标签:turn int line 绘图 strong 例子 set 椭圆 http
动态类型和动态绑定,id可以表示任何指针类型,定义id变量不加*
多态性是指在父类中定义的成员变量和方法被子类继承之后,可以具有不同的数据类型或表现出不同的行为。这使得同一个变量和方法在父类及其各个子类中具有不同的表现形式。我们通过一个例子理解什么多态,例如:“几何图形”类的“绘图”方法,在它的子类“椭圆形”和“三角形”中也都有“绘图”的方法,但是“绘图”方法功能都不同。
Graphics(几何图形)类是Ellipse(椭圆形)类和Triangle(三角形)类的父类,Ellipse和Triangle重写了onDraw方法。
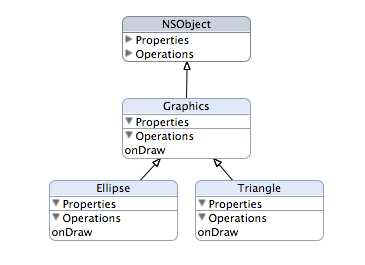
@interface Graphics : NSObject { } -(void)onDraw; @end
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Graphics.h" @interface Ellipse : Graphics { } @end #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Ellipse.h" @implementation Ellipse -(void)onDraw { NSLog(@"绘制椭圆形"); } @end
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Graphics.h" @interface Triangle: Graphics { } @end #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Triangle.h" @implementation Triangle -(void)onDraw { NSLog(@“绘制三角形"); } @end
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> #import "Graphics.h" #import "Ellipse.h" #import "Triangle.h" int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) { Graphics *graphics; graphics = [[Ellipse alloc] init]; [graphics onDraw]; [graphics release]; graphics = [[Triangle alloc] init]; [graphics onDraw]; [graphics release]; return 0; }
id 是泛类型 (generic data type), 可以用来存放各种类型的对象, 使用 id 也就是使用“动态类型”。
int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) { id graphics; graphics = [[Ellipse alloc] init]; [graphics onDraw]; [graphics release]; graphics = [[Triangle alloc] init]; [graphics onDraw]; [graphics release]; return 0; }
把Graphics *改成id类型,程序运行的结果没有任何影响。由于动态类型的关系,id 在执行时,Objective-C 的执行环境会找出该 id 所代表的原来类型,所以根本没有所谓的转型。id 并不是自动的转换成 Ellipse和 Triangle的父类,而是在执行期间, 由执行环境辨认出 id 实际代表的类型为Ellipse还是Triangle。因此在这个例子中id 与Graphics没有任何关系。
• 定义两个类:“矢量”和“标量”类。
• 矢量”即有方向和大小的量,如物理学中的“力”。标量为没有方向只有大小量,如物理学中的“功”。
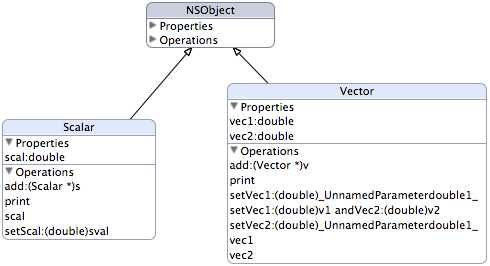
@interface Vector : NSObject { double vec1; double vec2; } @property double vec1,vec2; -(void)print; -(void)setVec1:(double)v1 andVec2:(double) v2; -(Vector *)add:(Vector *)v; @end
#import "Vector.h" @implementation Vector @synthesize vec1,vec2; -(void) setVec1:(double) v1 andVec2:(double)v2 { vec1 = v1; vec2 = v2; } -(Vector *)add:(Vector *)v { Vector *result = [[Vector alloc] init]; [result setVec1:vec1 + [v vec1] andVec2: vec2 + [v vec2]]; return result; } -(void)print { NSLog(@"%g, %g",vec1,vec2); } @end
@interface Scalar : NSObject { double scal; } @property double scal; -(void)print; -(void)setScal:(double)sval; -(Scalar *)add:(Scalar *)s; @end
#import "Scalar.h" @implementation Scalar @synthesize scal; -(void)print { NSLog(@"%g", scal); } -(void)setScal:(double)sval { scal = sval; } -(Scalar *)add:(Scalar *)s { Scalar *result = [[Scalar alloc] init]; [result setScal:scal + [s scal]]; return result; } @end
#import "Vector.h" #import "Scalar.h" int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) { Scalar *scA =[[Scalar alloc] init]; Scalar *scB =[[Scalar alloc] init]; Vector *vecA =[[Vector alloc] init]; Vector *vecB =[[Vector alloc] init]; id scAandB; id vecAandB; [scA setScal: 10.5]; [scB setScal: 13.1]; [vecA setVec1: 3.2 andVec2: 4.7]; [vecB setVec1: 32.2 andVec2: 47.7]; ... ... [vecA print]; NSLog(@" + "); [vecB print]; NSLog(@" = "); vecAandB = [vecA add: vecB]; [vecAandB print]; [scA print]; NSLog(@" + "); [scB print]; NSLog(@" = "); scAandB = [scA add: scB]; [scAandB print]; [scA release]; [scB release]; [scAandB release]; [vecA release]; [vecB release]; [vecAandB release]; return 0; }
运行结果:
3.2, 4.7
+
32.2, 47.7
=
35.4, 52.4
10.5
+
13.1
=
23.6
• scAandB和vecAandB对象都是动态类型,都可调用以 "print"和"add"方法。
• 虽然id类型可以任何类型的对象,但是不要滥用,如果能够确定对象数据类型时候,要使用“静态类型”,“静态类型”在编译阶段检查错误,而不是在执行阶段。而且“静态类型”程序可读性好。
标签:turn int line 绘图 strong 例子 set 椭圆 http
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ecollab/p/6123650.html