标签:元素 控件 多少 线性 class http strong 相对 btn
Android中的五大布局
1.了解布局
一个丰富的界面总是要由很多个控件组成的,那我们如何才能让各个控件都有条不紊地 摆放在界面上,而不是乱糟糟的呢?这就需要借助布局来实现了。布局是一种可用于放置很 多控件的容器,它可以按照一定的规律调整内部控件的位置,从而编写出精美的界面。当然, 布局的内部除了放置控件外,也可以放置布局,通过多层布局的嵌套,我们就能够完成一些 比较复杂的界面实现.
2.布局的分类
线性布局(LinearLayout)
相对布局(RelativeLayout)
表格布局(TableLayout)
帧布局(FrameLayout)
绝对布局(了解)
下面我们来看一下线性布局
创建线性布局步骤:
首先我们找到Android项目res/layout
然后右键,弹出下面操作
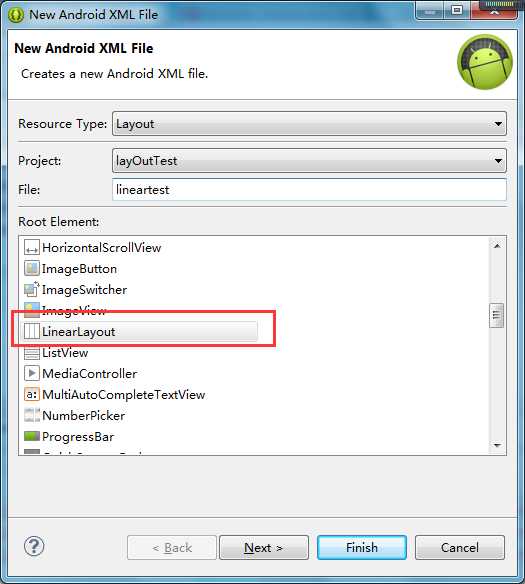
当创建布局文件后,我们来浏览一下该文件的内容
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
6 android:orientation="vertical" >
7
8
9 </LinearLayout>
然后我们修改一下文件中的内容
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical" > 7 8 34 35 36 <TextView 37 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 38 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 39 android:background="#ffff00" 40 android:text="AAA" 41 android:textSize="25sp" /> 45 46 <TextView 47 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 48 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 49 android:background="#eee" 50 android:text="BBB" 51 android:textSize="25sp" /> 52 55 <TextView 56 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 57 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 58 android:background="#ccc" 59 android:text="CCC" 60 android:textSize="25sp"/> 61 63 </LinearLayout>
下面我们部署一下Android项目,看看运行的结果是如何的
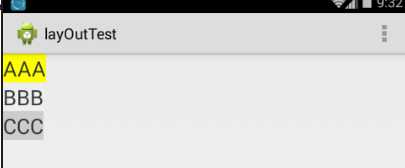

图1 图2
运行可以看到控件是垂直放置的,那么有垂直就有水平放置的,其实是垂直还是水平的根LinearLayout中的android:orientation有关,该属性有两个值,一个vertical(垂直的),另一个是horizontal(水平的),如果android:orientation属性设置为vertical那么效果图就是图1,如果android:orientation属性设置为horizontal,那么效果图就是图2
了解 LinearLayout 的排列规律后,我们再来学习一下它的几个关键属性的用法吧。
android:layout_gravity 属性
android:layout_gravity 是用于指定控件在布局中的对齐 方 式 。 android:layout_gravity 的 可 选 值 和 android:gravity 差 不 多 , 但 是 需 要 注 意 , 当 LinearLayout 的排列方向是 horizontal 时,只有垂直方向上的对齐方式才会生效,因为此时水 平方向上的长度是不固定的,每添加一个控件,水平方向上的长度都会改变,因而无法指定 该方向上的对齐方式。同样的道理,当 LinearLayout 的排列方向是 vertical 时,只有水平方 向上的对齐方式才会生效
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 2 android:layout_width="match_parent" 3 android:layout_height="match_parent" 4 android:orientation="horizontal" >
5 <Button 6 android:id="@+id/button1" 7 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 8 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 9 android:layout_gravity="top" 10 android:text="Button 1" />
11 <Button 12 android:id="@+id/button2" 13 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 14 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 15 android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" 16 android:text="Button 2" />
17 <Button 18 android:id="@+id/button3" 19 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 20 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 21 android:layout_gravity="bottom" 22 android:text="Button 3" /> 23 </LinearLayout>
我们一起来看看运行结果吧

android:layout_weight属性
layout_weight解析1
这个属性 允许我们使用比例的方式来指定控件的大小,它在手机屏幕的适配性方面可以起到非常重要的作用
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 android:baselineAligned="false"
6 android:orientation="horizontal" >
7
8 <TextView
9 android:layout_width="0dp"
10 android:layout_height="48dp"
11 android:layout_weight="1"
12 android:background="#ffff00"
13 android:gravity="center"
14 android:text="1"
15 android:textSize="25sp" />
16
17 <TextView
18 android:layout_width="0dp"
19 android:layout_height="48dp"
20 android:layout_weight="2"
21 android:background="#ccc"
22 android:gravity="center"
23 android:text="2"
24 android:textSize="25sp" />
25
26 <TextView
27 android:layout_width="0dp"
28 android:layout_height="48dp"
29 android:layout_weight="3"
30 android:background="#ff0000"
31 android:gravity="center"
32 android:text="3"
33 android:textSize="25sp" />
34 </LinearLayout>
运行结果:

结果为什么是这样的呢?其实系统会先把 LinearLayout 下所有控件指定的 layout_weight 值相加,得到一个总值,然后每个控件所占大小的比例就是用该控件的 layout_weight 值除以刚才算出的总值
layout_weight解析2
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 android:orientation="horizontal" >
6
7 <TextView
8 android:layout_width="0dp"
9 android:layout_height="48dp"
10 android:layout_weight="1"
11 android:background="#ffff00"
12 android:gravity="center"
13 android:text="1111111111"
14 android:textSize="25sp" />
15
16 <TextView
17 android:layout_width="0dp"
18 android:layout_height="48dp"
19 android:layout_weight="2"
20 android:background="#ccc"
21 android:gravity="center"
22 android:text="2"
23 android:textSize="25sp" />
24
25 <TextView
26 android:layout_width="0dp"
27 android:layout_height="48dp"
28 android:layout_weight="3"
29 android:background="#ff0000"
30 android:gravity="center"
31 android:text="3"
32 android:textSize="25sp" />
33 </LinearLayout>
运行结果

由于TextView会参考父元素LinearLayout的android:baselineAligned的基线,解决办法把baselineAligned设置为false,如:android:baselineAligned="false",运行结果如下:

layout_weight解析3
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 android:baselineAligned="false"
6 android:orientation="horizontal" >
7
8 <TextView
9 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
10 android:layout_height="48dp"
11 android:layout_weight="1"
12 android:background="#ffff00"
13 android:gravity="center"
14 android:text="1111111111"
15 android:textSize="25sp" />
16
17 <TextView
18 android:layout_width="0dp"
19 android:layout_height="48dp"
20 android:layout_weight="2"
21 android:background="#ccc"
22 android:gravity="center"
23 android:text="2"
24 android:textSize="25sp" />
25
26 <TextView
27 android:layout_width="0dp"
28 android:layout_height="48dp"
29 android:layout_weight="3"
30 android:background="#ff0000"
31 android:gravity="center"
32 android:text="3"
33 android:textSize="25sp" />
34 </LinearLayout>
运行结果:

结果明显不是我们预期想的那样,不再是按1:2:3的比例显示结果,其实原因是这样的,第一个TextView设置了android:layout_width="wrap_content",首先它会用屏幕的总宽度减去控件所占的宽度,然后再把剩下的屏幕宽度按比例分配给控件
layout_weight解析4
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:baselineAligned="false" 6 android:orientation="horizontal" > 7 8 <TextView 9 android:layout_width="match_parent" 10 android:layout_height="48dp" 11 android:layout_weight="1" 12 android:background="#ffff00" 13 android:gravity="center" 14 android:text="1111111111" 15 android:textSize="25sp" /> 16 17 <TextView 18 android:layout_width="match_parent" 19 android:layout_height="48dp" 20 android:layout_weight="2" 21 android:background="#ccc" 22 android:gravity="center" 23 android:text="2" 24 android:textSize="25sp" /> 25 26 <TextView 27 android:layout_width="match_parent" 28 android:layout_height="48dp" 29 android:layout_weight="2" 30 android:background="#ff0000" 31 android:gravity="center" 32 android:text="3" 33 android:textSize="25sp" /> 34 35 </LinearLayout>
运行结果
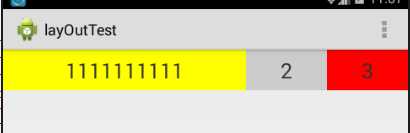
结果为什么不是按1:2:2显示呢?而且权重为1占的宽度比较大呢?其实当控件的属性设置为android:layout_width="match_parent"时,表示控件的宽度与屏幕的宽度一样宽,如果要计算出控件占屏幕的多少宽度,可以通过这个公式计算 : 控件的宽度+父控件剩余宽度*比例 ,假如整个屏幕宽度是480,而且每个控件的属性设置成了android:layout_width="match_parent" ,那么说明每一个控件也是480, 父控件剩余宽度=总屏幕宽度 - 每一个控件相加后的和 ,这里的是 480 - 3*480 = -2*480 ,根据控件的宽度+父控件剩余宽度*比例,可以算出第一个控件所占屏幕的宽度 : 480 + (-2*480)/5 ,第二,三个控件 480 + (-2*480)*2/5
相对布局(RelativeLayout)
RelativeLayout 又称作相对布局,也是一种非常常用的布局。和 LinearLayout 的排列规 则不同,RelativeLayout 显得更加随意一些,它可以通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在布局 的任何位置
创建相对布局步骤
创建完相对布局文件后,我们来看看内容
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent" >
5
6
7 </RelativeLayout>
下面我们添加控件到相对布局文件中
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent" >
5
6 <Button
7 android:id="@+id/btn1"
8 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
9 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
10 android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
11 android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
12 android:text="Button 1" />
13
14 <Button
15 android:id="@+id/btn2"
16 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
17 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
18 android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
19 android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
20 android:text="Button 2" />
21
22 <Button
23 android:id="@+id/btn3"
24 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
25 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
26 android:layout_centerInParent="true"
27 android:text="Button 3" />
28
29 <Button
30 android:id="@+id/btn4"
31 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
32 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
33 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
34 android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
35 android:text="Button 4" />
36
37 <Button
38 android:id="@+id/btn5"
39 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
40 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
41 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
42 android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
43 android:text="Button 5" />
44
45 </RelativeLayout>
运行结果
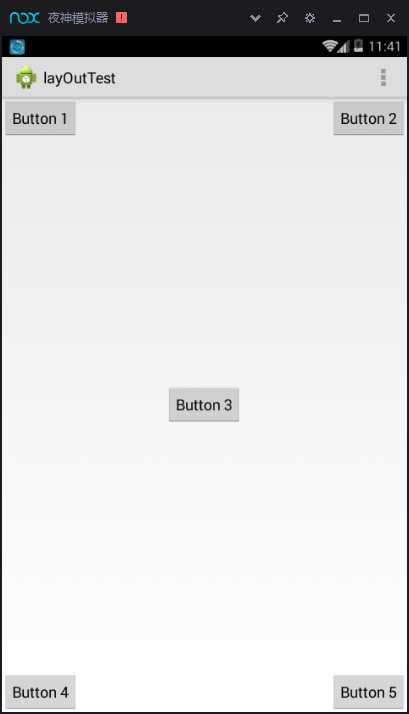
上面例子中的每个控件都是相对于父布局进行定位的,那控件可不可以相对于控件进行 定位呢?
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent" >
5
6 <Button
7 android:id="@+id/btn1"
8 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
9 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
10 android:layout_above="@+id/btn3"
11 android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3"
12 android:text="Button 1" />
13
14 <Button
15 android:id="@+id/btn2"
16 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
17 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
18 android:layout_above="@+id/btn3"
19 android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn3"
20 android:text="Button 2" />
21
22 <Button
23 android:id="@+id/btn3"
24 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
25 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
26 android:layout_centerInParent="true"
27 android:text="Button 3" />
28
29 <Button
30 android:id="@+id/btn4"
31 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
32 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
33 android:layout_below="@+id/btn3"
34 android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3"
35 android:text="Button 4" />
36
37 <Button
38 android:id="@+id/btn5"
39 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
40 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
41 android:layout_below="@+id/btn3"
42 android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn3"
43 android:text="Button 5" />
44 </RelativeLayout>
运行结果
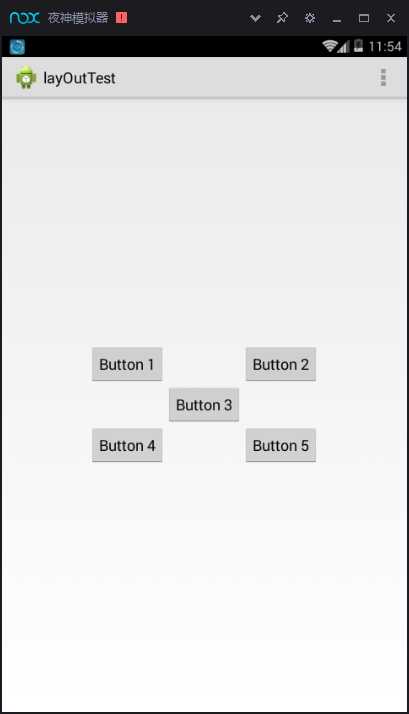
android:layout_above 属性可以让 一个控件位于另一个控件的上方,需要为这个属性指定相对控件 id 的引用,android:layout_below 表示让一个控件位于另一个控件的下方,android:layout_toLeftOf 表示让 一个控件位于另一个控件的左侧,android:layout_toRightOf 表示让一个控件位于另一个控件 的右侧。RelativeLayout 中还有另外一组相对于控件进行定位的属性,android:layout_alignLeft 表 示让一个控件的左边缘和另一个控件的左边缘对齐,android:layout_alignRight 表示让一个控件的右边缘和另一个控件的右边缘对齐,还有 android:layout_alignTop 和 android:layout_ alignBottom
帧布局(FrameLayout)
创建帧布局
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
2 <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent" >
5
6 <Button
7 android:id="@+id/btn1"
8 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
9 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
10 android:text="Button 1" />
11
12 <ImageView
13 android:id="@+id/image_view"
14 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
15 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
16 android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" />
17
18 </FrameLayout>
运行结果:
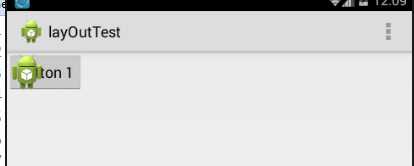
可以看到,按钮和图片都是位于布局的左上角。由于图片是在按钮之后添加的,因此图 片压在了按钮的上面
标签:元素 控件 多少 线性 class http strong 相对 btn
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/li1010425/p/6092139.html