标签:return hello path blog pyc cti mod src style
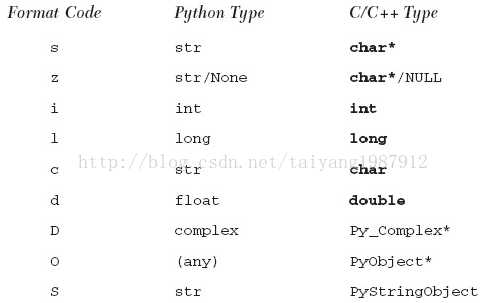
从Python到C的转换用PyArg_Parse*系列函数,int PyArg_ParseTuple():把Python传过来的参数转为C;int PyArg_ParseTupleAndKeywords()与PyArg_ParseTuple()作用相同,但是同时解析关键字参数;它们的用法跟C的sscanf函数很像,都接受一个字符串流,并根据一个指定的格式字符串进行解析,把结果放入到相应的指针所指的变量中去,它们的返回值为1表示解析成功,返回值为0表示失败。
从C到Python的转换函数是PyObject* Py_BuildValue():把C的数据转为Python的一个对象或一组对象,然后返回之;Py_BuildValue的用法跟sprintf很像,把所有的参数按格式字符串所指定的格式转换成一个Python的对象。
C与Python之间数据转换的转换代码:
1 #include "stdafx.h" 2 #include "python.h" 3 4 5 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) 6 { 7 Py_Initialize(); 8 9 if (!Py_IsInitialized()) 10 { 11 printf("initialization fail!"); 12 return -1; 13 } 14 15 PyRun_SimpleString("import sys"); 16 PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append(‘./‘)"); 17 18 PyObject *pModule = NULL, *pDict = NULL, *pFunc = NULL, *pArg = NULL, *result = NULL; 19 20 pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("demo"); //引入模块 21 22 if (!pModule) 23 { 24 printf("import module fail!"); 25 return -2; 26 } 27 28 pDict = PyModule_GetDict(pModule); //获取模块字典属性 //相当于Python模块对象的__dict__ 属性 29 if (!pDict) 30 { 31 printf("find dictionary fail!"); 32 return -3; 33 } 34 35 pFunc = PyDict_GetItemString(pDict, "add"); //从字典属性中获取函数 36 if (!pFunc || !PyCallable_Check(pFunc)) 37 { 38 printf("find function fail!"); 39 return -4; 40 } 41 42 /* 43 // 参数进栈 44 *pArgs; 45 pArgs = PyTuple_New(2); 46 47 PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 0, Py_BuildValue("l",3)); 48 PyTuple_SetItem(pArgs, 1, Py_BuildValue("l",4)); 49 */ 50 51 pArg = Py_BuildValue("(i, i)", 1, 2); //参数类型转换,传递两个整型参数 52 result = PyEval_CallObject(pFunc, pArg); //调用函数,并得到python类型的返回值 53 54 int sum; 55 PyArg_Parse(result, "i", &sum); //将python类型的返回值转换为c/c++类型 56 printf("sum=%d\n", sum); 57 58 PyRun_SimpleString("print ‘hello world!‘ "); 59 60 Py_DecRef(pModule); 61 Py_DecRef(pDict); 62 Py_DecRef(pFunc); 63 Py_DecRef(pArg); 64 Py_DecRef(result); 65 66 67 Py_Finalize(); 68 69 getchar(); 70 return 0; 71 }
标签:return hello path blog pyc cti mod src style
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hushaojun/p/6067698.html