标签:其他 rod eal efault python基础 too src str ima
一、map
Python内置函数,用法及说明如下:
class map(object):
"""
map(func, *iterables) --> map object
Make an iterator that computes the function using arguments from
each of the iterables. Stops when the shortest iterable is exhausted.
"""
map()函数接收两个参数,一个是函数,一个是Iterable,map将传入的函数依次作用到序列的每个元素,并把结果作为新的Iterator返回。
举例说明,比如我们有一个函数f(x)=x2,要把这个函数作用在一个list [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]上,就可以用map()实现如下:
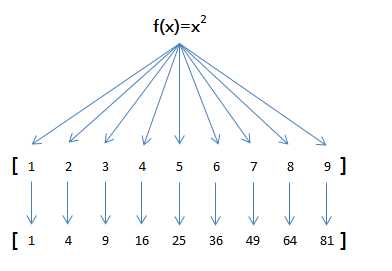
def f(x):
return x * x
r = map(f, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
list(r)
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
map()传入的第一个参数是f,即函数对象本身。由于结果r是一个Iterator,Iterator是惰性序列,因此通过list()函数让它把整个序列都计算出来并返回一个list。
#使用lambda匿名函数 list(map(lambda x: x * x, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])) [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
map()作为高阶函数,事实上它把运算规则抽象了,因此,我们不但可以计算简单的f(x)=x2,还可以计算任意复杂的函数,比如,把这个list所有数字转为字符串:
list(map(str, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])) [‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘]
map函数的优点:
二、 reduce
def reduce(function, sequence, initial=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
"""
reduce(function, sequence[, initial]) -> value
Apply a function of two arguments cumulatively to the items of a sequence,
from left to right, so as to reduce the sequence to a single value.
For example, reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) calculates
((((1+2)+3)+4)+5). If initial is present, it is placed before the items
of the sequence in the calculation, and serves as a default when the
sequence is empty.
"""
pass
reduce把一个函数作用在一个序列[x1, x2, x3, ...]上,这个函数必须接收两个参数,reduce把结果继续和序列的下一个元素做累积计算,其效果就是:
reduce(f, [x1, x2, x3, x4]) = f(f(f(x1, x2), x3), x4)
比方说对一个序列求和,就可以用reduce实现:
from functools import reduce
def add(x, y):
return x + y
reduce(add, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
25
匿名函数实现:
reduce(lambda x, y : x + y, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]) 25
当然求和运算可以直接用Python内建函数sum(),没必要动用reduce。
但是如果要把序列[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]变换成整数13579,reduce就可以派上用场:
from functools import reduce
def fn(x, y):
return x * 10 + y
reduce(fn, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
13579
匿名函数实现:
reduce(lambda x, y: x * 10 + y, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]) 13579
这个例子本身没多大用处,但是,如果考虑到字符串str也是一个序列,对上面的例子稍加改动,配合map(),我们就可以写出把str转换为int的函数:
from functools import reduce
def fn(x, y):
return x * 10 + y
def char2num(s):
return {‘0‘: 0, ‘1‘: 1, ‘2‘: 2, ‘3‘: 3, ‘4‘: 4, ‘5‘: 5, ‘6‘: 6, ‘7‘: 7, ‘8‘: 8, ‘9‘: 9}[s]
reduce(fn, map(char2num, ‘13579‘))
13579
整理成一个str2int的函数就是:
from functools import reduce
def str2int(s):
def fn(x, y):
return x * 10 + y
def char2num(s):
return {‘0‘: 0, ‘1‘: 1, ‘2‘: 2, ‘3‘: 3, ‘4‘: 4, ‘5‘: 5, ‘6‘: 6, ‘7‘: 7, ‘8‘: 8, ‘9‘: 9}[s]
return reduce(fn, map(char2num, s))
还可以用lambda函数进一步简化成:
from functools import reduce
def char2num(s):
return {‘0‘: 0, ‘1‘: 1, ‘2‘: 2, ‘3‘: 3, ‘4‘: 4, ‘5‘: 5, ‘6‘: 6, ‘7‘: 7, ‘8‘: 8, ‘9‘: 9}[s]
def str2int(s):
return reduce(lambda x, y: x * 10 + y, map(char2num, s))
小练习:
map()函数,把用户输入的不规范的英文名字,变为首字母大写,其他小写的规范名字。输入:[‘adam‘, ‘LISA‘, ‘barT‘],输出:[‘Adam‘, ‘Lisa‘, ‘Bart‘]: list(map(lambda x: x.capitalize(), [‘adam‘, ‘LISA‘, ‘barT‘])) [‘Adam‘, ‘Lisa‘, ‘Bart‘]
2. Python提供的sum()函数可以接受一个list并求和,请编写一个prod()函数,可以接受一个list并利用reduce()求积:
def prod(l):
return reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, l)
l = [1, 2 ,3, 4, 5]
print(prod(l))
120
匿名函数实现:
reduce(lambda x, y: x * y, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) 120
3. 利用map和reduce编写一个str2float函数,把字符串‘123.456‘转换成浮点数123.456:
from functools import reduce
def char2num(s):
return {‘0‘: 0, ‘1‘: 1, ‘2‘: 2, ‘3‘: 3, ‘4‘: 4, ‘5‘: 5, ‘6‘: 6, ‘7‘: 7, ‘8‘: 8, ‘9‘: 9}[s]
def str_split(s):
s1, s2 = s.split(‘.‘)
return s1, s2
def str2int_1(s1):
return reduce(lambda x, y: x * 10 + y, map(char2num, s1))
def str2int_2(s2):
return (reduce(lambda x, y: x * 10 + y, map(char2num, s2)))/pow(10, len(s2))
def str2float(s):
s1, s2 = str_split(s)
res = str2int_1(s1) + str2int_2(s2)
return res
a = str2float(‘123.456‘)
print(a)
123.456
待更新:
标签:其他 rod eal efault python基础 too src str ima
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/OldJack/p/6705897.html