标签:知识 等等 pid 速度 注意 append dataset 通过 方法
1、介绍
朴素贝叶斯方法,朴素指特征条件独立,贝叶斯指贝叶斯定理。算法可用来做分类,既可以是判别模型,也可以是生成模型。训练的时候,学习输入输出的联合概率分布,分类的时候,利用贝叶斯定理计算后验概率最大的输出。一句话总结:根据先验概率和条件概率分布,得到联合概率分布。如下所示:
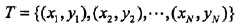
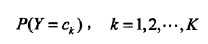
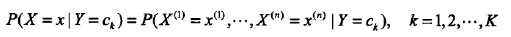
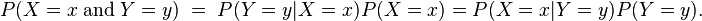
2、模型讲解
条件概率分布的参数数量是指数级的,也就是X和Y的组合很多,造成维数灾难,导致实际无法运算。此处,朴素贝叶斯法对它做了条件独立性的假设:
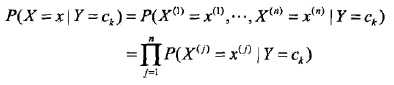
也就是各个维度的特征在类确定的情况下都是独立分布的。这一假设简化了计算,也牺牲了一定的分类准确率。基于此假设,以及贝叶斯定理,后验概率为:
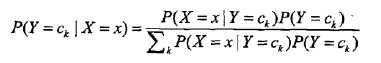
分母其实是P(X=x),等同于枚举ck求联合分布的和:∑P(X=x,Y=ck),此联合分布按公式:
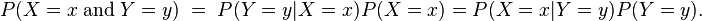
拆开,等于上式分母。将独立性假设代入上式,得到:
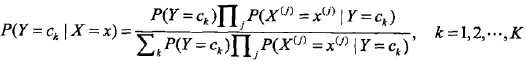
朴素贝叶斯分类器可以表示为:
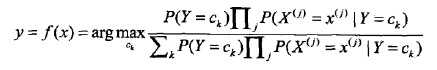
也就是给定参数,找一个概率最大的ck出来。注意到上式分母其实就是P(X=x),x给定了就固定了,跟ck一点关系都没有,所以分母可以去掉,得到:
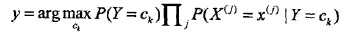
后验概率最大化等价于期望风险最小化。如下解释
选择0-1损失函数,如下:
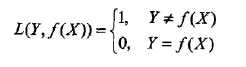
f(X)就是分类器的决策函数,损失函数的参数其实是一个联合分布。此时期望风险函数为:
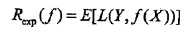
上面说过,这是一个联合分布P(X,Y),是一个and(连乘)的形式,由此取条件期望为风险函数:
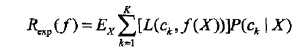
所谓条件期望,就是指X=x时,Y的期望。上式其实可以这么推回去:Ex∑[L()]P(ck|X)=∑P(X)∑[L()]P(X,ck)/P(X)=∑[L()]P(X,ck)=E[L()],格式比较乱,但愿意思到了。为了最小化上式,只需对每个X=x执行最小化,那么加起来肯定是极小化的,由此有:
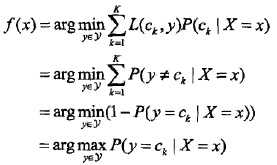
3、参数估计
极大似然估计:
前面说过,朴素贝叶斯法要学习的东西就是P(Y=ck)和P(X=x|Y=ck),这两个概率的估计用极大似然估计法(简单讲,就是用样本猜测模型参数,或者说使得似然函数最大的参数)进行:
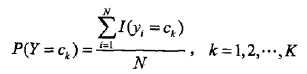
也就是用样本中ck的出现次数除以样本容量:
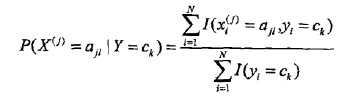
分子是样本中变量组合的出现次数,分母是上面说过的样本中ck的出现次数。
贝叶斯估计:
最大似然估计有个隐患,假设训练数据中没有出现某种参数和类别的组合怎么办?此时估计的概率值为0,但是这不代表真实数据中就没有这样的组合。解决办法是采用贝叶斯估计,以下显示的是先验概率的贝叶斯估计和条件概率的贝叶斯估计:
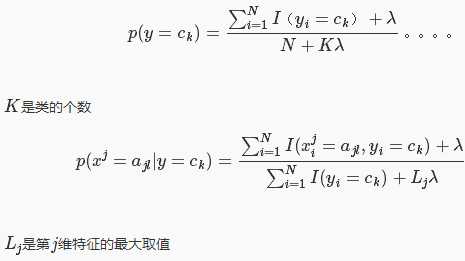
分子和分母分别比最大似然估计多了一点东西,其意义是在随机变量每个取值的频数上加一个常量,当此常量取0时,就是最大似然估计,当此常量取1时,称为拉普拉斯平滑,常用来解决零概率的问题。
4、算法流程
总结如下算法流程:

5、总结
关于贝叶斯,还有很多知识,比如贝叶斯决策论、贝叶斯判定准则等等。请自行百度扩充。
朴素的贝叶斯分类器优点:在接受大量数据训练和查询时的高速度(尤其当训练量递增时更是如此);其对分类器的学习情况有着比较简单的解释,我们可以简单的通过查询学习时计算的一些概率值来了解其分类原理。朴素的贝叶斯分类缺点是它无法处理特征符合所产生的变化(即前面提到过的实际上难以满足的相互独立)。
6、实现
简单放一点代码:
‘‘‘ Created on Oct 19, 2010 @author: Peter ‘‘‘ from numpy import * def loadDataSet(): postingList=[[‘my‘, ‘dog‘, ‘has‘, ‘flea‘, ‘problems‘, ‘help‘, ‘please‘], [‘maybe‘, ‘not‘, ‘take‘, ‘him‘, ‘to‘, ‘dog‘, ‘park‘, ‘stupid‘], [‘my‘, ‘dalmation‘, ‘is‘, ‘so‘, ‘cute‘, ‘I‘, ‘love‘, ‘him‘], [‘stop‘, ‘posting‘, ‘stupid‘, ‘worthless‘, ‘garbage‘], [‘mr‘, ‘licks‘, ‘ate‘, ‘my‘, ‘steak‘, ‘how‘, ‘to‘, ‘stop‘, ‘him‘], [‘quit‘, ‘buying‘, ‘worthless‘, ‘dog‘, ‘food‘, ‘stupid‘]] classVec = [0,1,0,1,0,1] #1 is abusive, 0 not return postingList,classVec def createVocabList(dataSet): vocabSet = set([]) #create empty set for document in dataSet: vocabSet = vocabSet | set(document) #union of the two sets return list(vocabSet) def setOfWords2Vec(vocabList, inputSet): returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList) for word in inputSet: if word in vocabList: returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] = 1 else: print "the word: %s is not in my Vocabulary!" % word return returnVec def trainNB0(trainMatrix,trainCategory): numTrainDocs = len(trainMatrix) numWords = len(trainMatrix[0]) pAbusive = sum(trainCategory)/float(numTrainDocs) p0Num = ones(numWords); p1Num = ones(numWords) #change to ones() p0Denom = 2.0; p1Denom = 2.0 #change to 2.0 for i in range(numTrainDocs): if trainCategory[i] == 1: p1Num += trainMatrix[i] p1Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i]) else: p0Num += trainMatrix[i] p0Denom += sum(trainMatrix[i]) p1Vect = log(p1Num/p1Denom) #change to log() p0Vect = log(p0Num/p0Denom) #change to log() return p0Vect,p1Vect,pAbusive def classifyNB(vec2Classify, p0Vec, p1Vec, pClass1): p1 = sum(vec2Classify * p1Vec) + log(pClass1) #element-wise mult p0 = sum(vec2Classify * p0Vec) + log(1.0 - pClass1) if p1 > p0: return 1 else: return 0 def bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, inputSet): returnVec = [0]*len(vocabList) for word in inputSet: if word in vocabList: returnVec[vocabList.index(word)] += 1 return returnVec def testingNB(): listOPosts,listClasses = loadDataSet() myVocabList = createVocabList(listOPosts) trainMat=[] for postinDoc in listOPosts: trainMat.append(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, postinDoc)) p0V,p1V,pAb = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(listClasses)) testEntry = [‘love‘, ‘my‘, ‘dalmation‘] thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry)) print testEntry,‘classified as: ‘,classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb) testEntry = [‘stupid‘, ‘garbage‘] thisDoc = array(setOfWords2Vec(myVocabList, testEntry)) print testEntry,‘classified as: ‘,classifyNB(thisDoc,p0V,p1V,pAb) def textParse(bigString): #input is big string, #output is word list import re listOfTokens = re.split(r‘\W*‘, bigString) return [tok.lower() for tok in listOfTokens if len(tok) > 2] def spamTest(): docList=[]; classList = []; fullText =[] for i in range(1,26): wordList = textParse(open(‘email/spam/%d.txt‘ % i).read()) docList.append(wordList) fullText.extend(wordList) classList.append(1) wordList = textParse(open(‘email/ham/%d.txt‘ % i).read()) docList.append(wordList) fullText.extend(wordList) classList.append(0) vocabList = createVocabList(docList)#create vocabulary trainingSet = range(50); testSet=[] #create test set for i in range(10): randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(trainingSet))) testSet.append(trainingSet[randIndex]) del(trainingSet[randIndex]) trainMat=[]; trainClasses = [] for docIndex in trainingSet:#train the classifier (get probs) trainNB0 trainMat.append(bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex])) trainClasses.append(classList[docIndex]) p0V,p1V,pSpam = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(trainClasses)) errorCount = 0 for docIndex in testSet: #classify the remaining items wordVector = bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex]) if classifyNB(array(wordVector),p0V,p1V,pSpam) != classList[docIndex]: errorCount += 1 print "classification error",docList[docIndex] print ‘the error rate is: ‘,float(errorCount)/len(testSet) #return vocabList,fullText def calcMostFreq(vocabList,fullText): import operator freqDict = {} for token in vocabList: freqDict[token]=fullText.count(token) sortedFreq = sorted(freqDict.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) return sortedFreq[:30] def localWords(feed1,feed0): import feedparser docList=[]; classList = []; fullText =[] minLen = min(len(feed1[‘entries‘]),len(feed0[‘entries‘])) for i in range(minLen): wordList = textParse(feed1[‘entries‘][i][‘summary‘]) docList.append(wordList) fullText.extend(wordList) classList.append(1) #NY is class 1 wordList = textParse(feed0[‘entries‘][i][‘summary‘]) docList.append(wordList) fullText.extend(wordList) classList.append(0) vocabList = createVocabList(docList)#create vocabulary top30Words = calcMostFreq(vocabList,fullText) #remove top 30 words for pairW in top30Words: if pairW[0] in vocabList: vocabList.remove(pairW[0]) trainingSet = range(2*minLen); testSet=[] #create test set for i in range(20): randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(trainingSet))) testSet.append(trainingSet[randIndex]) del(trainingSet[randIndex]) trainMat=[]; trainClasses = [] for docIndex in trainingSet:#train the classifier (get probs) trainNB0 trainMat.append(bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex])) trainClasses.append(classList[docIndex]) p0V,p1V,pSpam = trainNB0(array(trainMat),array(trainClasses)) errorCount = 0 for docIndex in testSet: #classify the remaining items wordVector = bagOfWords2VecMN(vocabList, docList[docIndex]) if classifyNB(array(wordVector),p0V,p1V,pSpam) != classList[docIndex]: errorCount += 1 print ‘the error rate is: ‘,float(errorCount)/len(testSet) return vocabList,p0V,p1V def getTopWords(ny,sf): import operator vocabList,p0V,p1V=localWords(ny,sf) topNY=[]; topSF=[] for i in range(len(p0V)): if p0V[i] > -6.0 : topSF.append((vocabList[i],p0V[i])) if p1V[i] > -6.0 : topNY.append((vocabList[i],p1V[i])) sortedSF = sorted(topSF, key=lambda pair: pair[1], reverse=True) print "SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**SF**" for item in sortedSF: print item[0] sortedNY = sorted(topNY, key=lambda pair: pair[1], reverse=True) print "NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**NY**" for item in sortedNY: print item[0]
相关博客:
http://www.hankcs.com/ml/naive-bayesian-method.html
http://blog.csdn.net/tanhongguang1/article/details/45016421
标签:知识 等等 pid 速度 注意 append dataset 通过 方法
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/taojake-ML/p/6114113.html