标签:
计数排序是一种线性时间的排序,同时也是一种非比较排序
代码如下:
1 void CountingSort(int *data, int k, int num) // A ~ data[], B ~ aimArray[], C ~ tempArray[]
2 {
3 int *aimArray = new int[num];
4 int *tempArray = new int[k + 1];
5 for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
6 tempArray[i] = 0;
7 for (int j = 0; j < num; j++)
8 tempArray[data[j]]++;
9 for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
10 tempArray[i] = tempArray[i] + tempArray[i - 1];11 for (int j = num - 1 ; j >= 0; j--)
12 {
13 aimArray[tempArray[data[j]]] = data[j];
14 tempArray[data[j]]--;
15 }
16 for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
17 data[i] = aimArray[i + 1];
18 }
排序例图如下:
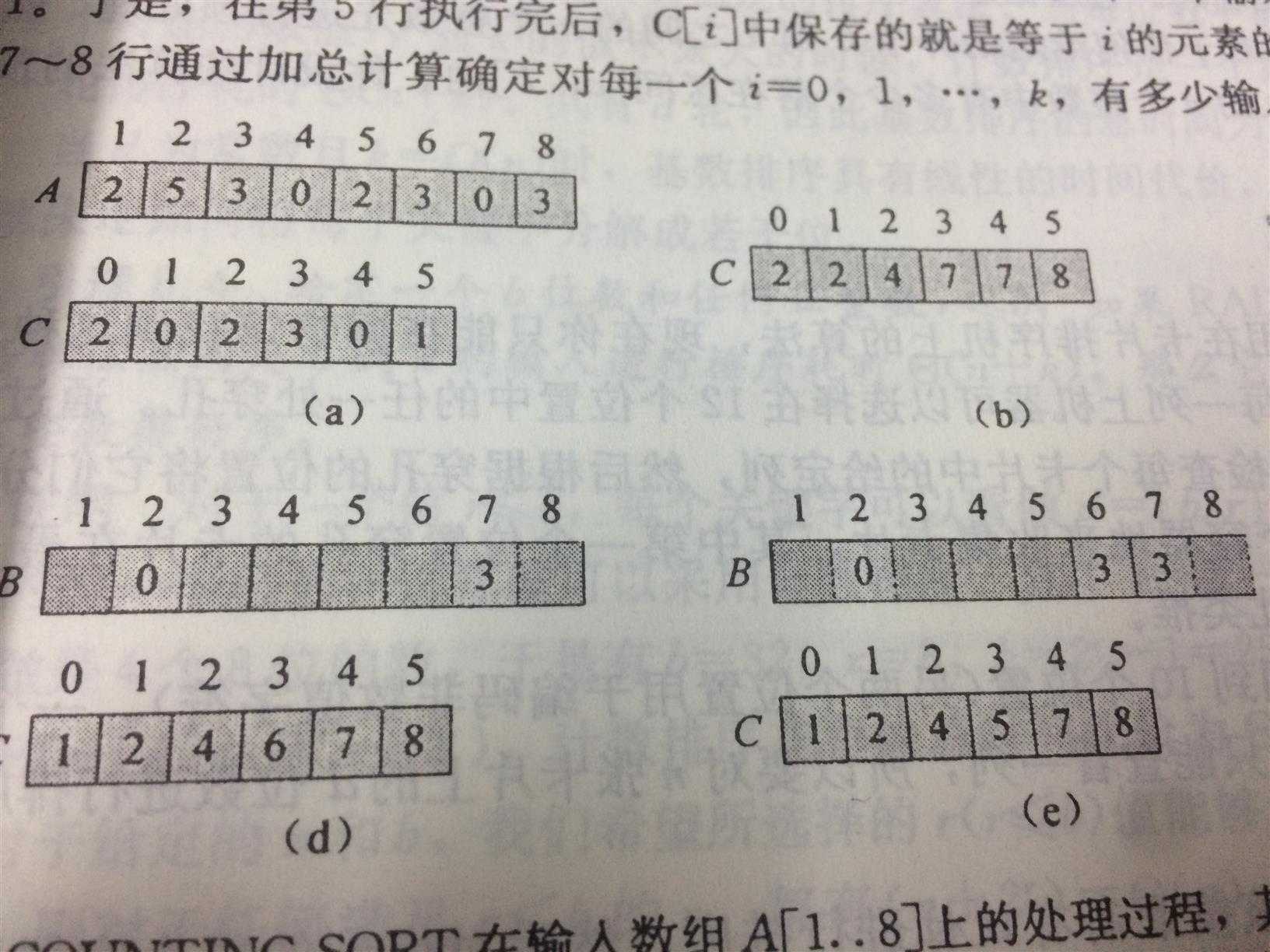
计数排序需要用到三个数组 :
代码中 数组data[A]是待排序数组,aimArray[B]是中间数组, tempArray[C]是保存数组元素相对位置的数组
5-6行,将tempArray数组清零
7-10行, 将原数组元素相对关系储存起来, 如图中原数组{2,5,3,0,2,3,0,3} 再对照储存后的tempArray数组,数组序号代表的是data数组拥有的元素,位置0的元素为2,意味着≤0的元素有两个,所以有两个零,重新定位的时候就应该将这两个0的位置定为 0和1,位置1的元素也为2,就是那两个0,所以原数组data中没有1。依次类推,在剩余的数组中将原数组data所有的元素定好位置再放入AimArray中,最后在转移回数组data中,就完成了计数排序
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Kevinlee21/p/5971655.html