标签:ring main 建立 [] system 类构造 简写 构造 print
一般情况下java中的类不能用static修饰,唯一可以修饰的是内部类
内部类的特点:
1.内部类可以直接访问外部类中的成员
2.外部类要访问内部类,必须建立内部类的对象
一般用于类的设计
分析事物时,发现该事物描述中还有事物,而且这个事物还在访问被描述的事物的内容。这时就是还有的事物定义成内部类来描述。
如果内部类中定义了静态成员,那么该内部类也必须是静态的。
为什么内部类能直接访问外部类的成员呢?
那是因为内部类持有了外部类的引用。 外部类名.this
内部类可以存放在局部位置上。
内部类在局部位置上只能访问局部中被final修饰的局部变量。
匿名内部类。就是内部类的简写格式。
前提:内部类必须继承或者实现一个外部类或者接口,其实就是一个匿名子类对象。
格式:new 父类or接口(){子类内容}.调用
代码实现:
1 class Demo2 2 { 3 public static void main(String[] args) 4 { 5 Outer1 o=new Outer1(); 6 o.method(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 abstract class Father//父类 11 { 12 abstract void show(); 13 } 14 class Outer1 15 { 16 int num=10; 17 void method() 18 { 19 new Father()//匿名内部类 20 { 21 void show() 22 { 23 System.out.println("SHOW......"+num); 24 } 25 }.show(); 26 } 27 }
通常的使用场景之一:
当函数参数是接口类型时,而且接口中的方法不超过3个,可以用匿名内部类作为实际参数进行传递
代码实现:
1 interface Inter 2 { 3 void show1(); 4 void show2(); 5 } 6 7 class Demo3 8 { 9 public static void main(String[] args) 10 { 11 int num=20; 12 show(new Inter(){ 13 public void show1() 14 { 15 System.out.println("show111111.........."+num); 16 } 17 public void show2() 18 { 19 System.out.println("show222222.........."+num); 20 } 21 }); 22 } 23 public static void show(Inter in) 24 { 25 in.show1(); 26 in.show2(); 27 } 28 }
java中创建对象是构造函数,构造代码块,父类构造函数之间的调用顺序:
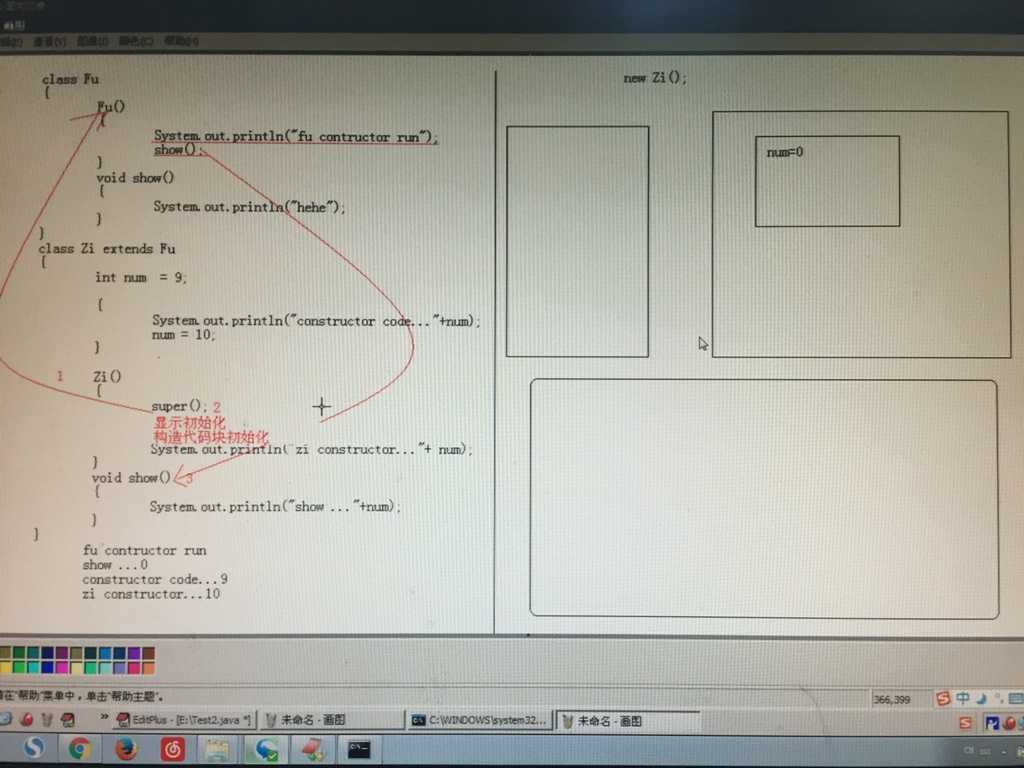
标签:ring main 建立 [] system 类构造 简写 构造 print
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/pushudepu/p/6002043.html