标签:原因 rip group tcp boolean 多少 ams path dex
WebSocket 通过“Upgrade handshake(升级握手)”从标准的 HTTP 或HTTPS 协议转为 WebSocket。因此,使用 WebSocket 的应用程序将始终以 HTTP/S 开始,然后进行升级。在什么时候发生这种情况取决于具体的应用;它可以是在启动时,或当一个特定的 URL 被请求时。
在我们的应用中,当 URL 请求以“/ws”结束时,我们才升级协议为WebSocket。否则,服务器将使用基本的 HTTP/S。一旦升级连接将使用的WebSocket 传输所有数据。
整个服务器逻辑如下:
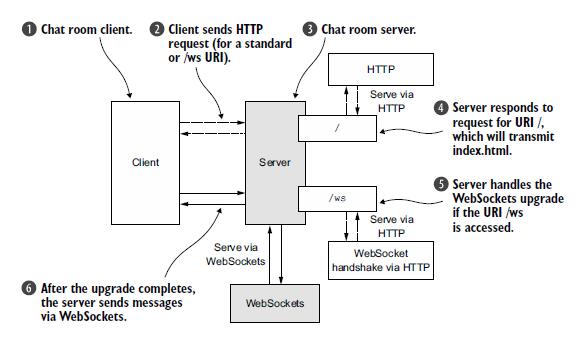
客户端/用户连接到服务器并加入聊天
HTTP 请求页面或 WebSocket 升级握手
服务器处理所有客户端/用户
响应 URI “/”的请求,转到默认 html 页面
如果访问的是 URI“/ws” ,处理 WebSocket 升级握手
升级握手完成后 ,通过 WebSocket 发送聊天消息
让我们从处理 HTTP 请求的实现开始。
public class HttpRequestHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> { //1
private final String wsUri;
private static final File INDEX;
static {
URL location = HttpRequestHandler.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation();
try {
String path = location.toURI() + "WebsocketChatClient.html";
path = !path.contains("file:") ? path : path.substring(5);
INDEX = new File(path);
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to locate WebsocketChatClient.html", e);
}
}
public HttpRequestHandler(String wsUri) {
this.wsUri = wsUri;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception {
if (wsUri.equalsIgnoreCase(request.getUri())) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(request.retain()); //2
} else {
if (HttpHeaders.is100ContinueExpected(request)) {
send100Continue(ctx); //3
}
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(INDEX, "r");//4
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(request.getProtocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8");
boolean keepAlive = HttpHeaders.isKeepAlive(request);
if (keepAlive) { //5
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, file.length());
response.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE);
}
ctx.write(response); //6
if (ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class) == null) { //7
ctx.write(new DefaultFileRegion(file.getChannel(), 0, file.length()));
} else {
ctx.write(new ChunkedNioFile(file.getChannel()));
}
ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT); //8
if (!keepAlive) {
future.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); //9
}
file.close();
}
}
private static void send100Continue(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.CONTINUE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"异常");
// 当出现异常就关闭连接
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
扩展 SimpleChannelInboundHandler 用于处理 FullHttpRequest信息
如果请求是 WebSocket 升级,递增引用计数器(保留)并且将它传递给在 ChannelPipeline 中的下个 ChannelInboundHandler
处理符合 HTTP 1.1的 “100 Continue” 请求
读取默认的 WebsocketChatClient.html 页面
判断 keepalive 是否在请求头里面
写 HttpResponse 到客户端
写 index.html 到客户端,判断 SslHandler 是否在 ChannelPipeline 来决定是使用 DefaultFileRegion 还是 ChunkedNioFile
写并刷新 LastHttpContent 到客户端,标记响应完成
如果 keepalive 没有要求,当写完成时,关闭 Channel
HttpRequestHandler 做了下面几件事,
WebSockets 在“帧”里面来发送数据,其中每一个都代表了一个消息的一部分。一个完整的消息可以利用了多个帧。 WebSocket “Request for Comments” (RFC) 定义了六中不同的 frame; Netty 给他们每个都提供了一个 POJO 实现 ,而我们的程序只需要使用下面4个帧类型:
在这里我们只需要显示处理 TextWebSocketFrame,其他的会由 WebSocketServerProtocolHandler 自动处理。
下面代码展示了 ChannelInboundHandler 处理 TextWebSocketFrame,同时也将跟踪在 ChannelGroup 中所有活动的 WebSocket 连接
TextWebSocketFrameHandler.java
public class TextWebSocketFrameHandler extends
SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
public static ChannelGroup channels = new DefaultChannelGroup(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { // (1)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
for (Channel channel : channels) {
if (channel != incoming){
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[" + incoming.remoteAddress() + "]" + msg.text()));
} else {
channel.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[you]" + msg.text() ));
}
}
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (2)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
// Broadcast a message to multiple Channels
channels.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[SERVER] - " + incoming.remoteAddress() + " 加入"));
channels.add(incoming);
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress() +"加入");
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (3)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
// Broadcast a message to multiple Channels
channels.writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[SERVER] - " + incoming.remoteAddress() + " 离开"));
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress() +"离开");
// A closed Channel is automatically removed from ChannelGroup,
// so there is no need to do "channels.remove(ctx.channel());"
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (5)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"在线");
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // (6)
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"掉线");
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause)
throws Exception {
Channel incoming = ctx.channel();
System.out.println("Client:"+incoming.remoteAddress()+"异常");
// 当出现异常就关闭连接
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
TextWebSocketFrameHandler 继承自 SimpleChannelInboundHandler,这个类实现了 ChannelInboundHandler 接口,ChannelInboundHandler 提供了许多事件处理的接口方法,然后你可以覆盖这些方法。现在仅仅只需要继承 SimpleChannelInboundHandler 类而不是你自己去实现接口方法。
覆盖了 handlerAdded() 事件处理方法。每当从服务端收到新的客户端连接时,客户端的 Channel 存入 ChannelGroup 列表中,并通知列表中的其他客户端 Channel
覆盖了 handlerRemoved() 事件处理方法。每当从服务端收到客户端断开时,客户端的 Channel 自动从 ChannelGroup 列表中移除了,并通知列表中的其他客户端 Channel
覆盖了 channelRead0() 事件处理方法。每当从服务端读到客户端写入信息时,将信息转发给其他客户端的 Channel。其中如果你使用的是 Netty 5.x 版本时,需要把 channelRead0() 重命名为messageReceived()
覆盖了 channelActive() 事件处理方法。服务端监听到客户端活动
覆盖了 channelInactive() 事件处理方法。服务端监听到客户端不活动
exceptionCaught() 事件处理方法是当出现 Throwable 对象才会被调用,即当 Netty 由于 IO 错误或者处理器在处理事件时抛出的异常时。在大部分情况下,捕获的异常应该被记录下来并且把关联的 channel 给关闭掉。然而这个方法的处理方式会在遇到不同异常的情况下有不同的实现,比如你可能想在关闭连接之前发送一个错误码的响应消息。
上面显示了 TextWebSocketFrameHandler 仅作了几件事:
由于 Netty 处理了其余大部分功能,唯一剩下的我们现在要做的是初始化 ChannelPipeline 给每一个创建的新的 Channel 。做到这一点,我们需要一个ChannelInitializer
public class WebsocketChatServerInitializer extends
ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { //1
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {//2
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(64*1024));
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpRequestHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/ws"));
pipeline.addLast(new TextWebSocketFrameHandler());
}
}
1.扩展 ChannelInitializer
2.添加 ChannelHandler 到 ChannelPipeline
initChannel() 方法设置 ChannelPipeline 中所有新注册的 Channel,安装所有需要的 ChannelHandler。
编写一个 main() 方法来启动服务端。
public class WebsocketChatServer {
private int port;
public WebsocketChatServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); // (1)
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); // (2)
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // (3)
.childHandler(new WebsocketChatServerInitializer()) //(4)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // (5)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // (6)
System.out.println("WebsocketChatServer 启动了");
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // (7)
// 等待服务器 socket 关闭 。
// 在这个例子中,这不会发生,但你可以优雅地关闭你的服务器。
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
System.out.println("WebsocketChatServer 关闭了");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int port;
if (args.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
} else {
port = 8080;
}
new WebsocketChatServer(port).run();
}
}
NioEventLoopGroup 是用来处理I/O操作的多线程事件循环器,Netty 提供了许多不同的 EventLoopGroup 的实现用来处理不同的传输。在这个例子中我们实现了一个服务端的应用,因此会有2个 NioEventLoopGroup 会被使用。第一个经常被叫做‘boss’,用来接收进来的连接。第二个经常被叫做‘worker’,用来处理已经被接收的连接,一旦‘boss’接收到连接,就会把连接信息注册到‘worker’上。如何知道多少个线程已经被使用,如何映射到已经创建的 Channel上都需要依赖于 EventLoopGroup 的实现,并且可以通过构造函数来配置他们的关系。
ServerBootstrap 是一个启动 NIO 服务的辅助启动类。你可以在这个服务中直接使用 Channel,但是这会是一个复杂的处理过程,在很多情况下你并不需要这样做。
这里我们指定使用 NioServerSocketChannel 类来举例说明一个新的 Channel 如何接收进来的连接。
这里的事件处理类经常会被用来处理一个最近的已经接收的 Channel。SimpleChatServerInitializer 继承自ChannelInitializer 是一个特殊的处理类,他的目的是帮助使用者配置一个新的 Channel。也许你想通过增加一些处理类比如 SimpleChatServerHandler 来配置一个新的 Channel 或者其对应的ChannelPipeline 来实现你的网络程序。当你的程序变的复杂时,可能你会增加更多的处理类到 pipline 上,然后提取这些匿名类到最顶层的类上。
你可以设置这里指定的 Channel 实现的配置参数。我们正在写一个TCP/IP 的服务端,因此我们被允许设置 socket 的参数选项比如tcpNoDelay 和 keepAlive。请参考 ChannelOption 和详细的 ChannelConfig 实现的接口文档以此可以对ChannelOption 的有一个大概的认识。
option() 是提供给NioServerSocketChannel 用来接收进来的连接。childOption() 是提供给由父管道 ServerChannel 接收到的连接,在这个例子中也是 NioServerSocketChannel。
我们继续,剩下的就是绑定端口然后启动服务。这里我们在机器上绑定了机器所有网卡上的 8080 端口。当然现在你可以多次调用 bind() 方法(基于不同绑定地址)。
恭喜!你已经完成了基于 Netty 聊天服务端程序。
在程序的 resources 目录下,我们创建一个 WebsocketChatClient.html 页面来作为客户端
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>WebSocket Chat</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var socket;
if (!window.WebSocket) {
window.WebSocket = window.MozWebSocket;
}
if (window.WebSocket) {
socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080/ws");
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById(‘responseText‘);
ta.value = ta.value + ‘\n‘ + event.data
};
socket.onopen = function(event) {
var ta = document.getElementById(‘responseText‘);
ta.value = "连接开启!";
};
socket.onclose = function(event) {
var ta = document