标签:line split() turn 数据 import == apache2 字节 glin
ubuntu中apache2的日志文件位于:
/var/log/apache2
代码:
# coding=utf-8 import sys ‘‘‘ 数据 127.0.0.1 - - [10/Jan/2017:10:08:16 +0800] "POST /cgi-bin/login.py HTTP/1.1" 200 335 "-" "curl/7.35.0" ‘‘‘ def dictify_logline(line): split_line = line.split() return { "remote_address": split_line[0], "status": split_line[8], "bytes_sent": split_line[9] } def generate_log_report(logfile): report_dict = {} for line in logfile: line_dict = dictify_logline(line) print line_dict try: bytes_send = int(line_dict["bytes_sent"]) except ValueError: continue #统计每一个ip,对应发送的字节数 report_dict.setdefault( line_dict["remote_address"], []).append(bytes_send) return report_dict if __name__ == "__main__": if not len(sys.argv) > 1: sys.exit(1) infile_name = sys.argv[1] try: infile = open(infile_name, ‘r‘) except IOError: print ‘You must specify a valid file to parse‘ sys.exit(1) log_report = generate_log_report(infile) print log_report infile.close() #正则表达式提取数据 import re log_line_re = re.compile(‘‘‘(?P<remote_address>\S+) #IP ADDRESS \s+ #whitespace \S+ #remote logname \s+ #whitepsace \S+ #remote user \s+ #whitespace \[[^\[\]]+\] #time \s+ #whitespace "[^"]+" #first line of request \s+ #whitesapce (?P<status>\d+) \s+ #whitespace (?P<bytes_sent>-|\d+) \s* ‘‘‘, re.VERBOSE) def dictify_logline(line): m = log_line_re.match(line) if m: groupdict = m.groupdict() if groupdict[‘bytes_sent‘] == ‘-‘: groupdict[‘bytes_sent‘] = ‘0‘ return groupdict else: return { "remote_address": None, "status": None, "bytes_sent": "0" }
效果:
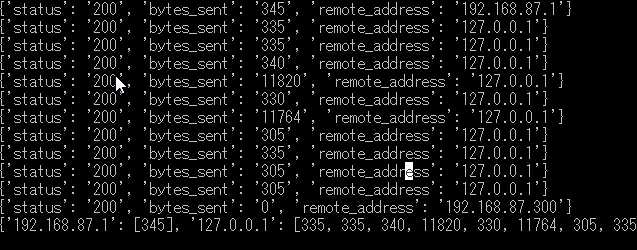
读取Apache访问日志,查看每一个独立客户端连接获得的字节数
标签:line split() turn 数据 import == apache2 字节 glin
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hupeng1234/p/6713785.html