标签:jvm osc res 程序 不同 nbsp imp mat void
1.请阅读并运行AboutException.java示例,然后通过后面的几页PPT了解Java中实现异常处理的基础知识。
import javax.swing.*; class AboutException { public static void main(String[] a) { double i=1, j=0, k; k=i/j; System.out.print(k); try { k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception //throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!"); } catch ( ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage()); } catch (Exception e) { if (e instanceof ArithmeticException) System.out.println("被0除"); else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } finally { JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK"); } } }
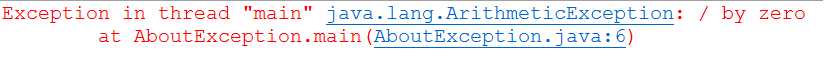
Try{
//可能发生运行错误的代码;
}
catch(异常类型 异常对象引用){
//用于处理异常的代码
}
finally{
//用于“善后” 的代码
}
2.
double d1=100,d2=0,result;
result=d1/d2;
System.out.println("浮点数除以零:" + result);
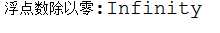
上述代码运行时没有出现错误,而在第一题中用int类型却出现了错误。为什么?
因为Int类型javac生成div字节码指令,而double类型javac生成ddiv字节码指令,JVM在具体实现这两个指令时,采用了不同的处理策略,导致两段代码运行时得到不同的结果。
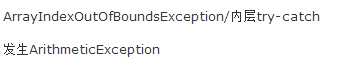
3.阅读以下代码(CatchWho.java),写出程序运行结果。
public class CatchWho {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
try {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
4.当有多个嵌套的try…catch…finally时,要特别注意finally的执行时机。
请先阅读 EmbedFinally.java示例,再运行它,观察其输出并进行总结。
特别注意:
当有多层嵌套的finally时,异常在不同的层次抛出 ,在不同的位置抛出,可能会导致不同的finally语句块执行顺序。
public class EmbededFinally { public static void main(String args[]) { int result; try { System.out.println("in Level 1"); try { System.out.println("in Level 2"); // result=100/0; //Level 2 try { System.out.println("in Level 3"); //result=100/0; //Level 3 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 3 finally"); } } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 2 finally"); } result = 100 / 0; //level 1 } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString()); } finally { System.out.println("In Level 1 finally"); } } }
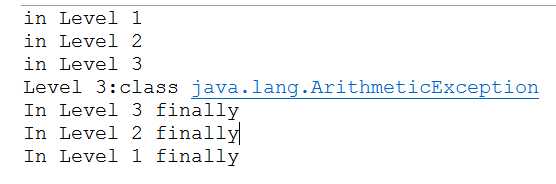

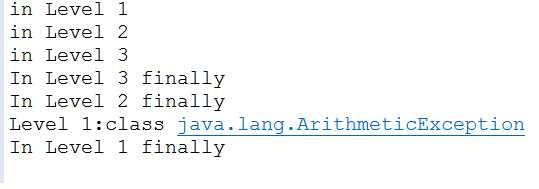
1.首先输出try里面的内容如果遇到异常,就会抛出异常,然后输出finally
2.在第一个中,将异常放到level3中,在运行时,首先运行level1的try并没有异常,然后运行level2的try也没有异常,在运行level3的try遇到异常,输出level3的catch错误。然后输出level3的finally,随后输出level2的finally,然后是level1的finally
3.第二个将异常放到level2中,先运行level1的try,没有遇到异常,所以运行level2的try,这时遇到错误,运行level2的catch,所以已经输出异常,并不再运行level3的异常,输出level2的finally然后输出level1的finally
4.第三个错误,一场在level1中抛出,因为level1的异常在level2和level3的try catch finally后面所以level1的try输出,level2 level3全部输出后,level1的catch才捕捉到异常输出,并且输出level1的finally
5.finally语句块一定会执行吗?请通过 SystemExitAndFinally.java示例程序回答上述问题
public class SystemExitAndFinally {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//getmessage()输出错误信息,可直接用对象调用。
//System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}


除非调用system.exit()让程序退出也就是将调用这个程序的进程断开了finally就不会执行,否则无论任何因素finally块都一定会执行
6.
编写一个程序,此程序在运行时要求用户输入一个 整数,代表某门课的考试成绩,程序接着给出“不及格”、“及格”、“中”、“良”、“优”的结论。
要求程序必须具备足够的健壮性,不管用户输入什么样的内容,都不会崩溃
import java.util.Scanner; class Nonumber extends Exception { public Nonumber(String str){ super(str); } } class NoInt extends Exception { public NoInt(String str){ super(str); } } class Noscore extends Exception { public Noscore(String str){ super(str); } } public class Test { static Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); public static void main(String args[]){ boolean p=true; while(p) { System.out.println("请输入成绩:"); String S=in.next(); try { for(int i=0;i<S.length();i++) { if(S.charAt(i)<48||S.charAt(i)>57&&S.charAt(i)!=46) { throw new Nonumber("输入的成绩形式不正确,请重新输入成绩!"); } } try { if(S.matches("//d+")) { throw new NoInt("输入的成绩形式不正确,请重新输入!"); } } catch(NoInt e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } try { int Q=Integer.parseInt(S); if(Q<0||Q>100) { throw new Noscore("输入的成绩形式不正确,请重新输入!"); } if(Q<60) { System.out.println("不及格"); } if(Q>=60&&Q<70) { System.out.println("及格"); } if(Q>=70&&Q<80) { System.out.println("中"); } if(Q>=80&&Q<90) { System.out.println("良"); } if(Q>=90&&Q<=100) { System.out.println("优"); } } catch(Noscore e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()) ; } } catch(Nonumber e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } } }

标签:jvm osc res 程序 不同 nbsp imp mat void
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/muxiaozhou/p/6103073.html