.Add(j0);
y12[y11.Count-1]=1;
}
}
xmax=y12[0];
j0=(object)y11[0];
for (i=1;i<y11.Count;i++)
{
if(y12[i]>xmax)
{
xmax=y12[i];
j0=(object)y11[i];
}
}
jj=xmax;
return j0;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
ArrayList Array1=new ArrayList();
int jj=0;
double j0=0;
object j1=0;
j0=2.3;
Array1.Add(j0);
j0=2.3;
Array1.Add(j0);
j0=1.000f;
Array1.Add(j0);
j0=2.3;
Array1.Add(j0);
j0=1;
Array1.Add(j0);
j1=Jmax0(Array1,ref jj);
MessageBox.Show(j1.ToString()+" "+jj.ToString());
}
if (x > 10)
if (y > 20)
Console.Write("Statement_1");
else
Console.Write("Statement_2");
<,<=,>,>=
等于:==
不等于:!=
判断字符串string和char用Equals方法。
与:a & b
或:a | b
非:! A
模数运算符 (%) 计算第二个操作数除第一个操作数后的余数。所有数值类型都具有预定义的模数运算符。如
Console.WriteLine(5 % 2); // =1
Console.WriteLine(-5 % 2); // =-1
Console.WriteLine(5.0 % 2.2); // =0.6
Console.WriteLine(-5.2 % 2.0); // =-1.2
经常用模数运算符来判断整数为奇数(=1)或偶数(=0)。
int sum,x;
sum=0;
for(x=1;x<=100;x++)
{
sum+=x;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
int sum=0;
int x=0;
while ((sum<100) & (x<20))
{
x++;
sum+=x;
}
string s2=Convert.ToString(x);
MessageBox.Show(s2);
}
运行显示14。
如果改为
while ((sum<100) | (x<20))
运行显示20。
switch (i)
{
case 0:
CaseZero();
break;
case 1:
CaseOne();
break;
default:
CaseOthers();
break;
}
每个case后面,必须有break或者goto,不允许贯穿。
goto 语句将程序控制直接传递给标记语句。
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < y; j++)
if (myArray[i,j].Equals(myNumber))
goto Found;
Console.WriteLine("The number {0} was not found.", myNumber);
goto Finish;
Found:
Console.WriteLine("The number {0} is found.", myNumber);
Finish:
Console.WriteLine("End of search.");
foreach 语句为对数组或者集合中的每个元素重复执行嵌入语句。对于数组示例为:
using System;
class MainClass
{
public static void Main()
{
int odd = 0, even = 0;
int[] arr = new int [] {0,1,2,5,7,8,11};
foreach (int i in arr)
{
if (i%2 == 0)
even++;
else
odd++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Found {0} Odd Numbers, and {1} Even Numbers.",
odd, even) ;
}
}
退出当前的循环。
也可以退出当前模块,使用一个空while循环,示例如下:
void CH(double X1)
{
bool bl=true;
while (bl)
{
if (X1==1.0)
{
MessageBox.Show("YES");
break;
}
MessageBox.Show("no");
bl=false;
}
}
对于控制台程序:
Console.WriteLine("Found {0} Odd Numbers, and {1} Even Numbers.",odd, even) ;
对于普通系统:
int x=1,y=2;
string s0;
s0=string.Format("Found {0} Odd Numbers, and {1} Even Numbers.",x, y);
MessageBox.Show(s0);
用指定字符和数字说明格式。C(货币格式,用NumberFormatInfo指定种类)D(十进制整数)E(科学计数法)F(固定点)G(常规)N(数字)P(百分比)等。
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture = new CultureInfo("en-us");
double MyDouble = 123456789;
Console.WriteLine(MyDouble.ToString("C1"));
Console.WriteLine(MyDouble.ToString("E"));
Console.WriteLine(MyDouble.ToString("P"));
Console.WriteLine(MyDouble.ToString("N3"));
Console.WriteLine(MyDouble.ToString("F"));
运行显示:
$123,456,789.0
1.234568E+008
12,345,678,900.00%
123,456,789.000
123456789.00
还可以这样使用:
String.Format("{0:F2} {1:F2} {2:F2}", x,y,z)
打开Visual C# .NET 2003,选择【新建】/【项目】,或者选择【新建项目】在Visual C#项目中选择【控制台应用程序】,选择程序名称和位置后,进入程序界面(IDE)。
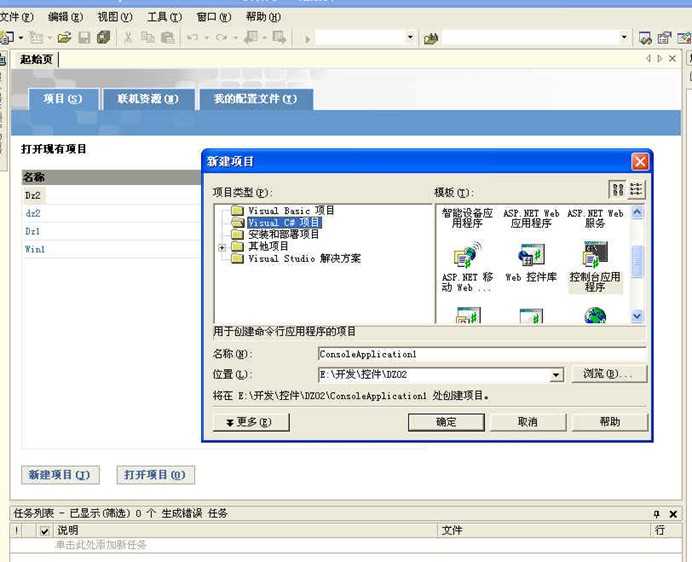
这时系统生成一个class1.cs的程序文件。修改成以下:
using System;
namespace Console2
{
// A "Hello World!" program in C#
class Hello
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
}
}
点击【调试】/【开始执行(不调试)】,就可以在DOS界面下看见结果。
选择程序名称和位置后,进入程序的一个Form1界面。
从左边的【工具箱】/【Windows窗体】中,添加一个Label控件和一个Button控件,双击Button1,添加程序如下:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Text="iiii";
}
就可以查看运行效果了。
如果修改成
label1.Left=label1.Left+10;
就可以看见点击Button后,标签右移的效果。
工具箱的控件主要有Button(按钮)、Label(标签)、TextBox(文本框)、RadioButton(单选按钮)、CheckBox(复选框)、ListBox(下拉框)等。
可以双击在Form上产生控件,也可以先点击,然后在Form上画矩形,决定控件的大小。
控件的基本特性有事件、方法和属性,详见2.2。
控件的事件主要有Click(单击)、DoubleClick(双击)、MouseOver(鼠标移过)等。
控件的方法主有Focus(聚焦)、Hide(隐藏)、Show(显示)等。
控件的主要属性有:
1.尺寸控制,主要有Width(宽度)、Height(高度)等;
2.位置控制,主要有Left(左边界)、Top(上边界)等;
3.颜色和字体控制,主要有BackColor(背景颜色)、ForeColor(前景颜色)、Font(字体)等;
4.名称控制,主要有Name(控件名字)、Caption(控件标题)等;
5.控件序号,主要有TabIndex(焦点的TAB顺序控制)、Index(控件数组序号);
6.其它,主要有Enabled(决定控件是否激活,True或 False)、ToolTipText(鼠标移过时显示的文字)等。
使用消息框,可以在程序运行到这里时弹出一个对话框,显示指定的文字。是向外输出信息的重要方式。
MessageBox.Show("def");
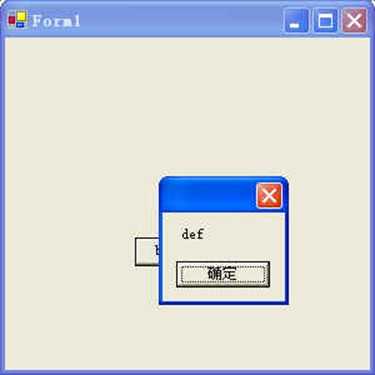
消息框输出必须为string类型,如果不是,则需要转换:
string s1;
s1=Convert.ToString(a);
MessageBox.Show(s1);
可以用以下函数简化使用方法:
private void msgbox(object a) //用消息框显示任意一个数
{
string s1;
s1=Convert.ToString(a);
MessageBox.Show(s1);
}
MessageBox.Show("name", "Name Entry", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon . Exclamation);
其中第二项开始依次为消息框的标题、按钮样式、图标样式。
MessageBoxButtons的数值为枚举型,为OK(缺省)、AbortRetryIgnore、OKCancel、RetryCancel、YesNo、YesNoCancel。
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
DialogResult result;
result = MessageBox.Show("name", "Name Entry", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Question);
MessageBox.Show(result.ToString());
}
如果要参与判断,则用
string ls=result.ToString();
本例检查textBox1中输入文本没有,如果没有就提示,并可以获取返回信息。
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
if(textBox1.Text.Length == 0)
{
string message = "You did not enter a server name. Cancel this operation?";
string caption = "No Server Name Specified";
MessageBoxButtons buttons = MessageBoxButtons.YesNo;
DialogResult result;
result = MessageBox.Show(this, message, caption, buttons,
MessageBoxIcon.Question, MessageBoxDefaultButton.Button1,
MessageBoxOptions.RightAlign);
if(result == DialogResult.Yes)
this.Close();
}
}
}
文本框主要是用来输入和显示文字的。
添加一个TextBox,系统自己产生名字textBox1,程序如下:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(textBox1.Text);
}
运行时,就可以在消息框中显示文本框输入的字符串。
TextBox一般显示单行,如果把属性Multiline改为Ture,还可以显示多行数字。
输入数字需要转换:
int a;
string s1;
a=Convert.ToInt16(textBox1.Text);
a=a+5;
s1=Convert.ToString(a);
MessageBox.Show(s1);
文本框的初始化就是向文本框赋初始值。可以从事件过程里写入,也可以在IDE的右边属性栏里输入,但是推荐采用在Form初始化时写入。
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
// TODO: 在 InitializeComponent 调用后添加任何构造函数代码
textBox1.Text="";
}
上面的例子都是在一个窗体中,实际程序需要几十甚至上百个窗体。以下例子创建两个窗体,然后实现相互调用。
在Form1中添加两个Button,一个标题为调用,一个标题为退出。
使用【项目】/【添加窗体】,添加一个窗体,缺省名称为Form2。添加一个Button,标题为返回。
窗体1程序为:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Form2 Nform2=new Form2();
Nform2.Show();
this.Hide();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
窗体2程序为:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Form1 Nform1=new Form1();
Nform1.Show();
this.Hide();
}
运行程序,可以在两个窗体之间来回调用,按"退出"就可以退出程序。
程序运行时,如果发现窗体位置不固定,这时需要在窗体的StartPosition属性上设置窗体固定位置,一般为屏幕中央。
注意,两个窗体要在一个命名空间,否则要引用。
在Form1中添加一个Button1和一个textBox1,程序为:
private Form2 otherForm=new Form2();
private void GetOtherFormTextBox()
{
textBox1.Text = otherForm.TextBox1.Text;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
GetOtherFormTextBox();
}
在Form2中添加一个textBox1,在
InitializeComponent();
后面添加一个赋值语句为:
textBox1.Text="abd";
然后添加一个属性:
public TextBox TextBox1
{
get
{
return textBox1;
}
}
运行时,点击Form1中的Button1,可以把Form2的TextBox的数值取到Form1的TextBox中来。
本例是移动一个标签,在两个Form之间来回移动。
先设计Form1如下:
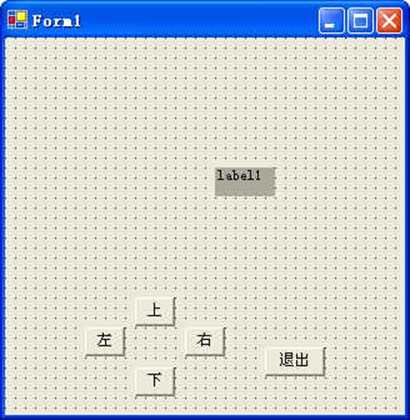
设计Form2,除了少了一个退出按钮外,其余相同。
在Form1的InitializeComponent()下面加上窗体定位语句:
Point tempPoint = new Point(100,100);
this.DesktopLocation = tempPoint;
然后把Form1的StartPosition属性改为Manual。其余程序为:
public Label L2
{
get
{
return label1;
}
set
{
label1=value;
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Form2 otherForm=new Form2();
label1.Left=label1.Left+10;
if (label1.Left>=this.Width-10)
{
otherForm.Show();
otherForm.L1.Top=label1.Top;
this.Hide();
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Left=label1.Left-10;
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Top=label1.Top-10;
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Top=label1.Top+10;
}
private void button5_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
同样在Form2的InitializeComponent()下面加上窗体定位语句:
Point tempPoint = new Point(300,100);
this.DesktopLocation = tempPoint;
然后把Form2的StartPosition属性改为Manual。其余程序为:
public Label L1
{
get
{
return label1;
}
set
{
label1=value;
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Left=label1.Left+10;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Form1 otherForm1=new Form1();
label1.Left=label1.Left-10;
if (label1.Left<=-10)
{
otherForm1.Show();
otherForm1.L2.Top=label1.Top;
otherForm1.L2.Left=otherForm1.Width-20;
this.Hide();
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Top=label1.Top-10;
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
label1.Top=label1.Top+10;
}
public void CreateMyForm()
{
Form form1 = new Form();
Label label1 = new Label();
Button button1 = new Button ();
TextBox text1 = new TextBox();
button1.Text = "确定";
button1.Location = new Point (110, 220);
label1.Location = new Point (50,100);
text1.Location = new Point (150,100);
form1.Text = "请输入";
label1.Text = "数据";
form1.FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.FixedDialog;
form1.ControlBox = false;
form1.CancelButton = button1;
form1.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
form1.Controls.Add(button1);
form1.Controls.Add(text1);
form1.Controls.Add(label1);
form1.ShowDialog();
ls=text1.Text;
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
CreateMyForm();
MessageBox.Show(ls);
}
在窗体上加上ToolBar
在界面上修改后,最后要加上:
toolBar1.Buttons.Add(toolBarButton1);
toolBar1.Buttons.Add(toolBarButton2);
toolBar1.Buttons.Add(toolBarButton3);
// Add the event-handler delegate.
toolBar1.ButtonClick += new ToolBarButtonClickEventHandler (this.toolBar1_ButtonClick);
或者把原有的程序
this.toolBar1.Buttons.AddRange(new System.Windows.Forms.ToolBarButton[] {
this.toolBarButton1,this.toolBarButton2,this.toolBarButton3});
改变位置,到toolBar1设置的最下面。
全部设置程序为:
this.toolBar1.DropDownArrows = true;
this.toolBar1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(0, 0);
this.toolBar1.Name = "toolBar1";
this.toolBar1.ShowToolTips = true;
this.toolBar1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(592, 42);
this.toolBar1.TabIndex = 0;
toolBar1.ButtonSize = new System.Drawing.Size(60, 50);
//
// toolBarButton1
//
this.toolBarButton1.Text = "Open";
toolBarButton1.Style = System.Windows.Forms.ToolBarButtonStyle.ToggleButton;
//
// toolBarButton2
//
this.toolBarButton2.Text = "Save";
toolBarButton2.Style = System.Windows.Forms.ToolBarButtonStyle.ToggleButton;
//
// toolBarButton3
//
this.toolBarButton3.Text = "Print";
toolBar1.Buttons.Add(toolBarButton1);
toolBar1.Buttons.Add(toolBarButton2);
toolBar1.Buttons.Add(toolBarButton3);
toolBar1.ButtonClick += new ToolBarButtonClickEventHandler (this.toolBar1_ButtonClick);
如下设置,可以正常居中显示9号字体。
toolBar1.ButtonSize = new System.Drawing.Size(60, 50);
可以用程序实现按钮的增加,但是无法全部实现自动化。
先需要手工添加toolBar1和imageList1,然后把imageList1中的图片一一加上。
void toolBarSet()
{
//添加按钮
ToolBarButton toolBarButton1=new ToolBarButton();
ToolBarButton toolBarButton2=new ToolBarButton();
toolBar1.Buttons.AddRange(new System.Windows.Forms.ToolBarButton[] { toolBarButton1,toolBarButton2});
toolBar1.DropDownArrows = true;
toolBar1.ImageList = imageList1;
toolBar1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(408, 37);
toolBar1.TabIndex = 0;
toolBar1.ButtonClick += new System.Windows.Forms.ToolBarButtonClickEventHandler(toolBar1_ButtonClick);
// toolBarButton1
toolBarButton1.ImageIndex = 0;
toolBarButton1.ToolTipText = "放大";
// toolBarButton2
toolBarButton2.ImageIndex = 1;
toolBarButton2.ToolTipText = "缩小";
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
toolBarSet();
}
private void toolBar1_ButtonClick(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.ToolBarButtonClickEventArgs e)
{
switch(toolBar1.Buttons.IndexOf(e.Button))
{
case 0: //放大
MessageBox.Show("放大");
break;
case 1: //缩小
MessageBox.Show("缩小");
break;
default:
MessageBox.Show("other");
break;
}
}
在窗体上放置一个listBox1,一个button1和一个label1。以下程序实现添加选项,双击选项就可以显示你的选择:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Clear();
listBox1.Items.Add("");
listBox1.Items.Add("选择1");
listBox1.Items.Add("选择2");
listBox1.SelectedIndex=0;
}
private void listBox1_DoubleClick(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Label1.Text=listBox1.SelectedIndex.ToString();
}
第一项是一个缺省空项,允许用户不选取退出。
Items是一个集合,因此增减选项可以按照集合那样操作。
System.Object[] ItemObject = new System.Object[10];
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
ItemObject[i] = "Item" + i;
}
listBox1.Items.AddRange(ItemObject);
ScrollBar是滚动条控件,分成HScrollBar(水平)和VScrollBar(垂直)两种。有些控件如ListBox,TextBox等可以自动添加滚动条,但是有些控件则需要用程序添加。主要属性意义为:
Value:滚动条的数值,反映当前移动块的位置。初始值设定后,运行时停留在这个位置。运行时拉动滚动条,由Scroll事件的e.NewValue参数传递过来。
Maximum:Value的最大值,一般为100。
Minimum:Value的最小值,即端点的数值。如果Maximum=100,Minimum=0,LargeChange=10,则从第一个端点开始Value=0,到另一个端点的Value=91。
SmallChange:每次点击移动的数值,一般为1。
LargeChange:移动块的长度,一般为10。
float vi; //每个单位的移动距离
float vk=0.8f; //PicturBox显示高度和实际高度的比例
int t0,ti; //PicturBox显示Top和Height。
private void vScrollBar1_Scroll(object sender,System.Windows.Forms.ScrollEventArgs e)
{
this.pictureBox1.Top = t0-Convert.ToInt32(e.NewValue*vi);
this.pictureBox1.Height = ti+Convert.ToInt32(e.NewValue*vi);
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Button oButton;
TextBox oTextBox;
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)
{
oButton = new Button();
oButton.Text = "按钮"+ i.ToString();
oButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, i*50);
oButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(oButton_Click);
this.pictureBox1.Controls.Add(oButton);
oTextBox = new TextBox();
oButton.Tag = oTextBox;
oTextBox.Text = "1000";
oTextBox.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(150, i*50);
this.pictureBox1.Controls.Add(oTextBox);
}
}
private void oButton_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Button btn = (Button)sender;
TextBox txt = (TextBox)btn.Tag;
txt.Text = Convert.ToString(Convert.ToInt32(txt.Text) + 1);
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
vi=vk*pictureBox1.Height/vScrollBar1.Maximum;
t0=pictureBox1.Top;
ti=pictureBox1.Height;
}
Windows 窗体 Panel(面板)控件用于为其他控件提供可识别的分组。在设计时所有控件均可轻松地移动,当移动 Panel 控件时,它包含的所有控件也将移动。分组在一个面板中的控件可以通过面板的 Controls 属性进行访问。
Panel 控件类似于 GroupBox 控件;但只有 Panel 控件可以有滚动条,而且只有 GroupBox 控件显示标题。
将 AutoScroll 属性设置为 true,可以自动显示滚动条。但是这时右边界和下边界顶头,不是太好看。这时需要增加一个不可见的控件或者图像来调整。
下例在Panel上用程序添加几个控件,产生滚动效果:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Button oButton;
TextBox oTextBox;
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)
{
oButton = new Button();
oButton.Text = "按钮"+ i.ToString();
oButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, i*50);
oButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(oButton_Click);
this.panel1.Controls.Add(oButton);
oTextBox = new TextBox();
oButton.Tag = oTextBox;
oTextBox.Text = "1000";
oTextBox.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(150, i*50);
this.panel1.Controls.Add(oTextBox);
}
//增加一个不可见按钮,调整右边界和下边界的位置
oButton = new Button();
oButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(260, 440);
oButton.Height=0;
oButton.Width=0;
this.panel1.Controls.Add(oButton);
}
private void oButton_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Button btn = (Button)sender;
TextBox txt = (TextBox)btn.Tag;
txt.Text = Convert.ToString(Convert.ToInt32(txt.Text) + 1);
}
在Panel控件上不能直接添加图像。需要在Panel控件上添加一个picturBox,然后把其SizeMode设置为AutoSize(随着图像大小调整控件大小)就可以实现图像的随意滚动察看。
Panel控件上也可以画图。但是滚动时遮盖的图像就消失了。这时候需要在Panel控件上添加一个picturBox,然后在picturBox上画图,然后用一个LocationChanged事件,每次滚动时重画一遍即可:
Pen pen1=new Pen(Color.Green,2);
Graphics g1;
void drawLine()
{
PointF p1=new PointF(0,0);
PointF p2=new PointF(100,100);
g1.DrawLine(pen1,p1,p2);
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g1=this.pictureBox1.CreateGraphics();
drawLine();
}
private void pictureBox1_LocationChanged(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
drawLine();
}
手工添加即可。可以直接在其上写各个菜单项的名字,双击可以添加程序,使用非常方便。
1.在设计时向菜单项添加选中标记
对于在"菜单设计器"内选定的菜单项(三级菜单以下),单击该菜单项左侧的区域,选中标记√。或者在"属性"窗口中将 Checked 属性设置为 True。
以编程方式向菜单项添加选中标记
myMnuItem.Checked = true;
2.在设计时向菜单项添加快捷键
在"菜单设计器"内选择菜单项。在"属性"窗口中,将 Shortcut 属性设置为下拉列表中提供的值之一。
以编程方式向菜单项添加快捷键
myMnuItem.Shortcut = System.Windows.Forms.Shortcut.F6;
3.向菜单项添加访问键
如键入"文件(&F)",显示"文件(F)"。
若要定位到此菜单项,请按 ALT 键,将焦点移动到菜单栏,然后按该菜单名称的访问键。当菜单打开并显示带访问键的项时,只需按该访问键就可选定该菜单项。或者直接按ALT+主菜单的访问键。
4.将分隔线作为菜单项添加
在菜单设计器中,右击需要有分隔线的位置,然后选择"插入分隔符"。或者在设置菜单项的 Text 属性(在"属性"窗口中、菜单设计器中或代码中)时,输入短划线 (–) 使该菜单项成为分隔线。
单选按钮是布置一组按钮,只能选择一组控件。
本例放置3个单选按钮,Text属性分别写上"已婚"、"未婚"和"离异",然后添加一个Label控件和一个Button控件,程序如下:
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
label1.Text="请选择";
……
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
if (radioButton1.Checked == true)
label1.Text=radioButton1.Text;
else if (radioButton2.Checked == true)
label1.Text=radioButton2.Text;
else
label1.Text=radioButton3.Text;
}
}
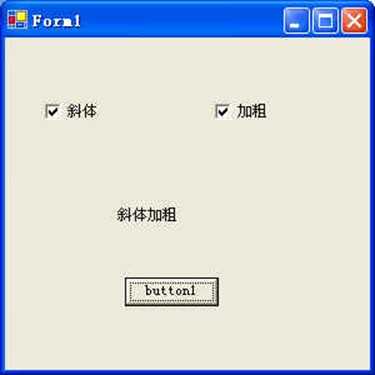
可以选择多个的一组控件。
本例放置2个复选按钮,Text属性分别写上"加粗"和"斜体",然后添加一个Label控件和一个Button控件,程序如下:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
if (checkBox1.Checked == true)
{
if (checkBox2.Checked == true)
label1.Text=checkBox1.Text+checkBox2.Text;
else if (checkBox2.Checked == false)
label1.Text=checkBox1.Text;
}
else
if (checkBox2.Checked == true)
label1.Text=checkBox2.Text;
else if (checkBox2.Checked == false)
label1.Text="";
}
CheckBox checkBox1=new CheckBox();
void checkSet()
{
this.Controls.Add(checkBox1);
checkBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, 64);
checkBox1.Name = "checkBox1";
checkBox1.TabIndex = 2;
checkBox1.Text = "图层1";
checkBox1.CheckedChanged += new System.EventHandler(checkBox1_CheckedChanged);
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
checkSet();
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
if (checkBox1.Checked)
MessageBox.Show("yes");
else
MessageBox.Show("no");
}
如果要实现标题在左边,用
check1.Width=90;
check1.CheckAlign=ContentAlignment.MiddleRight;
要在其它控件显示:
check3.BringToFront();
以下程序动态动态产生一组Button和TextBox控件,以及点击Button的事件。
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Button oButton;
TextBox oTextBox;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
oButton = new Button();
oButton.Text = "按钮"+ i.ToString();
oButton.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(50, i*50);
oButton.Click += new System.EventHandler(oButton_Click);
this.Controls.Add(oButton);
oTextBox = new TextBox();
oButton.Tag = oTextBox;
oTextBox.Text = "1000";
oTextBox.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(150, i*50);
this.Controls.Add(oTextBox);
}
}
private void oButton_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Button btn = (Button)sender;
TextBox txt = (TextBox)btn.Tag;
txt.Text = Convert.ToString(Convert.ToInt32(txt.Text) + 1);
}
Windows 窗体 splitter 控件用于在运行时调整停靠控件的大小。Splitter 控件常用于一类窗体,这类窗体上的控件所显示的数据长度可变,如 Windows 资源管理器,它的数据窗格所包含的信息在不同的时间有不同的宽度。
如果一个控件可由 splitter 控件调整其大小,则当用户将鼠标指针指向该控件的未停靠的边缘时,鼠标指针将更改外观,指示该控件的大小是可以调整的。拆分控件允许用户调整该控件紧前面的停靠控件的大小。因此,为使用户能够在运行时调整停靠控件的大小,请将要调整大小的控件停靠在容器的一条边缘上,然后将拆分控件停靠在该容器的同一侧。
以下例子自动产生几个控件,可以在运行中调整大小。
private void CreateMySplitControls()
{
TreeView treeView1 = new TreeView();
ListView listView1 = new ListView();
Splitter splitter1 = new Splitter();
treeView1.Dock = DockStyle.Left;
splitter1.Dock = DockStyle.Left;
splitter1.MinExtra = 100;
splitter1.MinSize = 75;
listView1.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
treeView1.Nodes.Add("TreeView Node");
listView1.Items.Add("ListView Item");
this.Controls.AddRange(new Control[]{listView1, splitter1, treeView1});
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
CreateMySplitControls();
}
Windows 窗体 TabControl 显示多个选项卡。使用时,先添加一个TabControl控件,把它拉的足够大。
然后在属性中添加按钮。每个按钮可以控制TabControl的其余页面,作为一个容器,可以添加其它空间。运行时只要点击按钮,就可以切换选项卡,实现不同的功能。
可以向statusBar添加面板(窗格),以分类显示信息:
public void CreateStatusBarPanels()
{
statusBar1.Panels.Add("");
statusBar1.Panels.Add("Two");
statusBar1.Panels.Add("Three");
statusBar1.Panels[0].Width=200;
statusBar1.Panels[0].Text="One";
statusBar1.ShowPanels = true;
}
字符串的操作在程序设计中非常有用,因此单独写成一章。
char 关键字用于声明一个字符。
char 类型的常数可以写成字符、十六进制换码序列或 Unicode 表示形式。您也可以显式转换整数字符代码。以下所有语句均声明了一个 char 变量并用字符 X 将其初始化:
char MyChar = ‘X‘; // Character literal
char MyChar = ‘\x0058‘; // Hexadecimal
char MyChar = (char)88; // Cast from integral type
char MyChar = ‘\u0058‘; // Unicode
char 类型可隐式转换为 ushort、int、uint、long、ulong、float、double 或 decimal 类型。但是,不存在从其他类型到 char 类型的隐式转换。
将字符串的部分字符复制到 Unicode 字符数组。示例
string str = "012wxyz789";
char[] arr;
arr = str.ToCharArray(3, 4);
显示:wxyz
由于英文和中文的显示长度不一样,所以一些场合要区分。
要引用
using System.Globalization;
程序为:
//计算一个字符的字符类型,=0汉字,=1英文
private int getCharType(char ch)
{
int i0;
UnicodeCategory ca1=new UnicodeCategory();
ca1=System.Char.GetUnicodeCategory(ch);
switch (ca1)
{
case UnicodeCategory.OtherPunctuation:
i0=0; //汉字
break;
case UnicodeCategory.OtherLetter:
i0=0; //汉字
break;
case UnicodeCategory.FinalQuotePunctuation:
i0=0; //汉字
break;
default:
i0=1; //英文
break;
}
return i0;
}
//计算字符串(ss,包含中文)的实际宽度(返回)、起点(x0)和高度(height)
//输入字号sz,只对于Pixel单位
public float StringWidth(string ss,float sz,ref float x0,ref float height)
{
char ch1;
int i,i0=0;
float width=0;
float k1=1.02f; //汉字系数
float k2=0.55f; //英文系数
float k3=0.15f; //x0系数
float k4=1.10f; //高度系数
int i1=0; //汉字个数
int i2=0; //英文个数
height=k4*sz;
x0=sz*k3;
for(i=0;i<ss.Length;i++)
{
ch1=(char)ss[i];
i0=getCharType(ch1);
if(i0==0)
i1++;
else
i2++;
}
width=x0+i1*k1*sz+i2*k2*sz;
return width;
}
//返回一个point单位的字体的宽度
public float PStringWidth(string ss,float sz,ref float x0,ref float height)
{
float width=0;
sz=sz*20/15;
width=StringWidth(ss,sz,ref x0,ref height);
return width;
}
这个方法在sz(字体大小)5~30内比较准确。很大时有误差。
//根据给定点,找到实际标注点,使得以画出的字符串以给定点为中心
PointF StringCenter(string s1,int sz,PointF p0)
{
PointF p1=new PointF();
float x0=0;
float height=0;
float width=StringWidth(s1,sz,ref x0,ref height);
p1.X=p0.X-+x0-width/2;
p1.Y=p0.Y-height/2;
return p1;
}
以下示例利用以上方法,把字符串的长度和高度画成一个方框。
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Graphics g= this.CreateGraphics();
SolidBrush myBrush=new SolidBrush(Color.Red);
float x0=0;
float height=0;
int sz=10;
float px=0,py=50;
PointF p0=new PointF(px,py);
string s1="我们还34fd还是和平使者";
Font myFont1 = new Font("宋体",sz,FontStyle.Bold,GraphicsUnit.Pixel);
float width=StringWidth(s1,sz,ref x0,ref height);
g.DrawString(s1, myFont1, myBrush, p0);
PointF p1=new PointF(px+x0,py);
PointF p2=new PointF(px+x0+width,py);
PointF p3=new PointF(px+x0+width,py+height);
PointF p4=new PointF(px+x0,py+height);
PointF[] cur ={p1,p2,p3,p4};
Pen pen1=new Pen(Color.Blue,2);
g.DrawPolygon(pen1,cur);
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Graphics g= this.CreateGraphics();
SolidBrush myBrush=new SolidBrush(Color.Red);
PointF ps=new PointF();
int sz=10;
PointF p0=new PointF(300,100);
string s1="我们还34fd还是和平使者";
Font myFont1 = new Font("宋体",sz,FontStyle.Bold,GraphicsUnit.Pixel);
ps=StringCenter(s1,sz,p0);
g.DrawString(s1, myFont1, myBrush, ps);
//以下画十字线表示中心位置
PointF p1=new PointF(0,p0.Y);
PointF p2=new PointF(600,p0.Y);
PointF p3=new PointF(p0.X,0);
PointF p4=new PointF(p0.X,300);
Pen pen1=new Pen(Color.Blue,1);
g.DrawLine(pen1,p1,p2);
g.DrawLine(pen1,p3,p4);
}
"\r\n"
显示换行的语句为:
textBox1.Text="ok\r\n";
textBox1.Text+="ok1";
string myString1 = "This is the first line of my string.\n" +
"This is the second line of my string.\n" +
"This is the third line of the string.\n";
string myString2 = @"This is the first line of my string.
This is the second line of my string.
This is the third line of the string.";
用@后边的字符串不被处理。
A1=@"c:\Docs\Source\a.txt";
string s1=@"c=""a.txt"; //显示:c="a.txt
string s1=@"c=""a.txt"""; //显示:c="a.txt"
If (s1 == @"""") Then //s1=""
string s1="fdkls我们";
string s2=Convert.ToString(s1.Length);
MessageBox.Show(s2);
运行显示为7,所有字符个数。
String s = "123abc456";
Console.WriteLine(s.Remove(3, 3));
打印"123456"。
标识此实例中的子字符串(它们由数组中指定的一个或多个字符进行分隔),然后将这些子字符串放入一个 String 数组中。
可以按照","分开,也可以去除空格。
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
string astring="123,456 78,789";
string [] split;
Char [] chr=new Char [] {‘,‘,‘ ‘};
split = astring.Split(chr);
MessageBox.Show("/"+split[0]+"/");
}
这时可以分成123,456,78,789四个字符串。
注意,前后空白也可以看成是一个字符串,要消除,用
astring=astring.Trim();
就可以了。
当存在两个空格时,就出现找出空字符串的错误。用以下方法可以去掉空的字符串:
string [] Split0(string [] sp)
{
string [] sp1=new string [sp.Length];
int i=0,j=0;
foreach (string s1 in sp)
{
if (s1!="")
{
sp1[i]=s1;
i=i+1;
}
}
string [] sp2=new string [i];
for (j=0;j<i;j++)
sp2[j]=sp1[j];
return sp2;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
string astring=" 123,456 78,789 ";
string [] split;
Char [] chr=new Char [] {‘,‘,‘ ‘};
split = astring.Split(chr);
split =Split0(split);
MessageBox.Show("/"+split[0]+"/");
}
以下均为在控制台应用程序中使用的程序。开始要进行以下三个引用:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
程序如下:
class Test
{
public static void Main()
{
string path = @"d:\chen\MyTest.txt";
if (File.Exists(path))
{
File.Delete(path);
}
}
}
如果采用相对路径,用
string sfile = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory() + @"\F8.txt";
对于在一个.net项目中,默认的路径是在\bin\debug中,如果要放在项目文件目录中,用
string sfile = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory() + @"\..\..\F8.txt";
可以用:
File.Create(path);
或者
FileStream fs = File.Create(path);
File.Copy(path,path1,true);
如果最后用false,则第二个文件有时,发生错误。
using System;
using System.IO;
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
string s1 = @"D:\chen\mytest.txt";
string s2 = @"D:\chen\mytest1.txt";
String input;
if (!File.Exists(s1))
{
MessageBox.Show("File does not exist.");
return;
}
StreamReader sr = File.OpenText(s1);
StreamWriter wr = new StreamWriter(s2);
while ((input=sr.ReadLine())!=null)
{
wr.WriteLine(input);
}
MessageBox.Show("The end.");
sr.Close();
wr.Close();
}
string s1 = @"d:\chen\a1.txt";
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(s1,Encoding.GetEncoding("gb2312"));
string rl;
while((rl=sr.ReadLine())!=null)
{
MessageBox.Show(rl);
}
sr.Close();
用openFileDialog控件。
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog openFileDialog1 = new OpenFileDialog();
openFileDialog1.InitialDirectory=Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
openFileDialog1.Filter = "Cursor Files|*.cur";
openFileDialog1.Title = "Select a Cursor File";
if(openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
System.IO.StreamReader sr = new
System.IO.StreamReader(openFileDialog1.FileName);
MessageBox.Show(sr.ReadToEnd());
sr.Close();
}
}
在工具箱上选择folderBrowserDialog:
folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog();
string s1 = folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath.ToString()+@"\mytest.txt";
StreamWriter wr = new StreamWriter(s1);
在Button1中加入以下程序:
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
formGraphics.DrawLine(myPen, 0, 0, 200, 200);
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
就可以在Form1上面画一条线了。用
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,3);
可以改变线的宽度。
Pen pen1=new Pen(Color.Green,2);
Graphics g1=this.CreateGraphics();
PointF p1=new PointF(0,0);
PointF p2=new PointF(100,100);
g1.DrawLine(pen1,p1,p2);
pen1.Dispose();
g1.Dispose();
最后两句可以不写,程序关闭时自动完成。
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
formGraphics.DrawEllipse(myPen, new Rectangle(0,0,200,300));
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
以下画一个椭圆并填充。
System.Drawing.SolidBrush myBrush = new System.Drawing.SolidBrush(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
formGraphics.FillEllipse(myBrush, new Rectangle(0,0,200,300));
myBrush.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
//以给定点找画椭圆的原始点,使得椭圆的中心点是给定点
PointF EllipseCenter(int xs,int ys,PointF p0)
{
float ek=0.5f;
PointF p1=new PointF();
p1.X=p0.X-xs*ek;
p1.Y=p0.Y-ys*ek;
return p1;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Graphics g= this.CreateGraphics();
Pen pen1=new Pen(Color.Yellow,1);
Pen pen2=new Pen(Color.Red,1);
PointF ps=new PointF();
int xs=1,ys=1; //半轴
PointF p0=new PointF(300,100);
ps=EllipseCenter(xs,ys,p0);
//以下画十字线表示中心位置
PointF p1=new PointF(0,p0.Y);
PointF p2=new PointF(600,p0.Y);
PointF p3=new PointF(p0.X,0);
PointF p4=new PointF(p0.X,300);
g.DrawLine(pen1,p1,p2);
g.DrawLine(pen1,p3,p4);
g.DrawEllipse(pen2,ps.X,ps.Y,xs,ys);
}
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
formGraphics.DrawArc(myPen, 100, 50, 140, 70, 30, 180);
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
PointF point1 = new PointF( 50.0F, 50.0F);
PointF point2 = new PointF(100.0F, 25.0F);
PointF point3 = new PointF(200.0F, 5.0F);
PointF point4 = new PointF(250.0F, 50.0F);
PointF point5 = new PointF(300.0F, 100.0F);
PointF point6 = new PointF(350.0F, 200.0F);
PointF point7 = new PointF(250.0F, 250.0F);
PointF[] curvePoints =
{
point1,
point2,
point3,
point4,
point5,
point6,
point7
};
formGraphics.DrawLines(myPen, curvePoints);
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
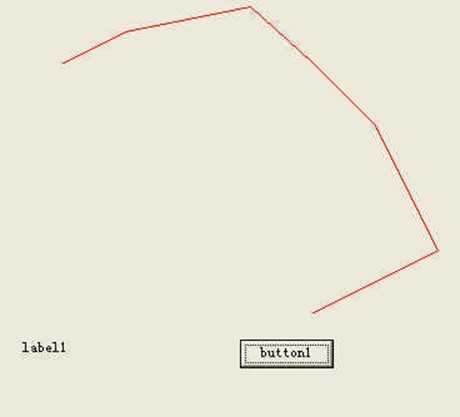
也可以用以下方式给数组赋值:
PointF[] pt=new PointF[]{new PointF(2,2),new PointF(25,150),new PointF(100,100)};
数据同上,修改如下:
int offset = 1; //开始点(从0开始)
int numSegments = 5; //包含后续点数
float tension = 1.0F;
formGraphics.DrawCurve(myPen, curvePoints, offset, numSegments, tension);
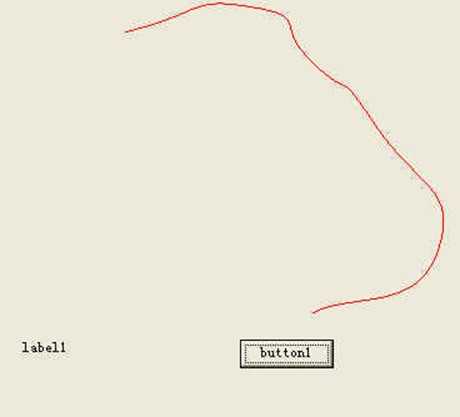
以下程序可以画一个封闭曲线:
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
PointF point1 = new PointF( 50.0F, 50.0F);
PointF point2 = new PointF(100.0F, 25.0F);
PointF point3 = new PointF(200.0F, 5.0F);
PointF point4 = new PointF(250.0F, 50.0F);
PointF point5 = new PointF(300.0F, 100.0F);
PointF point6 = new PointF(350.0F, 200.0F);
PointF point7 = new PointF(250.0F, 250.0F);
PointF point8 = new PointF(40.0F, 150.0F);
PointF[] curvePoints =
{
point1,
point2,
point3,
point4,
point5,
point6,
point7,
point8,
point1
};
int offset = 0;
int numSegments = 8;
float tension = 1.0F;
formGraphics.DrawCurve(myPen, curvePoints, offset, numSegments, tension);
// formGraphics.DrawLines(myPen, curvePoints);
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
}
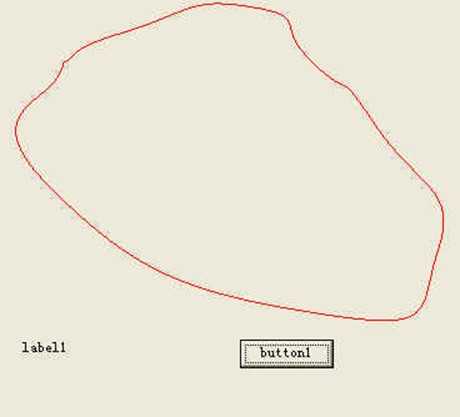
如果是任意3点(或多点),在起始点不容易圆滑。可以用以下方法画封闭曲线:
PointF[] curvePoints =
{
point3,
point1,
point2,
point3,
point1
};
int offset = 1;
int numSegments = 3;
float tension = 0.5F;
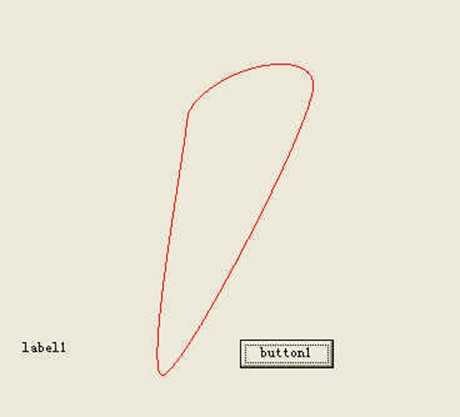
这样可以保证第一个点处比较圆滑。
设置线段宽度:
myPen.Width =3;
在pictrueBox上面画线,修改this:
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = picBox1.CreateGraphics();
System.Drawing.SolidBrush myBrush = new ystem.Drawing.SolidBrush(System.Drawing.Color.LightPink);
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,1);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = pictureBox1.CreateGraphics();
PointF point1 = new PointF( 50.0F, 50.0F);
PointF point2 = new PointF(100.0F, 25.0F);
PointF point3 = new PointF(200.0F, 5.0F);
PointF point4 = new PointF(250.0F, 50.0F);
PointF point5 = new PointF(300.0F, 100.0F);
PointF point6 = new PointF(350.0F, 200.0F);
PointF point7 = new PointF(250.0F, 250.0F);
PointF[] curvePoints =
{
point1,
point2,
point3,
point4,
point5,
point6,
point7
};
formGraphics.FillPolygon(myBrush,curvePoints);
formGraphics.DrawPolygon(myPen,curvePoints);
myPen.Dispose();
myBrush.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
普通颜色设置可以直接选取系统定义的颜色。高级设置采用RGB颜色。
Color myColor;
myColor = Color.FromArgb(23,56,78);
每个数字均必须是从 0 到 255 之间的一个整数,分别表示红、绿、蓝三种原色。其中 0 表示没有该颜色,而 255 则为所指定颜色的完整饱和度。如Color.FromArgb(0,255,0)表示绿色,Color.FromArgb(255,255,0)表示黄色,Color.FromArgb(0,0,0) 呈现为黑色,而 Color.FromArgb(255,255,255) 呈现为白色。
还可以设置透明度,如
Color myColor;
myColor = Color.FromArgb(127, 23, 56, 78);
127表示50%的透明度,255表示完全不透明。
以下程序可以从调色板选择一个颜色,在textBox上面显示。
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
ColorDialog MyDialog = new ColorDialog();
MyDialog.AllowFullOpen = false ;
MyDialog.ShowHelp = true ;
MyDialog.Color = textBox1.ForeColor ;
if (MyDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
textBox1.ForeColor = MyDialog.Color;
}
本程序在一个菜单里调用选择程序,产生一个动态的窗体,选择颜色后返回主程序,刷新原来的页面。
由于没有掌握控制动态控件集合的方法,只好用枚举的方法定义动态控件,对于多于10个的颜色序列,需要修改程序。
Form form1;
bool Cform=true;
//颜色设置
private void menuItem31_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
while (Cform)
{
CreateColorForm();
Tuli1();
DisLine();
}
Cform=true;
}
//产生颜色输入窗体
private void CreateColorForm()
{
int i;
form1=new Form();
Button [] ColorButton = new Button [myPloys.marks1.Count];
Label [] ColorLabel = new Label [myPloys.marks1.Count];
Button button0 = new Button ();
form1.Width=130;
form1.Height=130+myPloys.marks1.Count*30;
form1.Text = "等值线颜色输入";
form1.FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.FixedDialog;
form1.ControlBox = false;
form1.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
button0.Text = "退出";
button0.Width=80;
button0.Location=new Point(25,50+myPloys.marks1.Count*30);
form1.Controls.Add(button0);
form1.CancelButton = button0;
for (i=0;i<myPloys.marks1.Count;i++)
{
ColorLabel[i]=new Label();
ColorLabel[i].Location=(Point)new Point(30,30+30*i);
ColorLabel[i].Width=30;
ColorLabel[i].Text=myPloys.marks1[i].ToString();
form1.Controls.Add(ColorLabel[i]);
ColorButton[i]=new Button();
ColorButton[i].BackColor=cColor[i];
ColorButton[i].Location=(Point)new Point(60,26+30*i);
ColorButton[i].Width=30;
switch (i)
{
case 0:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton0_Click);
break;
case 1:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton1_Click);
break;
case 2:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton2_Click);
break;
case 3:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton3_Click);
break;
case 4:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton4_Click);
break;
case 5:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton5_Click);
break;
case 6:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton6_Click);
break;
case 7:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton7_Click);
break;
case 8:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton8_Click);
break;
case 9:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton9_Click);
break;
case 10:
ColorButton[i].Click += new System.EventHandler(ColorButton10_Click);
break;
default:
break;
}
form1.Controls.Add(ColorButton[i]);
}
button0.Click += new System.EventHandler(button0_Click);
form1.ShowDialog();
}
private void ColorSelect(int si)
{
ColorDialog MyDialog = new ColorDialog();
MyDialog.AllowFullOpen = true ;
MyDialog.ShowHelp = true ;
MyDialog.Color = cColor[si] ;
if (MyDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
cColor[si] = MyDialog.Color;
form1.Dispose();
}
private void ColorButton0_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(0); }
private void ColorButton1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(1); }
private void ColorButton2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(2); }
private void ColorButton3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(3); }
private void ColorButton4_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(4); }
private void ColorButton5_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(5); }
private void ColorButton6_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(6); }
private void ColorButton7_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(7); }
private void ColorButton8_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(8); }
private void ColorButton9_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(9); }
private void ColorButton10_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{ ColorSelect(10); }
private void button0_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Cform=false;
form1.Dispose();
}
可以在指定的点开始写字,也可以在一个范围(如矩形)内写字。
Font myFont = new Font("Times New Roman", 14);
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
Pen myPen=new Pen(Color.Black);
System.Drawing.SolidBrush myBrush=new SolidBrush(Color.Red);
g.DrawRectangle(myPen,10, 10, 100, 200);
g.DrawString("Look at this text!", myFont, myBrush, new RectangleF(10, 10, 100, 200));
g.DrawString("Look at this text!", myFont, myBrush, 10, 250);
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,1);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
System.Drawing.SolidBrush drawBrush = new System.Drawing.SolidBrush(System.Drawing.Color.Black);
System.Drawing.Font drawFont = new System.Drawing.Font("Arial", 8);
string drawString = "201";
float x = 100.0f;
float y = 100.0f;
formGraphics.DrawEllipse(myPen, x, y,4,4);
formGraphics.DrawString(drawString, drawFont, drawBrush, x, y);
myPen.Dispose();
drawFont.Dispose();
drawBrush.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
public Font(
FontFamily family,
float emSize,
FontStyle style,
GraphicsUnit unit
);
以下的例子可以改变字体,大小、字形、单位,还可以设置成垂直。
// Font myFont = new Font("Times New Roman",14,FontStyle.Italic,GraphicsUnit.Millimeter);
Font myFont = new Font("隶书",34,FontStyle.Underline,GraphicsUnit.Pixel);
Graphics g = this.CreateGraphics();
System.Drawing.SolidBrush myBrush=new SolidBrush(Color.Red);
System.Drawing.StringFormat drawFormat = new System.Drawing.StringFormat (StringFormatFlags.DirectionVertical);
g.DrawString("Hello!你好", myFont, myBrush, 10, 10,drawFormat);
//根据给定点,找到实际标注点,使得以画出的字符串以给定点为中心
public PointF StringCenter(string s1,float sz,PointF p0)
{
PointF p1=new PointF();
float x0=0;
float height=0;
float width=StringWidth(s1,sz,ref x0,ref height);
p1.X=p0.X-+x0-width/2;
p1.Y=p0.Y-height/2;
return p1;
}
和在form上面画图类似,只是把this替换成pictureBox1:
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,1);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = pictureBox1.CreateGraphics();
System.Drawing.SolidBrush drawBrush = new
System.Drawing.SolidBrush(System.Drawing.Color.Black);
System.Drawing.Font drawFont = new System.Drawing.Font("Arial", 8);
string drawString = "201";
float x = 200.0f;
float y = 100.0f;
formGraphics.DrawEllipse(myPen, x, y,4,4);
formGraphics.DrawString(drawString, drawFont, drawBrush, x, y);
myPen.Dispose();
drawFont.Dispose();
drawBrush.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
有固定模式和缩放模式,通过设置SizeMode实现。程序如下:
pictureBox1.SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.StretchImage; //按图像文件大小缩放
// pictureBox1.Image = Image.FromFile ("abc.bmp"); //文件放在\bin\Debug文件夹
pictureBox1.Image = Image.FromFile (@"..\..\abc1.bmp"); //文件放在程序文件夹
指示由矩形和由路径构成的图形形状的内部。
System.Drawing.Graphics e = this.CreateGraphics();
Rectangle regionRect = new Rectangle(20, 20, 100, 100);
e.DrawRectangle(Pens.Black, regionRect);
RectangleF complementRect = new RectangleF(90, 30, 100, 100);
e.DrawRectangle(Pens.Red,Rectangle.Round(complementRect));
Region myRegion = new Region(regionRect);
myRegion.Intersect(complementRect);
SolidBrush myBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Blue);
e.FillRegion(myBrush, myRegion);
主要图形操作还有Union和Xor。
采用异或(Xor)运算。需要把polygon转换成路径:
Graphics g1 = this.CreateGraphics();
GraphicsPath myPath1=new GraphicsPath();
PointF[] pts=new PointF[]{new PointF(2,20),new PointF(250,0)
,new PointF(100,100),new PointF(90,150),new PointF(10,70)};
myPath1.AddPolygon(pts);
g1.DrawPath(Pens.Black,myPath1);
GraphicsPath myPath2=new GraphicsPath();
PointF[] pts1=new PointF[]{new PointF(20,30),new PointF(50,70)
,new PointF(100,40)};
myPath2.AddPolygon(pts1);
g1.DrawPath(Pens.Black,myPath2);
Region myRegion = new Region(myPath1);
myRegion.Xor(myPath2);
SolidBrush myBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Blue);
g1.FillRegion(myBrush, myRegion);
如果要镂空多个空洞,需要把这些空洞都加入到myPath2中,其余操作同样。
采用交、并和异或运算,都可以把两个对象互换。
public void DisplayRegionData(Graphics e, int len,RegionData dat)
{
int i;
float x = 20, y = 140;
Font myFont = new Font("Arial", 8);
SolidBrush myBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Black);
e.DrawString("myRegionData = ",myFont, myBrush,new PointF(x, y));
y = 160;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if(x > 300)
{
y += 20;
x = 20;
}
e.DrawString(dat.Data[i].ToString(),myFont, myBrush,new PointF(x, y));
x += 30;
}
}
用GraphicsPath可以把各种绘图元素(包括文字)包含进来,最后用DrawPath画出来。
需要:using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Pen myPen = new Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,1);
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = this.CreateGraphics();
GraphicsPath myPath1=new GraphicsPath();
myPath1.AddLine(0, 0, 10, 20);
myPath1.AddEllipse(20,20,10,10);
myPath1.AddLine(40, 40, 50, 120);
formGraphics.DrawPath(myPen, myPath1);
myPath1.Dispose();
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
}
用一个半径为0的点加在中间:
myPath1.AddLine(0, 0, 10, 20);
myPath1.AddEllipse(20,20,0,0);
myPath1.AddLine(40, 40, 50, 120);
也可以用两个path,然后用
path2.AddPath(path3,false);
路径可以包含其它路径,汇总成一个大的图形。
还可以通过矩阵变换进行缩放、平移和旋转。
可以通过矩阵变换进行图形的变换。
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
System.Drawing.Graphics e1 = this.CreateGraphics();
Pen myPen = new Pen(Color.Blue, 1);
Pen myPen2 = new Pen(Color.Red, 1);
Matrix myMatrix1 = new Matrix(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // x和y方向都放大3倍
// Matrix myMatrix1 = new Matrix(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 50.0f, 50.0f); // 平移50,50
e1.DrawRectangle(myPen, 0, 0, 100, 100);
e1.Transform = myMatrix1;
e1.DrawRectangle(myPen2, 0, 0, 100, 100);
myPen.Dispose();
e1.Dispose();
}
下例显示缩放、旋转和移动变换。
public void MultiplyExample(PaintEventArgs e)
{
Pen myPen = new Pen(Color.Blue, 2);
Pen myPen2 = new Pen(Color.Red, 1);
Matrix myMatrix1 = new Matrix(3.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // Scale
Matrix myMatrix2 = new Matrix(0.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); // Rotate 90,
Matrix myMatrix3 = new Matrix(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 250.0f, 50.0f); // Translate
ListMatrixElements(e, myMatrix1, "Beginning Matrix", 6, 40);
myMatrix1.Multiply(myMatrix2, MatrixOrder.Append);
ListMatrixElements(e,myMatrix1,"Matrix After 1st Multiplication",6,60);
myMatrix1.Multiply(myMatrix3, MatrixOrder.Append);
ListMatrixElements(e, myMatrix1,"Matrix After 2nd Multiplication",6,80);
e.Graphics.DrawRectangle(myPen, 0, 0, 100, 100);
e.Graphics.Transform = myMatrix1;
e.Graphics.DrawRectangle(myPen2, 0, 0, 100, 100);
}
public void ListMatrixElements(PaintEventArgs e,Matrix matrix,string matrixName,
int numElements,int y)
{
int i;
float x = 20, X = 200;
Font myFont = new Font("Arial", 8);
SolidBrush myBrush = new SolidBrush(Color.Black);
e.Graphics.DrawString(matrixName + ": ", myFont,myBrush,x,y);
for(i=0; i<numElements; i++)
{
e.Graphics.DrawString(matrix.Elements[i].ToString() + ", ",myFont,myBrush,X,y);
X += 30;
}
}
放大后的线条全部变宽,无法应用于GIS变换。对于多个线条组成的图形需要缩放和平移时,可以重新生成一个点集(其中自己加上缩放和平移计算)来做。
从路径转换到点集用PathPoints属性。
可以利用Image类的Save方法保存目前显示的文件。需要在Form中定义:
public class Form1 : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button1;
private System.Windows.Forms.Button button2;
private System.Windows.Forms.PictureBox pictureBox1;
private Image cuurimage;
然后在程序中引用即可。
cuurimage=pictureBox1.Image;
cuurimage.Save("abc2.bmp");
PointF p1 = new PointF();
PointF p2 = new PointF();
Pen myPen = new Pen(Color.Black,1);
cuurimage = Image.FromFile("abc.bmp");
Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(cuurimage);
Color [] c ={Color.LightPink,Color.Red,Color.Blue,Color.Brown,Color.Black};
for(k=0;k<=LineColor.Count-1;k++)
{
myPen.Color = c[(int)LineColor[k]];
p1=(PointF)LineArray[i];
i++;
p2=(PointF)LineArray[i];
i++;
g.DrawLine(myPen,p1,p2);
}
myPen.Dispose();
g = CreateGraphics();
g.DrawImage(cuurimage,50,0,cuurimage.Width+100,cuurimage.Height+10);
g.Dispose();
在一个pictureBox上保存所画图像。
先需要加载一个背景图片,把图画在这个图片上,最后保存到另外一个文件中。
private Image cuurimage;
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Pen myPen = new Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,2);
pictureBox1.Image = Image.FromFile (@"..\..\abc1.bmp");
cuurimage = pictureBox1.Image;
Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(cuurimage);
g.DrawEllipse(myPen, 100, 100,44,14);
cuurimage.Save("abc0.bmp");
myPen.Dispose();
g.Dispose();
}
下例要先准备一个jpg图像文件。
先把jpg文件放在pictureBox的Graphics类g1上,然后在其上画图,保存在一个image类的变量中。需要擦除的图形画在另外一个Graphics类g2上,然后在g1上用DrawImage方法,就可以把g2上的图形全部擦除。
注意,中间不能有任何Refresh方法。擦除时才能使用一次Refresh方法。
Image imgBack;
System.Drawing.Graphics g1,g2;
Pen Pen1;
//新图形
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g2 = pictureBox1.CreateGraphics();
Pen1=new Pen(Color.Red,2);
g2.DrawLine(Pen1,10,10,200,200);
// pictureBox1.Refresh();
}
//原始图形
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
pictureBox1.Image = Image.FromFile (@"s4.jpg");
imgBack=pictureBox1.Image;
g1 = Graphics.FromImage(pictureBox1.Image);
Pen1=new Pen(Color.Blue,2);
g1.DrawLine(Pen1,10,100,200,20);
// pictureBox1.Refresh();
}
//擦除
private void button3_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g1.DrawImage(imgBack,0,0);
pictureBox1.Refresh();
}
以下程序可以找到一个存在的点,并在鼠标移动时改变光标和提示。点击显示其它信息。
PointF Pt1=new PointF();
PointF Pt2=new PointF();
System.Drawing.Graphics g;
int kk1=0; //判断是否重画,=1为已经重画
int kk2=0; //判断在距离内,=1为在距离内
double jl0=5; //距离
private static float Distance(PointF p1,PointF p2)
{
return (float)Math.Sqrt((p1.X-p2.X)*(p1.X-p2.X)+(p1.Y-p2.Y)*(p1.Y-p2.Y));
}
private void Form1_Closed(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g.Dispose();
}
private void Form1_MouseDown(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (kk2==1)
MessageBox.Show("xianshi");
}
private void Form1_MouseMove(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
double jl1;
Pt2.X=e.X;
Pt2.Y=e.Y;
jl1=Distance(Pt1,Pt2);
if (jl1<jl0)
{
this.Cursor=Cursors.Hand;
label1.Show();
label1.Left=(int)Pt1.X-6;
label1.Top=(int)Pt1.Y-20;
label1.Text="x="+Pt1.X.ToString()+" y="+Pt1.Y.ToString();
label1.Width=label1.Text.Length*7;
label1.Height=15;
kk2=1; //找到图像
kk1=0; //没有显示图像
}
else
{
if (kk1==0)
{
this.Cursor=Cursors.Arrow;
kk2=0;
label1.Hide();
g.FillEllipse(new SolidBrush(Color.Black),Pt1.X,Pt1.Y,5,5); //重新显示
kk1=1;
}
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Pt1.X=100;
Pt1.Y=100;
g.FillEllipse(new SolidBrush(Color.Black),Pt1.X,Pt1.Y,5,5);
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g = this.CreateGraphics();
label1.Hide();
}
可以实现发现点时改变鼠标光标和显示坐标提示,拖动鼠标完成点的移动。
在form上放置一个button1和label1,程序如下:
PointF Pt1=new PointF();
PointF Pt2=new PointF();
System.Drawing.Graphics g;
int kk1=0; //判断是否拖动,=1为拖动
int kk2=0; //判断在距离内,=1为在距离内
double jl0=5; //距离
private static float Distance(PointF p1,PointF p2)
{
return (float)Math.Sqrt((p1.X-p2.X)*(p1.X-p2.X)+(p1.Y-p2.Y)*(p1.Y-p2.Y));
}
private void Form1_Closed(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g.Dispose();
}
private void Form1_MouseUp(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (kk1==1 & kk2==1)
{
Pt2.X=e.X;
Pt2.Y=e.Y;
g.FillEllipse(new SolidBrush(this.BackColor),Pt1.X,Pt1.Y,5,5); //删除原来的点
g.FillEllipse(new SolidBrush(Color.Black),Pt2.X,Pt2.Y,5,5); //画新的点
Pt1=Pt2;
this.Cursor=Cursors.Arrow;
kk1=0;
kk2=0;
label1.Hide();
}
this.Cursor=Cursors.Arrow;
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
g = this.CreateGraphics();
label1.Hide();
}
private void Form1_MouseDown(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (kk2==1)
kk1=1;
else
kk1=0;
}
private void Form1_MouseMove(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
double jl1;
Pt2.X=e.X;
Pt2.Y=e.Y;
jl1=Distance(Pt1,Pt2);
if (jl1<jl0)
{
this.Cursor=Cursors.Hand;
label1.Show();
label1.Left=(int)Pt2.X-6;
label1.Top=(int)Pt2.Y-20;
label1.Text="x="+Pt1.X.ToString()+" y="+Pt1.Y.ToString();
kk2=1;
}
else if (kk1==0)
{
this.Cursor=Cursors.Arrow;
kk2=0;
label1.Hide();
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
Pt1.X=100;
Pt1.Y=100;
g.FillEllipse(new SolidBrush(Color.Black),Pt1.X,Pt1.Y,5,5);
}
PointF p1=new PointF();
PointF p2=new PointF();
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
System.Drawing.Pen myPen1;
System.Drawing.Pen myPen2;
System.Drawing.Graphics g1;
int dl;
private void Form1_MouseDown(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
p1.X=e.X;
p1.Y=e.Y;
dl=1;
}
private void Form1_MouseUp(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
p2.X=e.X;
p2.Y=e.Y;
g1.DrawRectangle(myPen,p1.X,p1.Y,p2.X-p1.X,p2.Y-p1.Y);
dl=0;
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,2);
myPen1 = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Yellow,1);
myPen2 = new System.Drawing.Pen(this.BackColor,1);
g1 = this.CreateGraphics();
dl=0;
}
private void Form1_Closed(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
myPen.Dispose();
myPen1.Dispose();
myPen2.Dispose();
g1.Dispose();
}
private void Form1_MouseMove(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (dl==1)
{
g1.DrawRectangle(myPen2,p1.X,p1.Y,p2.X-p1.X,p2.Y-p1.Y);
p2.X=e.X;
p2.Y=e.Y;
g1.DrawRectangle(myPen1,p1.X,p1.Y,p2.X-p1.X,p2.Y-p1.Y);
}
}
PointF p1=new PointF();
PointF p2=new PointF();
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
System.Drawing.Pen myPen1;
System.Drawing.Pen myPen2;
System.Drawing.Graphics g1;
int dl;
private void Form1_MouseDown(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
p1.X=e.X;
p1.Y=e.Y;
dl=1;
}
private void Form1_MouseUp(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
p2.X=e.X;
p2.Y=e.Y;
g1.DrawRectangle(myPen,p1.X,p1.Y,p2.X-p1.X,p2.Y-p1.Y);
dl=0;
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red,2);
myPen1 = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Yellow,1);
myPen2 = new System.Drawing.Pen(this.BackColor,1);
g1 = this.CreateGraphics();
dl=0;
}
private void Form1_Closed(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
myPen.Dispose();
myPen1.Dispose();
myPen2.Dispose();
g1.Dispose();
}
private void Form1_MouseMove(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (dl==1)
{
g1.DrawRectangle(myPen2,p1.X,p1.Y,p2.X-p1.X,p2.Y-p1.Y);
p2.X=e.X;
p2.Y=e.Y;
g1.DrawRectangle(myPen1,p1.X,p1.Y,p2.X-p1.X,p2.Y-p1.Y);
}
}
在Form1上放置控件Button1,picBox1(PictureBox),Form1.cs程序如下:
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
public string ss1;
//找到第一个字符串,直到空格或者行尾
string Qu1()
{
int i=0;
bool cbl=true;
int ls=ss1.Length;
while((i<ls)&(cbl))
{
char c1=ss1[i];
string s1=Convert.ToString(c1);
if (s1.Equals(" "))
cbl=false;
i++;
}
string s2=ss1.Remove(i,ls-i);
ss1=ss1.Remove(0,i-1);
// MessageBox.Show("ss1="+ss1);
return s2;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
string sfile = @"D:\chen\f8.txt";
String s0,s1;
int i,j,k;
float x1,y1;
bool Bl=true;
PointF [,] pta = new PointF[200,2000];
if (!File.Exists(sfile))
{
MessageBox.Show("File does not exist.");
return;
}
//画线设置
System.Drawing.Pen myPen;
float k1=0.08F;
float k2=0.08F;
float x0=0;
float y0=0;
myPen = new System.Drawing.Pen(System.Drawing.Color.Red);
myPen.Width =1;
System.Drawing.Graphics formGraphics = picBox1.CreateGraphics();
StreamReader sr = File.OpenText(sfile);
s0=sr.ReadLine();
s0=sr.ReadLine();
s0=sr.ReadLine();
//读取数值文件
k=0;
s0=sr.ReadLine();
ss1=s0.Trim();
while (s0!=null)
{
i=0;
while (Bl)
{
s1=Qu1();
x1=Convert.ToSingle(s1);
ss1=ss1.Trim();
s1=Qu1();
y1=Convert.ToSingle(s1);
pta[k,i] = new PointF( x0+x1*k1, y0+y1*k2);
i++;
s0=sr.ReadLine();
ss1=s0.Trim();
if (ss1.Equals("-1"))
Bl=false;
}
Bl=true;
PointF[] cPoints=new PointF[i+1];
for (j=0;j<i;j++)
{
cPoints[j]=pta[k,j];
}
cPoints[i]=pta[k,0];
k++;
//画线
formGraphics.DrawLines(myPen, cPoints);
s0=sr.ReadLine();
if(s0!=null)
ss1=s0.Trim();
}
myPen.Dispose();
formGraphics.Dispose();
sr.Close();
}
f8.txt格式:
0.00 0.00 8895.00 8895.00
25 28 29 29.5 30.5 31 32 35
5644.20 4625.40 32.00
5633.50 4641.57 32.00
5628.85 4655.05 32.00
5633.50 4681.35 32.00
5634.67 4684.70 32.00
5663.15 4703.27 32.00
5692.80 4700.70 32.00
5714.98 4684.70 32.00
5722.45 4668.68 32.00
5726.26 4655.05 32.00
5722.45 4640.66 32.00
5714.23 4625.40 32.00
5692.80 4612.07 32.00
5663.15 4613.03 32.00
5644.20 4625.40 32.00
5644.20 4625.40 32.00
-1
2463.28 8895.00 25.00
2487.03 8865.35 25.00
2490.60 8860.86 25.00
……
DateTime oldDate = new DateTime(2002,7,15);
DateTime newDate = DateTime.Now;
// Difference in days, hours, and minutes.
TimeSpan ts = newDate - oldDate;
// Difference in days.
int differenceInDays = ts.Days;
Console.WriteLine("Difference in days: {0} ", differenceInDays);
注意,TimeSpan是系统基础类。
public static bool JM(DateTime T0,int ii)
{
bool Bl=false;
DateTime T1 = DateTime.Now;
TimeSpan ts = T1-T0;
if (ts.Days>ii)
Bl=true;
return Bl;
}
DateTime oldDate = new DateTime(2007,1,29); //起始时间
if(Common1.JM(oldDate,100)) //有效期100天
{
MessageBox.Show("试用版到期,请和北京派得伟业公司联系,电话010-51503625");
Application.Exit();
}
以下程序在每隔2秒显示一个MessageBox提示。其中TimerEventProcessor方法在timer开始后就自动运行。
static System.Windows.Forms.Timer myTimer = new System.Windows.Forms.Timer();
static int alarmCounter = 1;
static bool exitFlag = false;
private static void TimerEventProcessor(Object myObject,EventArgs myEventArgs)
{
myTimer.Stop();
if(MessageBox.Show("继续?","计数:"+alarmCounter,MessageBoxButtons.YesNo)==DialogResult.Yes)
{
alarmCounter +=1;
myTimer.Enabled = true;
}
else
exitFlag = true;
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
myTimer.Tick += new EventHandler(TimerEventProcessor);
myTimer.Interval = 2000;
myTimer.Start();
while(exitFlag == false)
{
// Processes all the events in the queue.
Application.DoEvents();
}
}
以下为延时程序,单位为毫秒。由于ts.Milliseconds数值在大于1000时出错,所以要转换成ts.Seconds。
public void TimeDelay(int it)
{
bool Bl=true;
DateTime T1,T0;
TimeSpan ts;
int it0;
T0 = DateTime.Now;
while(Bl)
{
T1 = DateTime.Now;
ts=T1-T0;
if (it>1000)
{
it0=Convert.ToInt32(it/1000);
if (ts.Seconds>it0)
Bl=false;
}
else
if (ts.Milliseconds>it)
Bl=false;
Application.DoEvents();
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("开始");
TimeDelay(2900);
MessageBox.Show("时间到。");
}
注意:在延时程序没有完成前,不能退出。
动态链接库 (DLL) 在运行时链接到程序。本程序通过两个cs文件生成一个MyLibrary.DLL的库文件。
Add.cs:为源文件,其中包含 Add(long i, long j) 方法。该方法返回参数之和。包含 Add 方法的 AddClass 类是命名空间 MyMethods 的成员。
Mult.cs:为源文件,其中包含 Multiply(long x, long y) 方法。该方法返回参数之积。包含 Multiply 方法的 MultiplyClass 类也是命名空间 MyMethods 的成员。
MyClient.cs:包含 Main 方法的文件。它使用 DLL 文件中的方法来计算运行时参数的和与积。
文件:Add.cs
// Add two numbers
using System;
namespace MyMethods
{
public class AddClass
{
public static long Add(long i, long j)
{
return(i+j);
}
}
}
文件:Mult.cs
// Multiply two numbers
using System;
namespace MyMethods
{
public class MultiplyClass
{
public static long Multiply(long x, long y)
{
return (x*y);
}
}
}
文件:MyClient.cs
// Calling methods from a DLL file
using System;
using MyMethods;
class MyClient
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Calling methods from MyLibrary.DLL:");
if (args.Length != 2)
{
Console.WriteLine("Usage: MyClient <num1> <num2>");
return;
}
long num1 = long.Parse(args[0]);
long num2 = long.Parse(args[1]);
long sum = AddClass.Add(num1, num2);
long product = MultiplyClass.Multiply(num1, num2);
Console.WriteLine("The sum of {0} and {1} is {2}",
num1, num2, sum);
Console.WriteLine("The product of {0} and {1} is {2}",
num1, num2, product);
}
}
此文件包含使用 DLL 方法 Add 和 Multiply 的算法。它首先分析从命令行输入的参数 num1 和 num2。然后使用 AddClass 类中的 Add 方法计算和,使用 MultiplyClass 类中的 Multiply 方法计算积。
请注意,文件开头的 using 指令使您得以在编译时使用未限定的类名来引用 DLL 方法,例如:
MultiplyClass.Multiply(num1, num2);
否则,必须使用完全限定名,例如:
MyMethods.MultiplyClass.Multiply(num1, num2);
若要生成文件 MyLibrary.DLL,使用以下命令行编译文件 Add.cs 和文件 Mult.cs:
csc /target:library /out:MyLibrary.DLL Add.cs Mult.cs
如果对于一个文件以及缺省dll文件名,可以用:
csc /target:library Mult.cs
这样生成一个Mult.dll的文件。
若要生成可执行文件 MyClient.exe,请使用以下命令行:
csc /out:MyClient.exe /reference:MyLibrary.DLL MyClient.cs
使用命令行编译文件,在【开始】/【程序】/【Microsoft Visual Studio .NET 2003】/【Visual Studio .NET工具】/【Visual Studio .NET命令提示】。
默认目录为当前用户目录。如果你使用Administrator,则目录为C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator。你可以把几个cs文件拷贝到这个目录中。
若要运行程序,请输入 EXE 文件的名称,文件名的后面跟两个数字,例如:
MyClient 1234 5678
运行结果为:
Calling methods from MyLibrary.DLL:
The sum of 1234 and 5678 is 6912
The product of 1234 and 5678 is 7006652
建立一个bat文件如下:
c:\windows\microsoft.net\framework\v1.1.4322\csc.exe /target:library contour01.cs
就可以自动把contour01.cs编译成contour01.dll了。
把以上的文件编译成MyLibrary.DLL后,在一个控制台应用程序中使用MyClient.cs。先引用MyLibrary.DLL,然后修改程序为:
using System;
using MyMethods;
class MyClient
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Calling methods from MyLibrary.DLL:");
long num1 = 100;
long num2 = 550;
long sum = AddClass.Add(num1, num2);
long product = MultiplyClass.Multiply(num1, num2);
Console.WriteLine("The sum of {0} and {1} is {2}",
num1, num2, sum);
Console.WriteLine("The product of {0} and {1} is {2}",
num1, num2, product);
}
}
运行结果和以前一样。
1.编译dll文件。
2.把dll文件拷贝到工作文件夹下面。
3.在右边文件夹的【引用】上右击,选择【添加引用】,在【com】中浏览选择,即可添加。也可以在菜单【项目】/【添加引用】上添加。
4.如果需要修改,需要把管理员目录下的dll文件删除,再次生成。
定义从 System.Windows.Forms.Control 派生的类。
public class FirstControl:Control{...}
以下代码片段定义名为 TextAlignment 的属性,FirstControl 使用该属性来定义从 Control 继承的 Text 属性的显示格式。
// ContentAlignment is an enumeration defined in the System.Drawing
// namespace that specifies the alignment of content on a drawing
// surface.
private ContentAlignment alignment = ContentAlignment.MiddleLeft;
public ContentAlignment TextAlignment {
get {
return alignment;
}
set {
alignment = value;
// The Invalidate method invokes the OnPaint method described
// in step 3.
Invalidate();
}
}
在设置更改控件外观显示的属性时,必须调用 Invalidate 方法来重新绘制该控件。Invalidate 是在基类 Control 中定义的。
重写从 Control 继承的受保护的 OnPaint 方法,以便为控件提供呈现逻辑。如果不改写 OnPaint,您的控件将无法自行绘制。在下列代码片段中,OnPaint 方法显示了从 Control 继承的具有默认对齐方式的 Text 属性。
public class FirstControl : Control{
public FirstControl() {...}
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e) {
base.OnPaint(e);
e.Graphics.DrawString(Text, Font, new SolidBrush(ForeColor), ClientRectangle, style);
}
}
属性可使可视化设计器在设计时适当地显示控件及其属性和事件。以下代码片段将属性应用于 TextAlignment 属性。在 Microsoft Visual Studio .NET 这样的设计器中,Category 属性(如代码片段所示)使该属性显示在逻辑类别中。在选择 TextAlignment 属性时,Description 属性使说明字符串显示在"属性"窗口的底部。
[
Category("Alignment"),
Description("Specifies the alignment of text.")
]
public ContentAlignment TextAlignment {...}
通过使用编辑器选项(C# 中为 /res),可以为控件提供诸如位图之类的资源来打包控件的资源。在运行时,使用 System.Resources.ResourceManager 类的方法可检索该资源。有关创建和使用资源的更多信息,请参见 .NET 示例 – 如何获取:资源快速入门。
要编译和部署 FirstControl,请执行以下步骤:
将下列示例中的代码保存到源文件(如 FirstControl.cs)。
将源代码编译成程序集,并将其保存到应用程序的目录中。为了实现这一目的,需在包含源文件的目录中执行以下命令。
csc /t:library /out:[path to your application‘s directory]/CustomWinControls.dll /r:System.dll /r:System.Windows.Forms.dll /r:System.Drawing.dll FirstControl.cs
/t:library 编译器选项告诉编译器正在创建的程序集是一个库(而不是一个可执行程序)。/out 选项用来指定程序集的路径和名称。/r 选项提供代码所参考的程序集的名称。在本示例中,创建了一个仅供您自己的应用程序使用的专用程序集。因此,您必须将其保存到您的应用程序的目录中。有关打包和部署控件进行分发的更多信息,请参见部署 .NET Framework 应用程序。
以下示例显示了 FirstControl 的代码。该控件包含在命名空间 CustomWinControls 中。命名空间提供了相关类型的逻辑分组。可以在新命名空间或现有的命名空间中创建控件。在 C# 中,using 声明(在 Visual Basic 中,Imports)允许从命名空间访问类型,而无须使用完全限定的类型名称。在以下示例中,using 声明允许代码从 System.Windows.Forms 作为简单控件存取 Control 类,而无须使用完全限定的名称 System.Windows.Forms.Control。
namespace CustomWinControls {
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing;
public class FirstControl : Control {
private ContentAlignment alignment = ContentAlignment.MiddleLeft;
[
Category("Alignment"),
Description("Specifies the alignment of text.")
]
public ContentAlignment TextAlignment {
get {
return alignment;
}
set {
alignment = value;
// The Invalidate method invokes the OnPaint method.
Invalidate();
}
}
// OnPaint aligns text, as specified by the
// TextAlignment property, by passing a parameter
// to the DrawString method of the System.Drawing.Graphics object.
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e) {
base.OnPaint(e);
StringFormat style = new StringFormat();
style.Alignment = StringAlignment.Near;
switch (alignment) {
case ContentAlignment.MiddleLeft:
style.Alignment = StringAlignment.Near;
break;
case ContentAlignment.MiddleRight:
style.Alignment = StringAlignment.Far;
break;
case ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter:
style.Alignment = StringAlignment.Center;
break;
}
// Call the DrawString method of the System.Drawing class to write
// text. Text and ClientRectangle are properties inherited from
// Control.
e.Graphics.DrawString(Text, Font, new SolidBrush(ForeColor), ClientRectangle, style);
}
}
}
以下示例说明了一个使用 FirstControl 的简单窗体。它创建了三个 FirstControl 实例,每个实例都有不同的 TextAlignment 属性值。
将下列示例中的代码保存到源文件(SimpleForm.cs)。
通过从包含该源文件的目录中执行以下命令,将源代码编译成可执行的程序集。
csc /r:CustomWinControls.dll /r:System.dll /r:System.Windows.Forms.dll /r:System.Drawing.dll SimpleForm.cs
CustomWinControls.dll 是包含类 FirstControl 的程序集。该程序集必须与存取它的窗体源文件位于同一目录中(SimpleForm.cs 或 SimpleForms.vb)。
使用下列命令执行 SimpleForm.exe。
SimpleForm
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Drawing;
using CustomWinControls;
class SimpleForm : Form {
private FirstControl left;
private FirstControl center;
private FirstControl right;
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing) {
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
public SimpleForm() : base() {
left = new FirstControl();
left.Text = "Left";
left.Location = new Point(50, 50);
left.Size = new Size(50, 50);
Controls.Add(left);
center = new FirstControl();
center.TextAlignment = ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter;
center.Text = "Center";
center.Location = new Point(125, 50);
center.Size = new Size(50, 50);
Controls.Add(center);
right = new FirstControl();
right.TextAlignment = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight;
right.Text = "Right";
right.Location = new Point(200, 50);
right.Size = new Size(50, 50);
Controls.Add(right);
}
[STAThread]
public static void Main(string[] args) {
Form form = new SimpleForm();
form.Text = "Uses FirstControl";
form.Size = new Size(400, 150);
Application.Run(form);
}
}
用户控件相当于带界面的类模块,并可以编译成dll。具有以下优点:
1.可以把程序分离成内核部分和引用部分,便于开发和维护;
2.可以多进程调用;
3.安全性好。
自己创建一个简单用户控件的步骤为:
1.新建一个"Windows控件库"的项目;
2.编写控件程序,如需要传递参数,定义如下:
public PointF p1,p2;
3.在【生成】中生成dll;
4.用【文件】/【添加项目】/【新建项目】,新建一个使用控件项目,为"Windows应用程序";
5.用【项目】/【添加引用】/【项目】,引用控件项目;
6.在【工具箱】/【我的用户控件】中选择生成的控件;
7.把使用项目设置为启动;
8.编写程序。如果传递参数,用:
private void Form1_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
userControl11.p1=new PointF(20,20);
userControl11.p2=new PointF(100,200);
}
然后可以在这个解决方案中随意修改控件设计,只要运行调用程序,就可以自动编译和加载控件了。如果修改了控件的界面,还需要重新生成和加载。
如果在单独的使用程序中调用这个dll控件,则先需要添加引用,然后需要在"工具箱"上点击右键,选择【添加/移除项】,把这个控件添加到工具箱上,才可以添加到form上。
在使用程序中可以随意调用控件中的方法。如果要在控件中调用使用程序中的方法,则可以使用一个传递参数,如 int bi,每次点击事件时bi值改变。然后在使用程序中用一个timer控件,用事件timer1_Tick来监控bi的变化,来触发一个方法。
public class InputBox : System.Windows.Forms.Form
{
private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox txtData;
private System.Windows.Forms.Label lblInfo;
private System.ComponentModel.Container components = null;
private InputBox()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void Dispose( bool disposing )
{
if( disposing )
{
if(components != null)
{
components.Dispose();
}
}
base.Dispose( disposing );
}
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.txtData = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();
this.lblInfo = new System.Windows.Forms.Label();
this.SuspendLayout();
// txtData
this.txtData.Font = new System.Drawing.Font("宋体", 10.5F, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Regular, System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit.Point, ((System.Byte)(134)));
this.txtData.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(19, 8);
this.txtData.Name = "txtData";
this.txtData.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(317, 23);
this.txtData.TabIndex = 0;
this.txtData.Text = "";
this.txtData.KeyDown += new System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventHandler(this.txtData_KeyDown);
// lblInfo
this.lblInfo.Font = new System.Drawing.Font("宋体", 9F, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Regular, System.Drawing.GraphicsUnit.Point, ((System.Byte)(134)));
this.lblInfo.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(19, 32);
this.lblInfo.Name = "lblInfo";
this.lblInfo.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(317, 16);
this.lblInfo.TabIndex = 1;
this.lblInfo.Text = "按[Enter]键确认,按[Esc]键取消";
// InputBox
this.AutoScaleBaseSize = new System.Drawing.Size(6, 14);
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(350, 48);
this.ControlBox = false;
this.Controls.Add(this.lblInfo);
this.Controls.Add(this.txtData);
this.FormBorderStyle = System.Windows.Forms.FormBorderStyle.FixedDialog;
this.Name = "InputBox";
this.Text = "InputBox";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
//对键盘进行响应
private void txtData_KeyDown(object sender, System.Windows.Forms.KeyEventArgs e)
{
if(e.KeyCode == Keys.Enter)
{
this.Close();
}
else if (e.KeyCode == Keys.Escape )
{
txtData.Text = string.Empty ;
this.Close();
}
}
//显示InputBox
public static string ShowInputBox(string Title,string keyInfo)
{
InputBox inputbox = new InputBox();
inputbox.Text =Title;
if (keyInfo.Trim() != string.Empty )
inputbox.lblInfo.Text =keyInfo;
inputbox.ShowDialog();
return inputbox.txtData.Text;
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
string inMsg = InputBox.ShowInputBox("输入信息",string.Empty );
//对用户的输入信息进行检查
if (inMsg.Trim() != string.Empty )
{
MessageBox.Show(inMsg);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("输入为空!");
}
如果需要输入一个int数值,则程序如下:
string inMsg = InputBox.ShowInputBox("输入信息",string.Empty );
int a1;
if (inMsg.Trim() != string.Empty )
{
try
{
a1=Convert.ToInt32(inMsg.Trim());
MessageBox.Show(a1.ToString());
}
catch (Exception)
{
MessageBox.Show("输入错误!继续保持原有数据。");
}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("输入为空!");
}
在类中增加以下程序:
public static string ShowInputBox(string Title,string keyInfo,string textInfo)
{
InputBox inputbox = new InputBox();
inputbox.Text =Title;
inputbox.txtData.Text=textInfo;
if (keyInfo.Trim() != string.Empty )
inputbox.lblInfo.Text =keyInfo;
inputbox.ShowDialog();
return inputbox.txtData.Text;
}
可以在调用时输入textBox中的缺省值。
在文件AssemblyInfo.cs中修改
[assembly: AssemblyVersion("2.1.1.*")]
则在最后生成的EXE文件中显示版本号2.2.1.10803,最后一个号码随着每次编辑修改后递增。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yunyun0574/p/5930247.html