标签:应该 context ack 动态 pos 判断 基础 index lang
碰撞可以分为碰壁和互碰两种形式,上篇介绍了碰壁运动,本文将从浅入深地介绍碰撞运动的互碰形式
对于互碰形式的碰撞运动来说,首先要解决的是碰撞检测。对于矩形元素的碰撞检测前面的博文已经详细介绍过,下面主要介绍圆形元素的碰撞检测
矩形元素的碰撞检测利用九宫格分析法,而圆形元素的碰撞检测则简单很多,判断两个圆形元素的半径之和是否大于两个圆形元素的圆心点坐标之间的距离即可
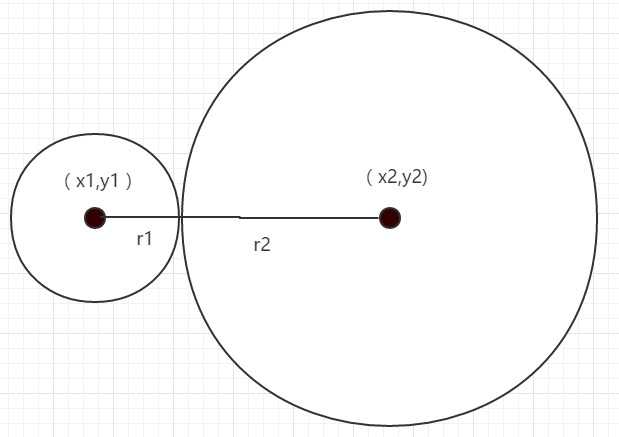
由示意图可知,元素一的圆心位置为(x1,y1),半径为r1,元素二的圆心位置为(x2,y2),半径为r2
两个元素圆心之间的距离len = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2) + (y1-y2)*(y1-y2))
当len<= r1+r2时,说明两个圆形元素发生碰撞
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="test1" style="height: 100px;width: 100px;background:pink;position:absolute;top:0;left:0;border-radius: 50%;"></div> <div id="test2" style="height: 200px;width: 200px;background:orange;position:absolute;top:150px;left:150px;border-radius: 50%;"></div> <script> function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } function bump(obj,objOther,bgColor){ /***被碰元素***/ var r1 = obj.offsetWidth/2; var x1 = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,‘left‘)) + r1; var y1 = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,‘top‘)) + r1; /**侵入元素**/ var r2 = objOther.offsetWidth/2; var x2 = parseFloat(getCSS(objOther,‘left‘)) + r2; var y2 = parseFloat(getCSS(objOther,‘top‘)) + r2; //碰撞检测 var len = Math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2) + (y1-y2)*(y1-y2)); if(len <= r1 + r2){ obj.style.backgroundColor = ‘red‘; }else{ obj.style.backgroundColor = bgColor; } } function drag(obj){ obj.onmousedown = function(e){ e = e || event; //提升当前元素的层级 obj.style.zIndex = ‘1‘; //获取元素距离定位父级的x轴及y轴距离 var x0 = this.offsetLeft; var y0 = this.offsetTop; //获取此时鼠标距离视口左上角的x轴及y轴距离 var x1 = e.clientX; var y1 = e.clientY; //鼠标按下时,获得此时的页面区域 var L0 = 0; var R0 = document.documentElement.clientWidth; var T0 = 0; var B0 = document.documentElement.clientHeight; //鼠标按下时,获得此时的元素宽高 var EH = obj.offsetHeight; var EW = obj.offsetWidth; document.onmousemove = function(e){ e = e || event; //获取此时鼠标距离视口左上角的x轴及y轴距离 x2 = e.clientX; y2 = e.clientY; //计算此时元素应该距离视口左上角的x轴及y轴距离 var X = x0 + (x2 - x1); var Y = y0 + (y2 - y1); /******范围限定*******/ //获取鼠标移动时元素四边的瞬时值 var L = X; var R = X + EW; var T = Y; var B = Y + EH; //在将X和Y赋值给left和top之前,进行范围限定 //只有在范围内时,才进行相应的移动 //如果脱离左侧范围,则left置L0 if(L < L0){X = L0;} //如果脱离右侧范围,则left置为R0 if(R > R0){X = R0 - EW;} //如果脱离上侧范围,则top置T0 if(T < T0){Y = T0;} //如果脱离下侧范围,则top置为B0 if(B > B0){Y = B0 - EH;} obj.style.left = X + ‘px‘; obj.style.top = Y + ‘px‘; //运行碰撞检测函数 bump(test2,test1,‘orange‘) } document.onmouseup = function(e){ //降低当前元素的层级 obj.style.zIndex = ‘0‘; //当鼠标抬起时,拖拽结束,则将onmousemove赋值为null即可 document.onmousemove = null; //释放全局捕获 if(obj.releaseCapture){ obj.releaseCapture(); } } //阻止默认行为 return false; //IE8-浏览器阻止默认行为 if(obj.setCapture){ obj.setCapture(); } } } drag(test1); drag(test2); </script> </body> </html>
假设两个元素的碰撞,对元素的速度并不产生损耗,而只是改变元素速度方向
假设元素一在与元素二碰撞前的瞬时速度是v,将该速度分解为平行于碰撞方向的速度v1和垂直于碰撞方向的速度v2
碰撞发生后,碰撞方向的速度v1变成了反向的v1
将反向的v1分解到水平方向v1x和垂直方向v1y
将垂直于碰撞方向的速度v2分解到水平方向v2x和垂直方向v2y
水平方向的速度vx = v2x - v1x
垂直方向的速度vy = v2y - v1y
元素二的速度分解形式与元素一类似,就不再赘述
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <button id="btn1">开始运动</button> <button id="reset">还原</button> <div id="test1" style="height: 150px;width: 150px;background:pink;position:absolute;top:50px;left:50px;border-radius: 50%;"></div> <div id="test2" style="height: 150px;width: 150px;background:orange;position:absolute;top:250px;left:250px;border-radius: 50%;"></div> <script> //声明元素的步长值 //步长值默认值为[-25,-20,-15,-10,-5,0,5,10,15,20]中的一个随机数 test1.stepX = 5*Math.floor(Math.random() * 10 - 5); test1.stepY = 5*Math.floor(Math.random() * 10 - 5); test2.stepX = 5*Math.floor(Math.random() * 10 - 5); test2.stepY = 5*Math.floor(Math.random() * 10 - 5); btn1.onclick = function(){ collisionMove({ obj:test1 }) collisionMove({ obj:test2 }) } reset.onclick = function(){ history.go(); } function collisionMove(json){ var obj = json.obj; var fn = json.fn; //声明x、y轴的当前值 var curX,curY; //声明x、y轴方向 var dirX = json.dirX; var dirY = json.dirY; dirX = obj.stepX > 0 ? ‘+‘ : ‘-‘; dirY = obj.stepY > 0 ? ‘+‘ : ‘-‘; //声明offset宽高 var offsetWidth = obj.offsetWidth; var offsetHeight = obj.offsetHeight; //声明元素活动区域宽高 var activeWidth = json.activeWidth; var activeHeight = json.activeHeight; //元素获取区域宽高默认值为可视区域宽高 activeWidth = Number(activeWidth) || document.documentElement.clientWidth; activeHeight = Number(activeHeight) || document.documentElement.clientHeight; //声明left、top样式值 var left,top; //清除定时器 if(obj.timer){return;} //开启定时器 obj.timer = setInterval(function(){ //获取x、y轴的当前值 curX = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,‘left‘)); curY = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,‘top‘)); bump(test1,test2); //更新left、top值 left = curX + obj.stepX; top = curY + obj.stepY; //右侧碰壁前一刻,步长大于剩余距离,且元素向右运动时 if((left > activeWidth - offsetWidth) && (dirX == ‘+‘)){ left = activeWidth - offsetWidth; } //左侧碰壁前一刻,步长大于剩余距离,且元素向左运动时 if((Math.abs(obj.stepX) > curX) && (dirX == ‘-‘)){ left = curX; } //下侧碰壁前一刻,步长大于剩余距离,且元素向下运动时 if((top > activeHeight - offsetHeight) && (dirY == ‘+‘)){ top = activeHeight - offsetHeight; } //上侧碰壁前一刻,步长大于剩余距离,且元素向上运动时 if((Math.abs(obj.stepY) > curY) && (dirY == ‘-‘)){ top = curY; } obj.style.left= left + ‘px‘; obj.style.top = top + ‘px‘; //左侧或右侧碰撞瞬间 if(left == activeWidth - offsetWidth || left == curX){ obj.stepX = -obj.stepX; } //上侧或下侧碰撞瞬间 if(top == activeHeight - offsetHeight || top == curY){ obj.stepY = -obj.stepY; } //更新运动方向 dirX = obj.stepX > 0 ? ‘+‘ : ‘-‘; dirY = obj.stepY > 0 ? ‘+‘ : ‘-‘; },20); } function getCSS(obj,style){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[style]; } return obj.currentStyle[style]; } //碰撞检测函数 function bump(obj,objOther){ /***动态元素***/ obj.r = obj.offsetWidth/2; obj.x0 = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,‘left‘)) + obj.r; obj.y0 = parseFloat(getCSS(obj,‘top‘)) + obj.r; /**静态元素**/ objOther.r = objOther.offsetWidth/2; objOther.x0 = parseFloat(getCSS(objOther,‘left‘)) + objOther.r; objOther.y0 = parseFloat(getCSS(objOther,‘top‘)) + objOther.r; //圆心之间的距离 var len = Math.sqrt((obj.x0-objOther.x0)*(obj.x0-objOther.x0) + (obj.y0-objOther.y0)*(obj.y0-objOther.y0)); //发生碰撞 if(len <= obj.r + objOther.r){ //碰撞方向与水平负方向的夹角a var a = Math.atan(Math.abs((obj.y0-objOther.y0)/(obj.x0-objOther.x0))); stepChange(test1,test2,a); stepChange(test2,test1,a); } } //碰撞时,步长变化函数 function stepChange(obj,objOther,a){ //步长合并 obj.step = Math.sqrt(obj.stepX*obj.stepX + obj.stepY*obj.stepY); //假设总步长方向与x轴方向的夹角为b obj.b = Math.atan(Math.abs(obj.stepY/obj.stepX)); //假设总步长方向与碰撞方向的夹角为c obj.c = Math.abs(a - obj.b); //步长分解 //碰撞方向 obj.step1 = obj.step*Math.cos(obj.c); //垂直方向 obj.step2 = obj.step*Math.sin(obj.c); //按照运动元素(侵入元素)的起始运动方向对步长进行重新分解 //左上 if(obj.x0 <= objOther.x0 && obj.y0 <= objOther.y0){ obj.stepX = -obj.step1*Math.cos(a) + obj.step2*Math.sin(a) obj.stepY = -obj.step1*Math.sin(a) - obj.step2*Math.cos(a) } //左下 if(obj.x0 < objOther.x0 && obj.y0 > objOther.y0){ obj.stepX = -obj.step1*Math.cos(a) + obj.step2*Math.sin(a) obj.stepY = obj.step1*Math.sin(a) + obj.step2*Math.cos(a) } //右上 if(obj.x0 > objOther.x0 && obj.y0 < objOther.y0){ obj.stepX = obj.step1*Math.cos(a) - obj.step2*Math.sin(a) obj.stepY = -obj.step1*Math.sin(a) - obj.step2*Math.cos(a) } //右下 if(obj.x0 > objOther.x0 && obj.y0 > objOther.y0){ obj.stepX = obj.step1*Math.cos(a) - obj.step2*Math.sin(a) obj.stepY = obj.step1*Math.sin(a) + obj.step2*Math.cos(a) } } </script> </body> </html>
匀速有损碰撞是在无损碰撞的基础上,每次碰撞都有一定的速度损耗,在碰撞或碰壁的瞬间乘以损耗因子即可
变速有损碰撞类似于击打台球,元素运动时,速度就一直在减小,碰撞或碰壁时,除了速度方向改变外,速度也有所损耗,当速度减小到0时,停止运动。由于代码相似,就不再重复,源码见此
标签:应该 context ack 动态 pos 判断 基础 index lang
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohuochai/p/6003860.html