标签:不能 static char code sha win tostring open 语言
最近搞了一个调用第三方so库做登录认证的任务,以前对JNI没什么概念,最近学习了 《java核心技术》 本地方法 一章,把自己写的一些例子记录一下。 自己C语言真是渣渣,所以所有的例子都在可以包括基本API的基础上尽可能简单。以下所有例子都是在centos 7中测试的,window不太熟。
java调用本地方法,首先需要加载包含对应方法的so库(linux),一般使用下面这种方式加载so库。
1 public class Test{ 2 static 3 { 4 //so库的名字是libTest.so 5 System.loadLibrary("Test"); 6 } 7 8 public static native void hello(); 9 }
在static代码块中加载so库,这样就能在这个类被classLoader 加载的时候就被载入。要想正确载入so,必须将so库放在java.library.path 指定的路径中,我们可以通过以下两种方式来指定java.library.path 的值
1. 配置 LD_LIBRARY_PATH 环境变量
2. 通过java的运行参数指定 -Djava.library.path= .....
当我们调用本地方法时,会在加载的so库中去寻找与我们所调用方法对应的本地方法,比如上面定义的hello方法,就应该有一个对应的本地方法为
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Test_hello(JNIEnv *, jclass)
我们可以使用javah产生这个一个头文件,在其中就包含了这个方法的声明。
我们编写完c文件后,就可以用它生成一个对应的so了
gcc -fPIC -I jdk/include -I jdk/include/linux -shared -o libTest.so Test.c
其中jdk是含有jdk的目录,以我的环境为例,jdk目录为 /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.79-2.5.5.1.el7_1.x86_64/, 配置JAVA_HOME指向这个目录,所以编译命令就是:
gcc -fPIC -I ${JAVA_HOME}/include -I ${JAVA_HOME}/include/linux -shared -o libTest.so Test.c
之所以要使用-I 参数指定这两个目录,是因为在其中包含了c文件需要的两个头文件, <jni.h>和 <jni_md.h>
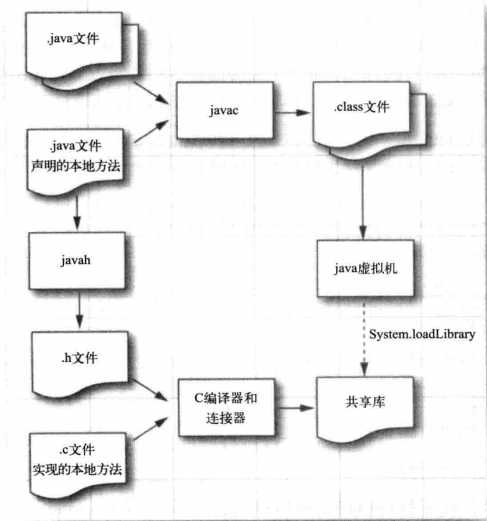
总结出将一个本地方法链接到java程序中的步骤:
1)在java类中声明一个native方法
2)运行javah 得到一个本地方法需要的头文件
3)使用C实现本地方法
4)使用C代码编译出so文件,并将它放置在java.library.path中
5)使用java调用就可以了
下面的案例中重要的api都用红色标记了。
class Calc { static{ System.loadLibrary("Calc"); } public static native int add(int a, int b); public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(add(11,23)); } }
对应的C代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include "Calc.h" /* jint 对应着java 的int类型 */ JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_Calc_add(JNIEnv *env, jclass jc, jint a, jint b) { jint ret = a + b; return ret; }
class Hello { static { System.loadLibrary("Hello"); } public static native String hello(String name); public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(hello("zhangsan")); } }
对应的C代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "Hello.h" /*拼接字符串 */ char* join(const char *s1, const char *s2) { char *result = malloc(strlen(s1)+strlen(s2)+1);//+1 for the zero-terminator //in real code you would check for errors in malloc here if (result == NULL) exit (1); strcpy(result, s1); strcat(result, s2); return result; } JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_Hello_hello(JNIEnv* env, jclass cl, jstring name) { /* 从java String 获得 C char* */ const char* cname; cname = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, name, NULL); char* hello_s = join("hello, ", cname); /* 从 C char* 再获得 java String */ jstring ret = (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, hello_s); /* 主动释放内存, 表明不再需要通过 name 来访问 cname*/ (*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, name, cname); return ret; }
感觉这种调用和反射基本类似。
import java.io.*; public class Hello { static { System.loadLibrary("Hello"); } public static native void sayHello(PrintWriter out, String message); public static void main(String[] args) { PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out); Hello.sayHello(out, "Hello world!\n"); out.flush(); } }
C代码实现:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include "Hello.h" /*java 的Object类型对应jobject */ JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Hello_sayHello(JNIEnv* env, jclass jc, jobject out, jstring message) { const char* cmessage; /*从 java String 得到 c char* */ cmessage = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, message, NULL); /* 处理得到的字符串,加上前缀 */ const char* append = "I‘m say: "; char* result = (char*)malloc(strlen(cmessage) + strlen(append) + 1); strcpy(result, append); strcat(result, cmessage); /*从 c char* 得到 java String */ jstring jresult = (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, result); /* 主动释放, 不再需要通过message获得cmessage */ (*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, message, cmessage); /* 下面就是 调用PrintWriter.print(String) */ /* 获得class */ jclass class_PrintWriter = (*env)->GetObjectClass(env, out); /* 获得 method ID , 最后一个参数是 print方法的签名 返回值为void(V), 参数为java.lang.String */ jmethodID id_print = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, class_PrintWriter, "print", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V"); /* 调用方法 */ (*env)->CallVoidMethod(env, out, id_print, jresult); }
案例四: 在C代码中调用System.getProperty静态方法(调用java静态方法)
public class Test { static { System.loadLibrary("Test"); } public static native String getClassPath(); public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getClassPath()); } }
c代码实现:
#include <stdio.h> #include "Test.h" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_Test_getClassPath(JNIEnv* env, jclass jc) { /*获得System的class */ jclass class_System = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/lang/System"); /*获得 getProperty 方法的 方法id */ jmethodID id_getProperty = (*env)->GetStaticMethodID(env, class_System, "getProperty", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;"); /* 执行 静态方法 */ jobject obj_ret = (*env)->CallStaticObjectMethod(env, class_System, id_getProperty, (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, "version")); return (jstring)obj_ret; }
这个例子在运行的时候 增加 -Dversion=xxxx 就可以得到version运行参数了。
public class Employee { static { System.loadLibrary("Employee"); } public static String a = "Good Employee"; private String name; private double salary; public Employee(String name, double salary) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; } public String toString(){ return name + " " + salary; } public native void raiseSalary(double byPercent); public static native void updateDescription(String description); public static void main(String[] args) { Employee e = new Employee("zhangsan", 1000); System.out.println(e); e.raiseSalary(0.1); System.out.println(e); System.out.println("###############################"); System.out.println(e.a); Employee.updateDescription("Bad Employee"); System.out.println(e.a); } }
c代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include "Employee.h" JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Employee_raiseSalary(JNIEnv* env, jobject this_obj, jdouble byPercent) { /* get the class */ jclass class_Employee = (*env)->GetObjectClass(env, this_obj); /* get the field Id */ jfieldID id_salary = (*env)->GetFieldID(env, class_Employee, "salary", "D"); //"D" 代表类型double /* get the field value */ jdouble salary = (*env)->GetDoubleField(env, this_obj, id_salary); salary *= 1 + byPercent / 100; /* set the field value */ (*env)->SetDoubleField(env, this_obj, id_salary, salary); } JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Employee_updateDescription(JNIEnv* env, jclass jc, jstring description) { /* get static class field */ /*一定要注意类的签名方式, 前面的L 和最后的;(分号)都不能少,那个分号不是分隔符,是签名的一部分 */ jfieldID desc_id = (*env)->GetStaticFieldID(env, jc, "a", "Ljava/lang/String;"); /* set new static description field */ (*env)->SetStaticObjectField(env, jc, desc_id, description); }
class Test { static { System.loadLibrary("Test"); } public static native void scaleArray(double[] arr); public static void main(String[] args) { double[] arr = {1.1, 2.2}; scaleArray(arr); for(double d : arr){ System.out.println(d); } } }
C代码实现:
#include <stdio.h> #include "Test.h" JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_Test_scaleArray(JNIEnv* env, jclass jc, jdoubleArray arr) { double scaleFactor = 2.0; /*获得 一个指向 数组的指针 */ double* a = (*env)->GetDoubleArrayElements(env, arr, NULL); int i; for(i = 0; i< (*env)->GetArrayLength(env, arr); i++) a[i] = a[i] * scaleFactor; (*env)->ReleaseDoubleArrayElements(env, arr, a, 0); }
import java.util.Random; public class Test { static { System.loadLibrary("Test"); } public static native int nextInt(); public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(nextInt()); } }
在C代码中调用Random类的构造方法构造一个Random实例,然后调用nextInt实例方法。
#include <stdio.h> #include "Test.h" JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_Test_nextInt(JNIEnv* env, jclass jc) { /* 获得 Random 类, 注意表示类的字符串 */ jclass class_Random = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/util/Random"); /* 获得 Random 构造器 方法id, "<init>"代表构造方法 */ jmethodID id_Random = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, class_Random, "<init>", "()V"); /* 构造一个Random类型的对象 */ jobject obj_random = (*env)->NewObject(env, class_Random, id_Random, NULL); /* 下面调用这个对象的 nextInt 方法 */ jmethodID id_nextInt = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, class_Random, "nextInt", "()I"); jint ret = (*env)->CallIntMethod(env, obj_random, id_nextInt, NULL); return ret; }
public class Test { static { System.loadLibrary("Test"); } /* 这里的luckyNumber方法纯粹测试目的: 当name为zhangsan时一定会抛出一个IllegalArgumentException异常 当name为lisi时,会调用Random.next(-10)主动抛出一个IllegalArgumentException异常,但是可以使用第二个参数来决定是否要抛出到 jvm 当name为其他值时,无异常 */ public static native int luckyNumber(String name, boolean nativeHandleException); public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Test.luckyNumber("zhangsan", false)); } }
C代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include "Test.h" JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_Test_luckyNumber(JNIEnv* env, jclass jc, jstring name, jboolean nativeHandleException) { const char* cname; cname = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, name, NULL); /* 当name为zhangsan时我们主动抛出一个异常 */ if(strcmp(cname, "zhangsan") == 0) { jclass class_Exception = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException"); /* 主动抛出异常 */ (*env)->ThrowNew(env, class_Exception, "zhangsan is a bad guy, he can‘t be given a lucky number"); /* 本地方法抛出异常后并不会主动终止,所以要手动return */ return; } /* 调用Random.nextInt 产生一个随机幸运数 */ jclass class_Random = (*env)->FindClass(env, "java/util/Random"); jmethodID id_Random = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, class_Random, "<init>", "()V"); jobject obj_random = (*env)->NewObject(env, class_Random, id_Random, NULL); jmethodID id_nextInt = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, class_Random, "nextInt", "(I)I"); jint ret; /* 当name为lisi时,我们使用负数来作为nextInt的参数,从而让他抛出一个异常 */ if(strcmp(cname, "lisi") == 0) { ret = (*env)->CallIntMethod(env, obj_random, id_nextInt, (-10) ); /*检查是否有异常挂起 */ jboolean hasException = (*env)->ExceptionCheck(env); /*当有异常挂起并且要求在native中主动处理异常时,主动clear,这样就不会通知 虚拟机 了*/ if(hasException && nativeHandleException) { /* 主动清除挂起的异常 */ (*env)->ExceptionClear(env); printf("the exception is handled in native function/n"); }else if(hasException){ return; } }else{ ret = (*env)->CallIntMethod(env, obj_random, id_nextInt, 10); } return ret; }
标签:不能 static char code sha win tostring open 语言
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zh1164/p/6283831.html