标签:开头 hello 建议 als auto 2.0 -128 java程序 false
1.自动转换类型:容量小的数据类型与容量大的数据类型做运算,容量小的会自动转换为容量大的数据类型。
2.自动转换:char,byte,short=>int=>long=>float=>double。Char,byte,short之间做运算默认的是int类型。
3.强制类型转换;容量大的转换为容量小的,要使用强制类型转换符:(),可能导致精度损失。
例:long l1=121345;
Int m1=(int)l1;
System.out.println(ml)
4.字符串(string,加””)与基本数据类型之间的运算,只能是连接运算(如+),得到的结果仍为一个字符串。
题1:string str1=”hello”;
Int myInt1=12;
Char chr1=’a’;
System.out.println(strl+myInt1+chr1);//hello12a
System.out.println(myInt1+chr1+str1);//109hello
System.out.println(chrl+strl+myInt1);//ahello12
题2:string str1=4;//错
String str2=3.5f+””;//对
System.out.println(str2);//输出3.5
System.out.println(3+4+”hello!”);//输出7hello!
System.out.println(“hello!”+3+4);//输出hello!34
System.out.println(‘a’+1+”hello!”);//输出98hello!
System.out.println(“hello”+’a’+1);//输出helloa1
5.进制;二进制:0或1,以0b或0B开头,开头符号位,0为正、1为负;
十进制:0-9;
八进制:0-7,以0开头;
十六进制:0-9及A-F,以0x或0X开头,不区分A-F的大小写。
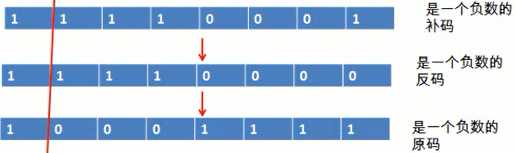
6.原码、反码和补码;①正数时,原码、反码和补码三码合一;②负数时,反码为在原码基础上符号位不动其余取反;补码为在反码基础上+1。
题3:
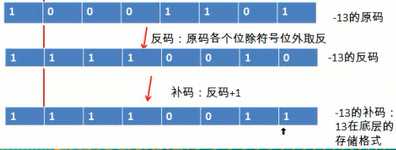
题4:byte的值(计算机底层-15)
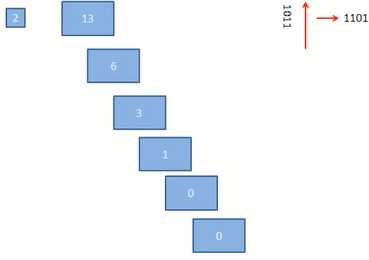
7.十进制=>二进制:除2取余数的逆向
例:
8.二进制=>八进制

9.二进制=>十六进制
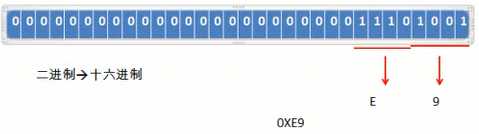
10.算术运算符;+、-、*、/、%、++、--
11.除号;/
题5:int i=12;
Int j=i/5;
Double d=i/5;
Double d2=(double)i/5;
Double d1=i/5.0;
System.out.println(j);//2
System.out.println(d);//2.0
System.out.println(d2);//2.4
System.out.println(d1);2.4
12.取模;%,取余,结果的符号取决于被模数
题6:int i1=12%5;
Int i2=-12%5;
Int i3=-12%(-5);
Int i4=12%(-5);
System.out.println(i1);//2
System.out.println(i2);//-2
System.out.println(i3);//-2
System.out.println(i4);//2
13.加加,减减;++,--
①前++:先自增1,后做运算;
后++:先做运算,后自增1;
题7:int myInt1=10;
Int myInt2=myInt1++;//后++
System.out.println(myInt1);//11
System.out.println(myInt2);//10
Int myInt3=10;
Int myInt4=++myInt;//前++
System.out.println(myInt3);//11
System.out.println(myInt4);//11
②前--:先自减1,后做运算;
后--:先做运算,后自减1;
14.命令行方式;dir,md,rd,cd,cd..,cd/,del,exit
15.JDK、JRE和JVM三者关系,Java程序:编写=>编译=>运行。
16.单行注释、多行注释和文档注释,文档注释/** */。
解析文档注释:javadoc-d文件目录名-autor-version源文件名.java;
17.赋值运算;+、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=。
①+=:既可以实现运算,又不会更改s的数据类型;
题8:i+=3相当于i=i+3;
题9:short s=10;
S=s+3;//编译不会通过
S=(short)(s+3);//编译通过,不建议此编译
S+=3;//既可以实现运算,又不更改s的数据类型
②=:赋值非等号;
题10:boolean b1=false;
If(b1=true){system.out.println(“结果为真”)}
Else{system.out.println(“结果为假”)}
//输出结果为真
题11:boolean b1=false;
If(b1==true){system.out.println(“结果为真”)}
Else{system.out.println(“结果为假”)}
//输出结果为假
题12:int i=1;
i*=0.1;
System.out.println(i);//0,类型仍为int,0.1即0
18.比较运算符;①==,相等于;②!=,不等于;③<、>、<=、>=;
④instanceof,检查是否是类的对象;
例:”Hello” instanceof string//为true
标签:开头 hello 建议 als auto 2.0 -128 java程序 false
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wanglele-1988/p/6680214.html