标签:back guest most log change his origin comm err
This post will cover how to increase the disk space for a VMware virtual machine running Linux that is using logical volume manager (LVM). Firstly we will be increasing the size of the actual disk on the VMware virtual machine, so at the hardware level – this is the VM’s .vmdk file. Once this is complete we will get into the virtual machine and make the necessary changes through the operating system in order to take advantage of the additional space that has been provided by the hard drive being extended. This will involve creating a new partition with the new space, expanding the volume group and logical group, then finally resizing the file system.
As there are a number of different ways to increase disk space I have also posted some different methods here:
Update 18/04/2015: I have created a video guide of this post in CentOS 7 shown below.
Important Note: Be very careful when working with the commands in this article as they have the potential to cause a lot of damage to your data. If you are working with virtual machines make sure you take a snapshot of your virtual machine beforehand, or otherwise have some other form of up to date backup before proceeding. Note that a snapshot must not be taken until after the virtual disk has been increased, otherwise you will not be able to increase it. It could also be worth cloning the virtual machine first and testing out this method on the clone.
Prerequisites: As this method uses the additional space to create a primary partition, you must not already have 4 partitions as you will not be able to create more than 4. If you do not have space for another partition then you will need to consider a different method, there are some others in the above list.
Throughout my examples I will be working with a VMware virtual machine running Debian 6, this was set up with a 20gb disk and we will be increasing it by 10gb for a total final size of 30gb.
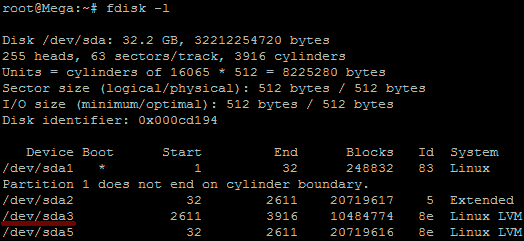
As this method focuses on working with LVM, we will first confirm that our partition type is actually Linux LVM by running the below command.
fdisk -l
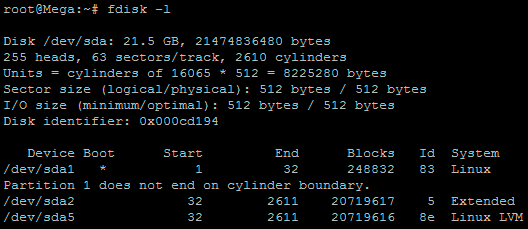
As you can see in the above image /dev/sda5 is listed as “Linux LVM” and it has the ID of 8e. The 8e hex code shows that it is a Linux LVM, while 83 shows a Linux native partition. Now that we have confirmed we are working with an LVM we can continue. For increasing the size of a Linux native partition (hex code 83) see this article.
Below is the disk information showing that our initial setup only has the one 20gb disk currently, which is under the logical volume named /dev/mapper/Mega-root – this is what we will be expanding with the new disk.
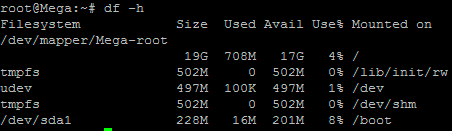
Note that /dev/mapper/Mega-root is the volume made up from /dev/sda5 currently – this is what we will be expanding.
First off we increase the allocated disk space on the virtual machine itself. This is done by right clicking the virtual machine in vSphere, selecting edit settings, and then selecting the hard disk. In the below image I have changed the previously set hard disk of 20gb to 30gb while the virtual machine is up and running. Once complete click OK, this is all that needs to be done in VMware for this process.
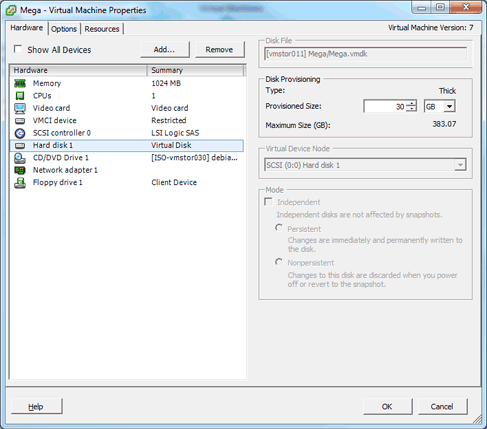
If you are not able to modify the size of the disk, the provisioned size setting is greyed out. This can happen if the virtual machine has a snapshot in place, these will need to be removed prior to making the changes to the disk. Alternatively you may need to shut down the virtual machine if it does not allow you to add or increase disks on the fly, if this is the case make the change then power it back on.
Once the physical disk has been increased at the hardware level, we need to get into the operating system and create a new partition that makes use of this space to proceed.
Before we can do this we need to check that the new unallocated disk space is detected by the server, you can use “fdisk -l” to list the primary disk. You will most likely see that the disk space is still showing as the same original size, at this point you can either reboot the server and it will detect the changes on boot or you can rescan your devices to avoid rebooting by running the below command. Note you may need to change host0 depending on your setup.
echo "- - -" > /sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
Below is an image after performing this and confirming that the new space is displaying.
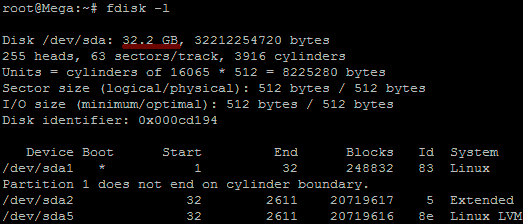
As outlined in my previous images the disk in my example that I am working with is /dev/sda, so we use fdisk to create a new primary partition to make use of the new expanded disk space. Note that we do not have 4 primary partitions already in place, making this method possible.
fdisk /dev/sda
We are now using fdisk to create a new partition, the inputs I have entered in are shown below in bold. Note that you can press ‘m’ to get a full listing of the fdisk commands.
‘n’ was selected for adding a new partition.
WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It‘s strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command ‘c‘) and change display units to
sectors (command ‘u‘).
Command (m for help): n
‘p’ is then selected as we are making a primary partition.
Command action l logical (5 or over) p primary partition (1-4) p
As I already have /dev/sda1 and /dev/sda2 as shown in previous images, I have gone with using ‘3’ for this new partition which will be created as /dev/sda3
Partition number (1-4): 3
We just press enter twice above as by default the first and last cylinders of the unallocated space should be correct. After this the partition is then ready.
First cylinder (2611-3916, default 2611): "enter"
Using default value 2611
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (2611-3916, default 3916): "enter"
Using default value 3916
‘t’ is selected to change to a partition’s system ID, in this case we change to ‘3’ which is the one we just created.
Command (m for help): t Partition number (1-5): 3
The hex code ‘8e’ was entered as this is the code for a Linux LVM which is what we want this partition to be, as we will be joining it with the original /dev/sda5 Linux LVM.
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e Changed system type of partition 3 to 8e (Linux LVM)
‘w’ is used to write the table to disk and exit, basically all the changes that have been done will be saved and then you will be exited from fdisk.
Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy. The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8) Syncing disks.
You will see a warning which basically means in order to use the new table with the changes a system reboot is required. If you can not see the new partition using “fdisk -l” you may be able to run “partprobe -s” to rescan the partitions. In my test I did not require either of those things at this stage (I do a reboot later on), straight after pressing ‘w’ in fdisk I was able to see the new /dev/sda3 partition of my 10gb of space as displayed in the below image.
For CentOS/RHEL run a “partx -a /dev/sda3” to avoid rebooting later on.
That’s all for partitioning, we now have a new partition which is making use of the previously unallocated disk space from the increase in VMware.
We use the pvcreate command which creates a physical volume for later use by the logical volume manager (LVM). In this case the physical volume will be our new /dev/sda3 partition.
root@Mega:~# pvcreate /dev/sda3 Device /dev/sda3 not found (or ignored by filtering).
In order to get around this you can either reboot, or use partprobe/partx as previously mentioned to avoid a reboot, as in this instance the disk does not appear to be there correctly despite showing in “fdisk -l”. After a reboot or partprobe/partx use the same command which will succeed.
root@Mega:~# pvcreate /dev/sda3 Physical volume "/dev/sda3" successfully created
Next we need to confirm the name of the current volume group using the vgdisplay command. The name will vary depending on your setup, for me it is the name of my test server. vgdisplay provides lots of information on the volume group, I have only shown the name and the current size of it for this example.
root@Mega:~# vgdisplay --- Volume group --- VG Name Mega ... VG Size 19.76 GiB
Now we extend the ‘Mega’ volume group by adding in the physical volume of /dev/sda3 which we created using the pvcreate command earlier.
root@Mega:~# vgextend Mega /dev/sda3 Volume group "Mega" successfully extended
Using the pvscan command we scan all disks for physical volumes, this should confirm the original /dev/sda5 partition and the newly created physical volume /dev/sda3
root@Mega:~# pvscan PV /dev/sda5 VG Mega lvm2 [19.76 GiB / 0 free] PV /dev/sda3 VG Mega lvm2 [10.00 GiB / 10.00 GiB free] Total: 2 [29.75 GiB] / in use: 2 [29.75 GiB] / in no VG: 0 [0 ]
Next we need to increase the logical volume (rather than the physical volume) which basically means we will be taking our original logical volume and extending it over our new partition/physical volume of /dev/sda3.
Firstly confirm the path of the logical volume using lvdisplay. This path name will vary depending on your setup.
root@Mega:~# lvdisplay --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/Mega/root
The logical volume is then extended using the lvextend command.
root@Mega:~# lvextend /dev/Mega/root /dev/sda3 Extending logical volume root to 28.90 GiB Logical volume root successfully resized
There is then one final step which is to resize the file system so that it can take advantage of this additional space, this is done using the resize2fs command for ext based file systems. Note that this may take some time to complete, it took about 30 seconds for my additional space.
root@Mega:~# resize2fs /dev/Mega/root resize2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010) Filesystem at /dev/Mega/root is mounted on /; on-line resizing required old desc_blocks = 2, new_desc_blocks = 2 Performing an on-line resize of /dev/Mega/root to 7576576 (4k) blocks. The filesystem on /dev/Mega/root is now 7576576 blocks long.
Alternatively if you’re running the XFS file system (default as of RedHat/CentOS 7) you can grow the file system with “xfs_growfs /dev/Mega/root”.
That’s it, now with the ‘df’ command we can see that the total available disk space has been increased.
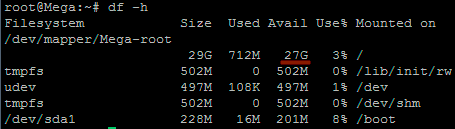
With this method we have increased the virtual disk drive through VMware, created a new partition out of this newly unallocated space within the guest OS, turned it into a physical volume, extended the volume group, and then finally extended the original logical volume over the newer physical volume resulting in overall disk space being increased successfully.
标签:back guest most log change his origin comm err
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wucg/p/6116085.html