标签:编译 virtual 分享 include 失败 函数 需要 height virt
C++ 代码:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class Parent { public: void fun() {cout<<"Parent fun"<<endl;} void fun(int a) {cout<<"Parent fun int a"<<endl;} void fun(int a, int b) {cout<<"Parent fun int a int b"<<endl;} }; class Child:public Parent { public: void fun() {cout<<"Child fun"<<endl;} //void fun(int a) //{cout<<"Child fun int a"<<endl;} //void fun(int a, int b) //{cout<<"Child fun int a int b"<<endl;} }; int main() { Child x; x.fun(); //x.fun(0); return 0; }
运行结果:
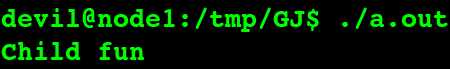
若是将主函数修改为:
int main() { Child x; x.fun(); x.fun(0); return 0; }
运行结果:
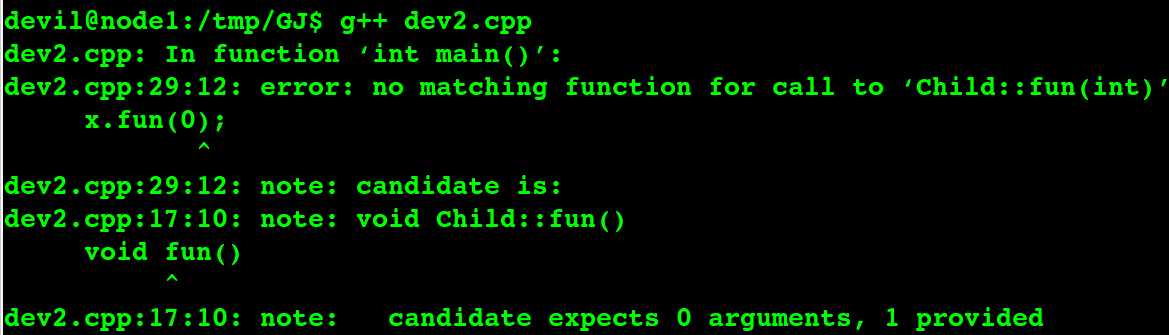
分析,说明:
在c++中,重载不会发生在基类与派生类之间,重载 制发生在同一类中!当基类和派生类中存在同名函数时,无论同名函数的形参个数或者类型是否相同,派生类中的同名函数都会将基类中的同名函数隐藏(将在下边说明隐藏)掉,而不会是重载关系。这时,当你通过派生类对象调用该同名函数时,只能访问派生类的该函数,如果硬要访问基类的该函数,则需要在函数名前加上类作用域!
如果将派生类中的同名函数 设为 static 静态, 运行效果如上不变。
class Child:public Parent { public: static void fun() {cout<<"Child fun"<<endl;} //void fun(int a) //{cout<<"Child fun int a"<<endl;} //void fun(int a, int b) //{cout<<"Child fun int a int b"<<endl;} };
如果将父类中的同名函数 设为 static 静态, 运行效果如上仍不变。
class Parent { public: static void fun() {cout<<"Parent fun"<<endl;} static void fun(int a) {cout<<"Parent fun int a"<<endl;} static void fun(int a, int b) {cout<<"Parent fun int a int b"<<endl;} };
C++ 中 同名函数是否为 静态 static , 不影响 继承中的覆盖 关系。总之, c++中的 重载 只发生在同一类中, 也就是说 C++的继承存在隐藏。
在c++中隐藏只能出现在基类和派生类之间,而不能发生在同一个类内(否则会引起编译器出现二义性)。当基类和派生类中存在同名函数时,无论同名函数的形参个数或者类型是否相同,派生类中的同名函数都会将基类中的同名函数(这个函数不论是静态或者是非静态都可以,如上述例子)隐藏掉,而不会是重载关系。这时,当你通过派生类对象调用该同名函数时,只能访问派生类的该函数,如果硬要访问基类的该函数,则需要在函数名前加上类作用域!
若是 子类中的同名函数 返回值不同,如下,仍然会覆盖父类同名函数,即c++继承中的 覆盖及其隐藏 只和 函数名 相同与否 有关。
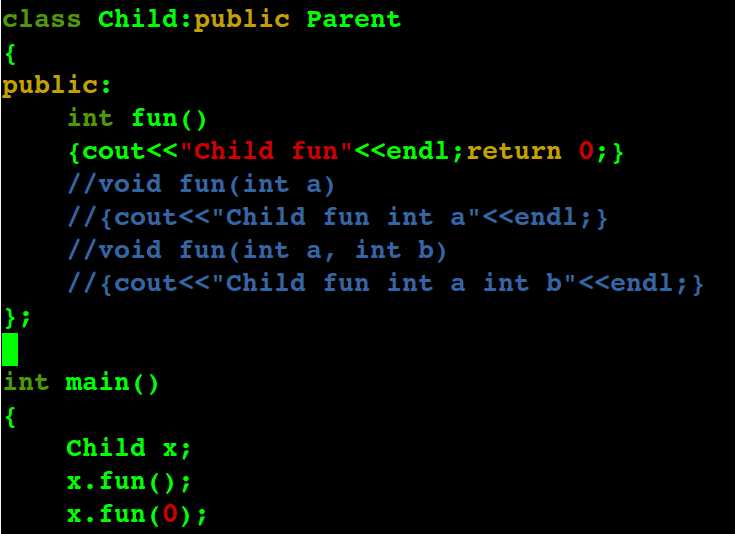
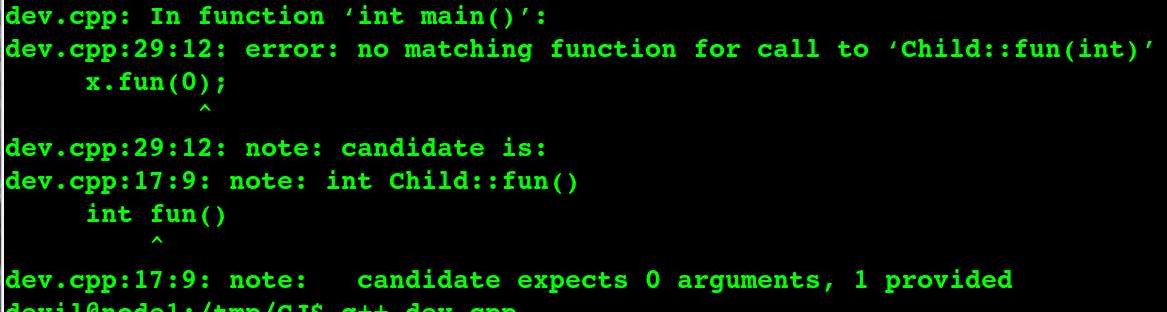
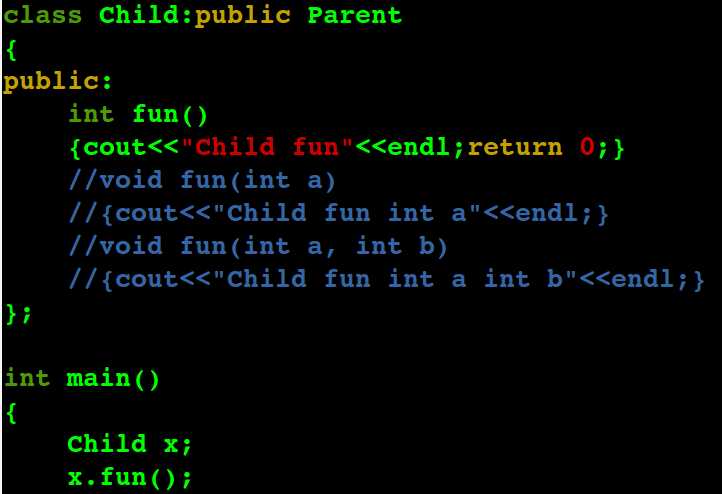
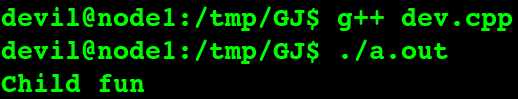
当是虚函数的情况:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class Parent { public: virtual void fun() {cout<<"Parent fun"<<endl;} void fun(int a) {cout<<"Parent fun int a"<<endl;} void fun(int a, int b) {cout<<"Parent fun int a int b"<<endl;} }; class Child:public Parent { public: int fun() {cout<<"Child fun"<<endl;return 0;} }; int main() { Child x; x.fun(); return 0; }
运行结果:
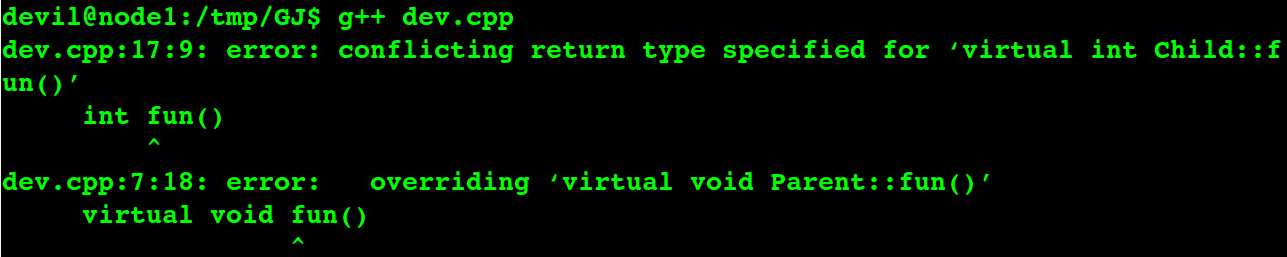
对于虚函数(用virtual修饰的),如果基类中有一个虚函数,派生类中同样有一个同名同参的函数(那么该函数将自动虚化), 那么其返回值一定要和基类的虚函数的返回值相同!否则 覆盖失败,编译不通过,隐藏失败!
java 部分:
如上述代码所示。而在java中子类会将父类中的方法继承过来,子类中同名方法会和父类中的同名方法要么是重载关系,要么是覆盖关系,要么就错误(比如同名同参却是不同的返回类型!)
class Parent { public static void fun() {System.out.println("Parent fun");} public static void fun(int a) {System.out.println("Parent fun int a");} public static void fun(int a, int b) {System.out.println("Parent fun int a int b");} }; class Child extends Parent { public static void fun() {System.out.println("Child fun");} //public void fun(int a) // {System.out.println("Child fun int a");} //public void fun(int a, int b) // {System.out.println("Child fun int a int b");} }; public class dev { public static void main(String []args) { Child x=new Child(); x.fun(); x.fun(0); } }
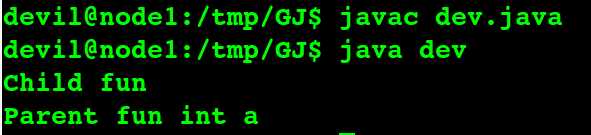
若是,去掉 子类中 的 static , 无法编译, 即 java 继承中的覆盖 要求 区分 static, 即static 同名函数 覆盖父类的static 同名函数。
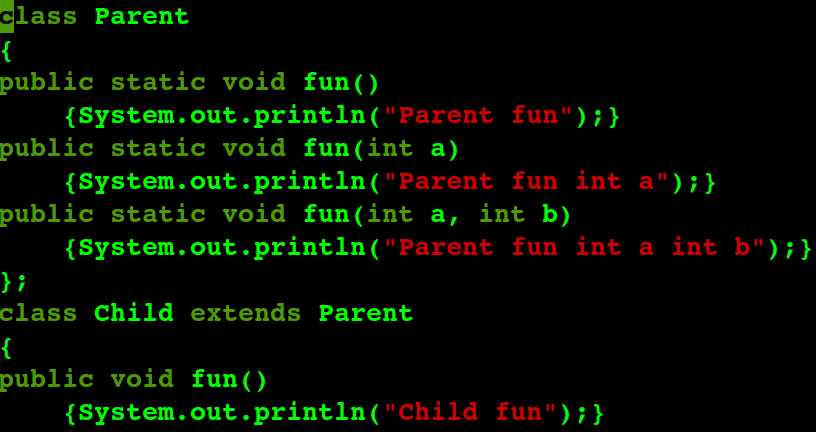
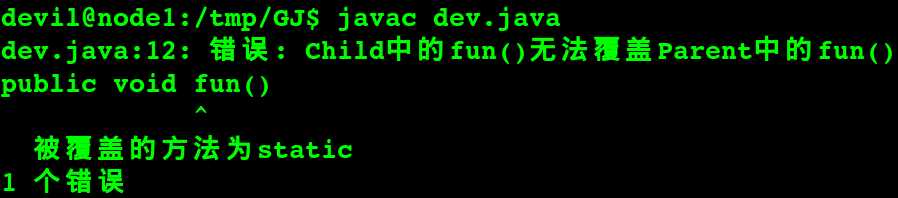
如果父类 同名函数 无static , 子类同名函数有 static, 即
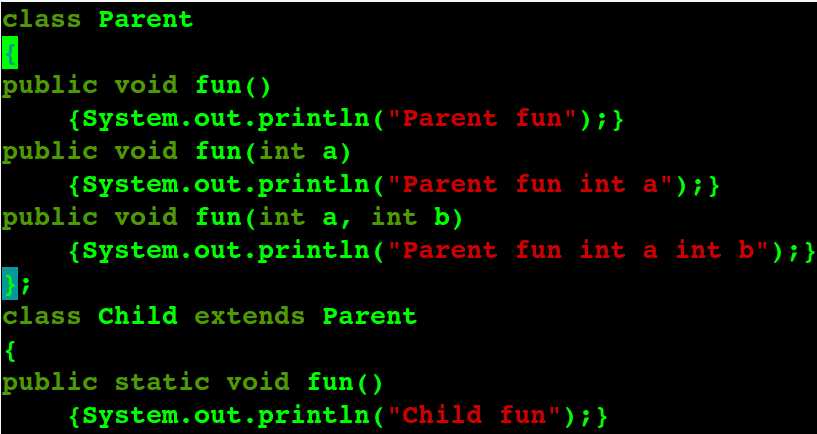
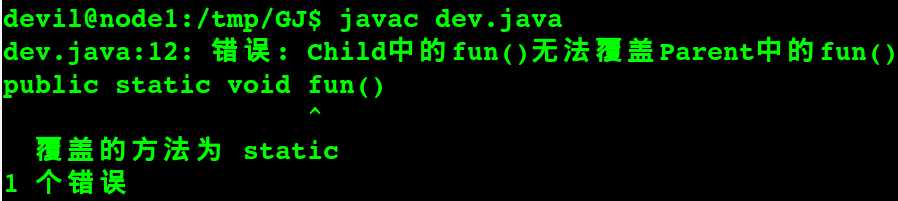
在java中, 非静态方法只能由(或被)非静态方法 覆盖! 静态方法只能由(或被)静态方法 覆盖!
即,static 对应相同。
标签:编译 virtual 分享 include 失败 函数 需要 height virt
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/devilmaycry812839668/p/6358431.html