标签:project ada tab framework init pass 框架 build protected
JPA(Java Persistence API)是Spring Boot访问关系型数据库的一个标准接口,它使用ORM(Object-Relational Mapping)方式为数据对象建模和实现持久化。当然JAP也可以应用于其它支持Java的开发框架之中。
在JPA中使用MySQL数据库,只要为其进行建模,就可以自动生成表结构,省略了一些数据库设计的工作。而且,当数据模型更改的时候,应用程序也会对表结构进行更新。需要实现这一功能,主要取决你对使用JPA的配置。
例如,我们有一个数据的实体-关系模型如下图所示。
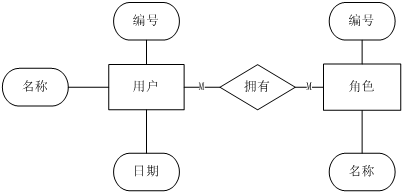
首先,我们创建项目工程,并引入Spring Boot和JPA的依赖。
其中,Spring Boot依赖如下所示:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.4.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
JPA和MySQL的依赖如下所示:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
现在,可以对实体对象进行建模和持久化设计。
用户实体建模,其中User与Role的多对多关系使用一个关系表user_role来存储:
package com.demo.mysql.entity; import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat; import javax.persistence.*; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; @Entity @Table(name = "user") public class User implements java.io.Serializable{ @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String name; @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") private Date createdate; @ManyToMany(cascade = {}, fetch = FetchType.EAGER) @JoinTable(name = "user_role", joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "user_id")}, inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "roles_id")}) private List<Role> roles; public User() { } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Date getCreatedate() { return createdate; } public void setCreatedate(Date createdate) { this.createdate = createdate; } public List<Role> getRoles() { return roles; } public void setRoles(List<Role> roles) { this.roles = roles; } }
角色建模:
package com.demo.mysql.entity; import javax.persistence.*; @Entity @Table(name = "role") public class Role implements java.io.Serializable{ @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; private String name; public Role() { } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } }
用户实体持久化:
package com.demo.mysql.repository; import com.demo.mysql.entity.User; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> { }
角色实体持久化:
package com.demo.mysql.repository; import com.demo.mysql.entity.Role; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface RoleRepository extends JpaRepository<Role, Long> { }
JPA及数据源配置,注意其中一行“hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "update");”,将Hibernate的自动处理设置为“update”,表示表结构更改时即进行更新:
package com.demo.mysql.test; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.dao.annotation.PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.Database; import org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; import org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate; import javax.sql.DataSource; import java.util.Properties; @Configuration @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "com.**.repository") public class JpaConfiguration { @Bean PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor persistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor(){ return new PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor(); } @Bean public DataSource dataSource() { DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8"); dataSource.setUsername("root"); dataSource.setPassword("12345678"); return dataSource; } @Bean public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory() { LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean(); entityManagerFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan("com.**.entity"); entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaProperties(buildHibernateProperties()); entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaVendorAdapter(new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter() {{ setDatabase(Database.MYSQL); }}); return entityManagerFactoryBean; } protected Properties buildHibernateProperties() { Properties hibernateProperties = new Properties(); hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", "true"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.use_sql_comments", "false"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.format_sql", "true"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "update"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("hibernate.generate_statistics", "false"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("javax.persistence.validation.mode", "none"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("org.hibernate.envers.store_data_at_delete", "true"); hibernateProperties.setProperty("org.hibernate.envers.global_with_modified_flag", "true"); return hibernateProperties; } @Bean public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() { return new JpaTransactionManager(); } @Bean public TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate() { return new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager()); } }
测试用例:
package com.demo.mysql.test; import com.demo.mysql.entity.Role; import com.demo.mysql.entity.User; import com.demo.mysql.repository.RoleRepository; import com.demo.mysql.repository.UserRepository; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.domain.Page; import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import java.util.Date; import java.util.List; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = {JpaConfiguration.class}) public class MysqlTest { @Autowired UserRepository userRepository; @Autowired RoleRepository roleRepository; @Before public void initData(){ Role role = new Role(); role.setName("admins"); roleRepository.save(role); Assert.notNull(role.getId()); User user = new User(); user.setName("user"); user.setCreatedate(new Date()); List<Role> roles = roleRepository.findAll(); roles.add(role); user.setRoles(roles); userRepository.save(user); Assert.notNull(user.getId()); } @Test public void findPage(){ Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(0, 10, new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "id")); Page<User> page = userRepository.findAll(pageable); Assert.notNull(page); } }
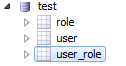
运行通过,在数据库test中即可以看到生成的表,并且具有上面的一些测试数据,如下图:
(原文:https://my.oschina.net/syic/blog/798994)
标签:project ada tab framework init pass 框架 build protected
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/chrischen662/p/6129218.html