标签:word top cti diff pen href append ado img
推荐先看视频(youtube) Ned Batchelder - Facts and Myths about Python names and values - PyCon 2015
Change variable # rebinding x = x + 1 # mutating nums.append(7)
# can also rebind lists:
nums = nums + [7]
# but you can‘t mutate immutable
make a new list, don‘t change the mutable param
def append_twice(a_list, val):
a_list.append(val)
a_list.append(val)
def append_twice_bad(a_list, val):
"""This function is useless"""
a_list = a_list + [val, val]
def append_twice_good(a_list, val):
a_list = a_list + [val, val]
return a_list
shadowcopy and deepcopy
The difference between shallow and deep copying is only relevant for compound objects (objects that contain other objects, like lists or class instances):
A shallow copy constructs a new compound object and then (to the extent possible) inserts references into it to the objects found in the original.
A deep copy constructs a new compound object and then, recursively, inserts copies into it of the objects found in the original.
通过图片了解 compound objects
# objects that contain other objects, like lists or class instances
items = [{‘id‘: 1, ‘name‘: ‘laptop‘, ‘value‘: 1000}, {‘id‘: 2, ‘name‘: ‘chair‘, ‘value‘: 300},]
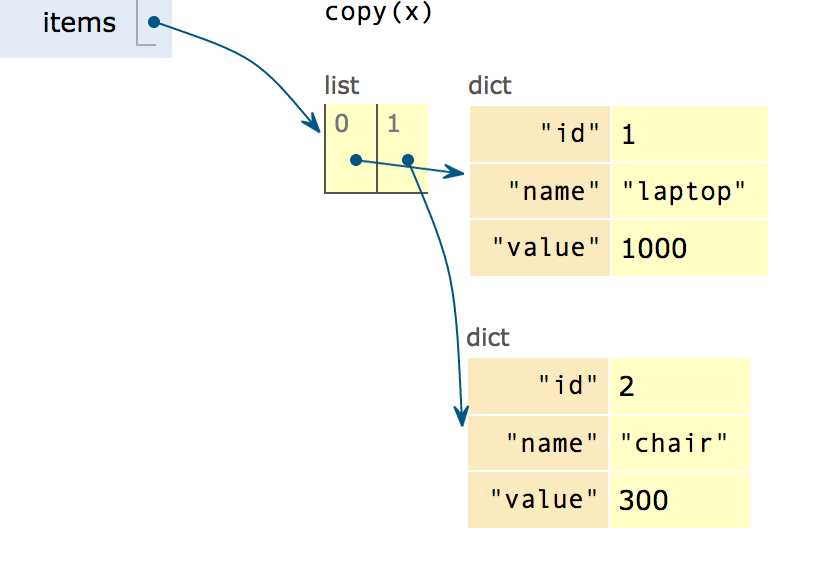
# 但是含有的是 int 这样的就不属于 compound objects int 疑问:难道不属于 object?
items = [1, 2, 3]
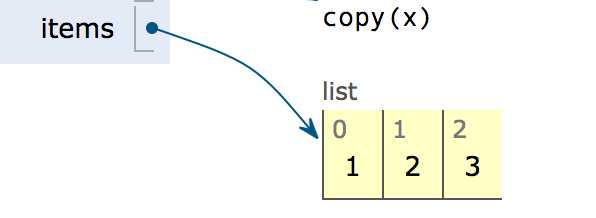
看看 shadow copy 与 deepcopy 对 compound object 的不同
from copy import deepcopy, copy
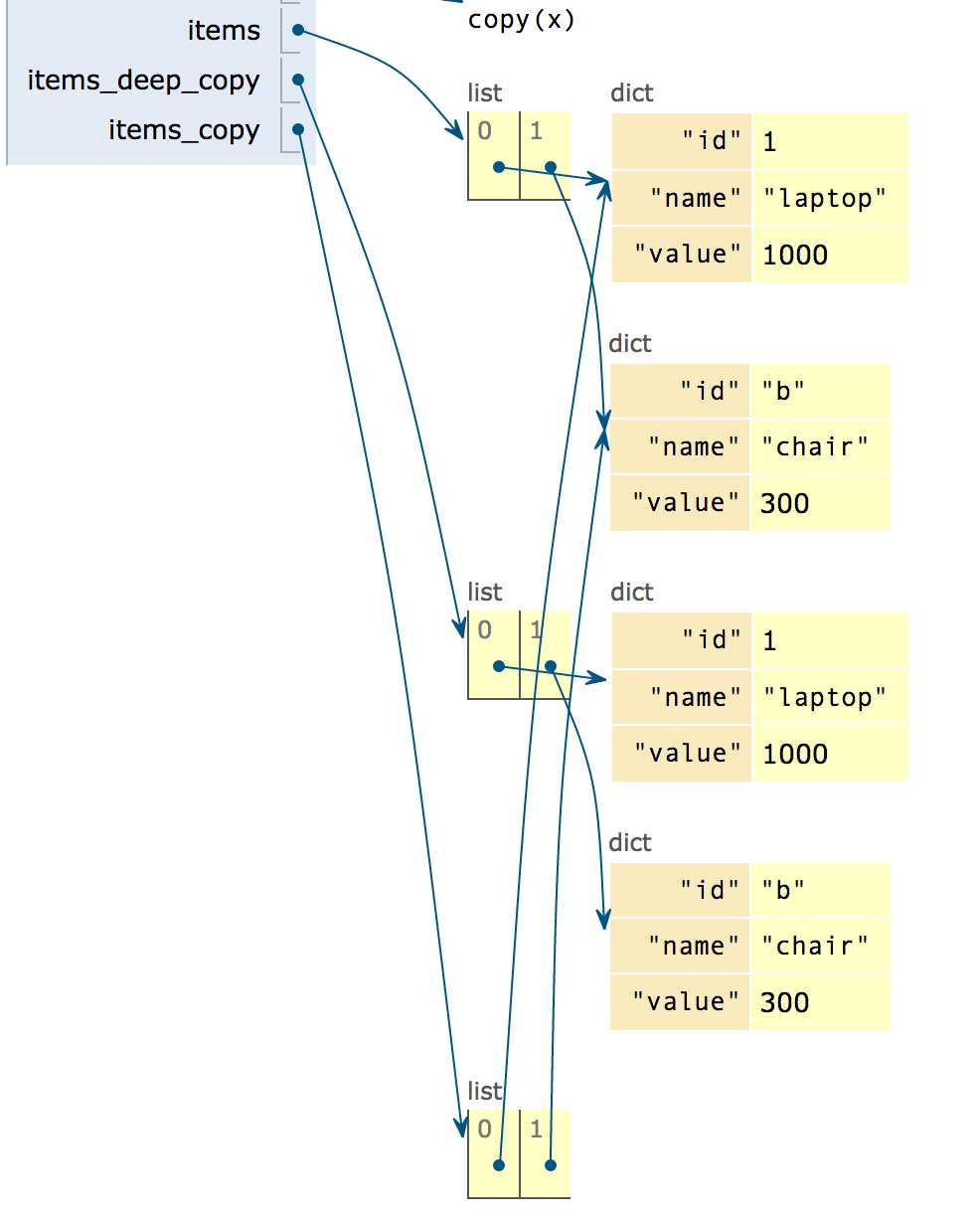
items = [{‘id‘: 1, ‘name‘: ‘laptop‘, ‘value‘: 1000}, {‘id‘: 2, ‘name‘: ‘chair‘, ‘value‘: 300},]
items_deep_copy = deepcopy(items)
items_deep_copy[1][‘id‘] = ‘b‘
items_deep_copy == items
items_copy = copy(items)
items_copy[1][‘id‘] = ‘b‘
items_copy == items
可以看出,deep_copy 是全部重新复制,而 shadow copy 只 deep copy复制了第一层,嵌套的只是复制了引用
疑问:
Python 3.6.0 (default, Dec 24 2016, 08:01:42) [GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 8.0.0 (clang-800.0.42.1)] on darwin items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] items_copy = items[:] items_copy[0] = ‘a‘ items_copy == items False # I think this is a shallow copy, and items_copy == items should return True but it‘s False.
# But another example return True items = [{‘id‘: 1, ‘name‘: ‘laptop‘, ‘value‘: 1000}, {‘id‘: 2, ‘name‘: ‘chair‘, ‘value‘: 300},] items_copy = items[:] items_copy[0][‘id‘] = ‘a‘ items_copy == items True
疑问:Do all mutable objects are composed of immutable objects
[1, 2, 3] from 1, 2, 3
Like language are composed of words
Python: names, values, assignment and mutability
标签:word top cti diff pen href append ado img
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jay54520/p/6531445.html