标签:form 视图 relink namespace 加载 软件 erp ted 实例化
?
简介
?
js 是基础,angularJs 是 js 框架
?
起源
?
简介
?
ajax 开发是单页应用
?
【以前模板和数据是在后端装配完的,如servlet】
?
MVC
?
?
经典模板系统中的数据绑定
?
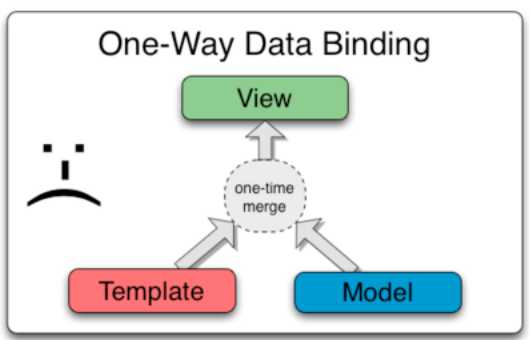 大多数模板系统中的数据绑定都是单向的
大多数模板系统中的数据绑定都是单向的
?
Anguarjs 模板中的数据绑定
?
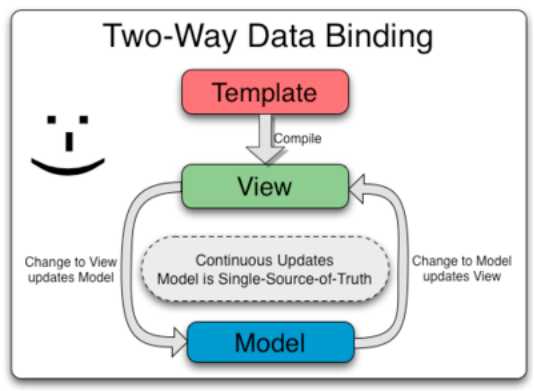 模板是在浏览器中编译的,在编译阶段产生了一个实时更新(live)的视图
模板是在浏览器中编译的,在编译阶段产生了一个实时更新(live)的视图
依赖注入是一种软件设计模式,用来处理代码的依赖关系。【如java spring Ioc】
?
?
【写在body里面,管理整个body里面的元素,管理整个页面】
?
模版显示文本 && ng-bind
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body ng-app>
<!--
view => 12131
model => 12131
3个 view
数据是双向绑定的
-->
<input type="text" ng-model="name" value=""/>
<!--angular的表达式-->
{{ name }}
<input type="text" ng-model="name" value=""/>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
创建一个字符串,使用函数eval解析
?
?
【var a=3,是针对window的属性】
2.宽容:表达式求值,对于undefined和null,angular是宽容的,但Javascript会产生NullPointerExceptions=
3.没有流程控制语句:在angular表达式里,不能做以下任何的事:条件分支、循环、抛出异常
4.过滤器(filters):我们可以就将表达式的结果传入过滤器链(filter chains)
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<input type="text" value="" ng-model="name"/>
<input type="text" value="" ng-model="age"/>
{{name}}
{{age}}
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
var firstController = function($scope){
//$scope 我们叫做作用域,是管理firstController控制器范围所有的数据的作用域,和js函数的作用域一样
// 申明一个默认的Model
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
$scope.age = 20;
}
?
?
?
AngularJs 多个controller作用域和 js 函数变量左右域的原理类似, 函数里面使用变量的时候,优先找函数作用域里面的是否有该变量,如果没有,就去访问函数外面的变量.
?
下面的demo中,总共有三个作用域,一个是ng-app, 另外两个分别是firstController、secondController
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<input type="text" value="" ng-model="name"/>
<div ng-controller="secondController">
<input type="text" value="" ng-model="name"/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
function first(){
var name = ‘张三‘;
function second(){
var name = ‘张三12121212121‘;
alert(name);
}
}
</script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
Index.js
?
var firstController = function($scope){
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
console.log($scope);
}
var secondController = function($scope){
console.log($scope);
}
?
?
ng-bind 也可以展现$scope里面的数据,比{{}} 展示数据的优势在于,使用ng-bind,当angularJs 没有加载完的时候,不会显示任何东西,而使用{{}},会显示乱码
?
?
什么是 scope
?
?
scope的特性
?
?
【$apply方法有什么用?当apply 方法执行完之后,会触发angular里面的脏检查,检查每一个scope里面的属性是否有变化,如果有变化,所对应的其他的model 、value 都会变化】
?
?
angular是怎么知道变量发生了改变
?
?
angular的策略
?
?
什么时候去脏检查
?
?
手动触发脏检查
?
【只有需要手动触发的时候脏检查,才需要调用apply方法。否则,比如,:controller 初始化的时候,系统会自动在后台调用apply方法。】
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
{{date}}
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
Index.js
var firstController = function($scope){
$scope.date = new Date();
// setInterval(function(){
// // 这里虽然变 但是并没有触发 脏检查
// $scope.date = new Date();
// },1000)
setInterval(function(){
$scope.$apply(function(){
$scope.date = new Date(); //....会去触发脏检查
})
},1000) // 触发一次脏检查
}
?
?
?
?
函数
参数:
watchFn: angular表达式或函数的字符串【表达式是有上下文关系的】
watchAction(newValue,oldValue,scope): watchFn发生变化会被调用
deepWacth: 可选的,布尔值命令检查被监控的对象的每个属性是否发生变化
?
应用场景,可以是购物车 当你购买到一定数量的商品的时候,折扣发生变化。
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<input type="text" value="" ng-model="name"/>
改变次数:{{count}}-{{name}}
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
var firstController = function($scope){
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
$scope.data = {
name :‘李四‘,
count:20
}
$scope.count = 0;
// 监听一个model【变量】, 当一个model每次改变时 都会触发第2个函数
$scope.$watch(‘name‘,function(newValue,oldValue){
++$scope.count;
if($scope.count > 30){
$scope.name = ‘已经大于30次了‘;
}
});
//监听的是data是一个对象,如果要监听date中的name、age变化,那么第三个参数必须设置为true才行
$scope.$watch(‘data‘,function(){},true)
}
?
?
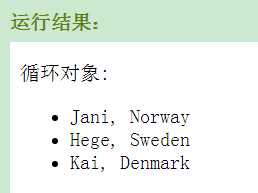
ng-repeat 指令用在一个对象数组上:
?
<div ng-app="" ng-init="names=[
{name:‘Jani‘,country:‘Norway‘},
{name:‘Hege‘,country:‘Sweden‘},
{name:‘Kai‘,country:‘Denmark‘}]">
<p>循环对象:</p>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="x in names">
{{ x.name + ‘, ‘ + x.country }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
?
?
ng-repeat指令会重复一个 HTML 元素:
<div ng-app="" ng-init="names=[‘Jani‘,‘Hege‘,‘Kai‘]">
<p>使用 ng-repeat 来循环数组</p>
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="x in names">
{{ x }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../vendor/bootstrap3/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
</head>
<body ng-app>
<div ng-controller="cartController" class="container">
<table class="table" ng-show="cart.length">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>产品编号</th>
<th>产品名字</th>
<th>购买数量</th>
<th>产品单价</th>
<th>产品总价</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr ng-repeat="item in cart">
<td>{{item.id}}</td>
<td>{{item.name}}</td>
<td>
<button type="button" ng-click="reduce(item.id)" class="btn tn-primary">-</button>
<input type="text" value="{{item.quantity}}" ng-model="item.quantity" >
<button type="button" ng-click="add(item.id)" class="btn tn-primary">+</button>
</td>
<td>{{item.price}}</td>
<td>{{item.price * item.quantity}}</td>
<td>
<button type="button" ng-click="remove(item.id)" class="btn btn-danger">移除</button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
总购买价
</td>
<td>
{{totalPrice()}}
</td>
<td>
总购买数量
</td>
<td>
{{totalQuantity()}}
</td>
<td colspan="2">
<button type="button" ng-click="cart = {}" class="btn btn-danger">清空购物车</button>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p ng-show="!cart.length">您的购物车为空</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
Js文件
?
var cartController = function ($scope) {
$scope.cart = [
{
id: 1000,
name: ‘iphone5s‘,
quantity: 3,
price: 4300
},
{
id: 3300,
name: ‘iphone5‘,
quantity: 30,
price: 3300
},
{
id: 232,
name: ‘imac‘,
quantity: 4,
price: 23000
},
{
id: 1400,
name: ‘ipad‘,
quantity: 5,
price: 6900
}
];
/**
* 计算购物总价
*/
$scope.totalPrice = function () {
var total = 0;
angular.forEach($scope.cart, function (item) {
total += item.quantity * item.price;
})
return total;
}
/**
* 计算总购买数
*/
$scope.totalQuantity = function () {
var total = 0;
angular.forEach($scope.cart, function (item) {
total += parseInt(item.quantity);
})
return total;
}
/**
* 找一个元素的索引
*/
var findIndex = function (id) {
var index = -1;
angular.forEach($scope.cart, function (item, key) {
if (item.id === id) {
index = key;
return;
}
});
return index;
}
/**
* 为某个产品添加一个数量
*/
$scope.add = function (id) {
var index = findIndex(id);
?
if (index !== -1) {
++$scope.cart[index].quantity;
}
}
/**
* 为某个产品减少一个数量
*/
$scope.reduce = function (id) {
var index = findIndex(id);
if (index !== -1) {
var item = $scope.cart[index];
if(item.quantity > 1){
--item.quantity;
}else{
var returnKey = confirm(‘是否从购物车内删除该产品!‘);
if(returnKey){
$scope.remove(id);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 移除一项
*/
$scope.remove = function (id) {
var index = findIndex(id);
// 如果找到了那个item
if (index !== -1) {
$scope.cart.splice(index, 1);
}
//ng-click ,是ng开头的,调用之后,会自动做脏检查。会更新所有的参数、表达式值,这就是双向绑定的好处。
}
// 监听数量 如果小于 1 则让用户判断是否要删除产品????
$scope.$watch(‘cart‘,function(newValue,oldValue){
angular.forEach(newValue,function(item,key){
if(item.quantity < 1){
var returnKey = confirm(‘是否从购物车内删除该产品!‘);
if(returnKey){
$scope.remove(item.id);
}else{
item.quantity = oldValue[key].quantity;
}
}
})
},true);
}
?
?
?
?
scope生命周期
?
?
$eval && $evalAsync
?
?
$broadcast && $emit && $on
?
?
$new && $destroy
?
?
?
AngularJS中的Module类负责定义应用如何启动,它还可以通过声明的方式定义应用中的各个片段。我们来看看它是如何实现这些功能的。
一.Main方法在哪里
如果你是从Java或者Python编程语言转过来的,那么你可能很想知道AngularJS里面的main方法在哪里?这个把所有东西启动起来,并且第一个被执行的方法在哪里?JavaScript代码里面负责实例化并且把所有东西组合到一起,然后命令应用开始运行的那个方法在哪里?
事实上,AngularJS并没有main方法,AngularJS使用模块的概念来代替main方法。模块允许我们通过声明的方式来描述应用中的依赖关系,以及如何进行组装和启动。使用这种方式的原因如下:
1.模块是声明式的。这就意味着它编写起来更加容易,同时理解起来也很容易,阅读它就像读普通的英文一样!
2.它是模块化的。这就迫使你去思考如何定义你的组件和依赖关系,让它们变得更加清晰。
3.它让测试更加容易。在单元测试中,你可以有选择地加入模块,并且可以避免代码中存在无法进行单元测试的内容。同时,在场景测试中,你可以加载其他额外的模块,这样就可以更好地和其他组件配合使用。
例如,在我们的应用中有一个叫做"MyAwesomeApp"的模块。在HTML里面,只要把以下内容添加到<html>标签中(或者从技术上说,可以添加到任何标签中):
<html ng-app="MyAwesomeApp">
ng-app指令就会告诉AngularJS使用MyAwesomeApp模块来启动你的应用。那么,应该如何定义模块呢?举例来说,我们建议你为服务、指令和过滤器分别定义不同的模块。然后你的主模块可以声明依赖这些模块。
这样可以使得模块管理更加容易,因为它们都是良好的、完备的代码块,每个模块有且只有一种职能。同时,单元测试可以只加载它们所关注的模块,这样就可以减少初始化的次数,单元测试也会变得更精致、更专注。
二.加载和依赖
模块加载动作发生在两个不同的阶段,这一点从函数名上面就可以反映出来,它们分别是Config代码块和Run代码块(或者叫做阶段)。
1.Config代码块
在这一阶段里面,AngularJS会连接并注册好所有数据源。因此,只有数据源和常量可以注入到Config代码块中。那些不确定是否已经初始化好的服务不能注入进来。
2.Run代码块
Run代码块用来启动你的应用,并且在注射器创建完成之后开始执行。为了避免在这一点开始之后再对系统进行配置操作,只有实例和常量可以被注入到Run代码块中。你会发现,在AngularJS中,Run代码块是与main方法最类似的东西。
三.快捷方法
利用模块可以做什么呢?我们可以用它来实例化控制器、指令、过滤器以及服务,但是利用模块类还可以做更多事情。如下模块配置的API方法:
1.config(configFn)
利用此方法可以做一些注册工作,这些工作需要在模块加载时完成。
http://www.cnblogs.com/sean-/p/4952183.html、
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
ng-app
?
?
参数:
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<!--这块区域由myApp 模块来管理-->
<!--一个页面中不能有多个ng-app ,模块也不能嵌套-->
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
{{name}}
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<!--index.js文件不能放在angularjs.js 文件之前,否则读取 index.js文件的内容的时候,还没有读取angularjs.js,而报错-->
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
//模块创建完之后,返回模块对象,赋值给myApp
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘,[]);
//这样写表示,firstController控制器是属于,myApp模块的
myApp.controller(‘firstController‘,function($scope){
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
});
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
{{name}}
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
//因模块先于controller执行,故在模块启动的时候,我们可以在模块中配置一些相关的信息,给controller使用
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘,[],function($provide){
//自定义服务,模块myApp定义好服务CustomService之后,在模块的任意的controller中都可以调用该服务。
$provide.provider(‘CustomService‘,function(){//服务名:CustomService
this.$get = function(){
return {
message : ‘CustomService Message‘
}
}
});
$provide.provider(‘CustomService2‘,function(){
this.$get = function(){
return {
message : ‘CustomService2 Message‘
}
}
});
});
myApp.controller(‘firstController‘,function(CustomService,$scope,CustomService2){//参数的顺序遂意
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
console.log(CustomService2);
});
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
{{name}}
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘,[],function($provide){
// 自定义服务
$provide.provider(‘CustomService‘,function(){
this.$get = function(){
return {
message : ‘CustomService Message‘
}
}
});
// 自定义工厂,返回的内容可以是任何类型
$provide.factory(‘CustomFactory‘,function(){
return [1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
});
// 自定义服务
$provide.service(‘CustomService2‘,function(){
return ‘aaa‘;//l 和factory类似,但返回的东西必须是对象,不能事字符串、数字等基本类型。数组是引用类型
})
});
myApp.controller(‘firstController‘,function($scope,CustomFactory,CustomService2){
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
console.log(CustomFactory);
console.log(CustomService2);
});
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<!--两个Controller不存在包含关系,存在两个$scope 域-->
<div ng-controller="firstController">
first.data <input type="text" ng-model="data.name" />
first.Data <input type="text" ng-model="Data.message" />
<p>
first-name:{{data.name}}
</p>
<p>
first-message:{{Data.message}}
</p>
</div>
<div ng-controller="secondController">
<p>
second-name:{{data.name}}
</p>
<p>
second-message:{{Data.message}}
</p>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘,[])
.factory(‘Data‘,function(){ // this.$get = function(){}
return {
message : ‘共享的数据‘
};
})
.controller(‘firstController‘,function($scope,Data){
$scope.data = {//对象,引用类型,一个地方变了,全部都变了
name : ‘张三‘
};
$scope.Data = Data;
})
.controller(‘secondController‘,function($scope,Data){
$scope.data = $scope.$$prevSibling.data;//prevSibling上一个sope域中的数据
$scope.Data = Data;
});
?
?
?
显式和隐式依赖注入
?
?
?
什么是angular 过滤器
?
?
过滤器种类
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<!--[1,2,3,4,5] 显示前5位-->
<p>{{[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] | limitTo:5}}</p>
<!--[3,4,5,6,7],显示最后五位-->
<p>{{[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] | limitTo:-5}}</p>
<!-- hello world -->
<p>{{data.message | lowercase}}</p>
<!-- HELLO WORLD -->
<p>{{data.message | uppercase}}</p>
<p>
<!-- [{"name":"上海11212","py":"shanghai"}],【过滤包含:上海的项】-->
{{ data.city | filter : ‘上海‘}}
</p>
<p>
<!-- [],【只匹配value值】-->
{{ data.city | filter : ‘name‘}}
</p>
?
<p>
<!-- name":"上海11212","py":"shanghai"},{"name":"北京","py":"beijing"},【拼音里面是否有g】-->
{{ data.city | filter : {py:‘g‘} }}
</p>
?
<p>
<!-- [{"name":"上海11212","py":"shanghai"},{"name":"四川","py":"sichuan"}]-->
{{ data.city | filter : checkName }}
</p>
?
<p>
<!-- [{"name":"北京","py":"beijing"},{"name":"上海11212","py":"shanghai"},{"name":"四川","py":"sichuan"}] -->
<!-- 默认顺序是 正序 asc a~z 【按照拼音排序】 -->
{{ data.city | orderBy : ‘py‘}}
?
<!-- 默认顺序是 反序 desc z~a -->
<!-- [{"name":"四川","py":"sichuan"},{"name":"上海11212","py":"shanghai"},{"name":"北京","py":"beijing"}] -->
{{ data.city | orderBy : ‘-py‘}}
</p>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘,[])
.factory(‘Data‘,function(){
return {
message : ‘Hello World‘,
city : [
{
name:‘上海11212‘,
py : ‘shanghai‘
},
{
name:‘北京‘,
py : ‘beijing‘
},
{
name:‘四川‘,
py : ‘sichuan‘
}
]
};
})
.controller(‘firstController‘,function($scope,Data,$filter){
$scope.data = Data;
$scope.today = new Date;
// 在控制器中使用,过滤器
var number = $filter(‘number‘)(3000);
console.log(number);
//json过滤器,主要用途是方便调试,看起来代码更加清楚
var jsonString = $filter(‘json‘)($scope.data);
console.log(jsonString);
console.log($scope.data);
//自动义过滤器,自定义一个方法解决过滤问题
$scope.checkName = function(obj){
if(obj.py.indexOf(‘h‘) === -1)
return false;
return true;
}
?
})
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../vendor/bootstrap3/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
<style>
.orderColor{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="product">
?
<div class="container" ng-controller="productController">
<nav class="navbar navbar-default" role="navigation">
?
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="bs-example-navbar-collapse-1">
<form class="navbar-form navbar-left" role="search">
<div class="form-group">
<input type="text" ng-model="search.id" class="form-control" placeholder="Search">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</nav>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th ng-click="changeOrder(‘id‘)" ng-class="{dropup:order === ‘‘}">
产品编号
<span ng-class="{orderColor:orderType === ‘id‘}" class="caret"></span>
</th>
<th ng-click="changeOrder(‘name‘)" ng-class="{dropup:order === ‘‘}">
产品名称
<span ng-class="{orderColor:orderType === ‘name‘}" class="caret"></span>
</th>
<th ng-click="changeOrder(‘price‘)" ng-class="{dropup:order === ‘‘}">
产品价钱
<span ng-class="{orderColor:orderType === ‘price‘}" class="caret"></span>
</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!--filter:{id:search} 【order + orderType= -id、id …… 】-->
<tr ng-repeat="product in productData | filter:search | orderBy:order + orderType">
<td>
{{product.id}}
</td>
<td>
{{product.name}}
</td>
<td>
{{product.price | currency : ‘(RMB)‘}}
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
angular.module(‘product‘, [])
.service(‘productData‘, function () {
return [
{
id:3333,
name:‘iphone‘,
price : 5400
},
{
id:885,
name:‘ipad‘,
price : 3420
},
{
id:980,
name:‘imac‘,
price : 15400
},
{
id:1212,
name:‘ipad air‘,
price : 2340
},
{
id:3424,
name:‘ipad mini‘,
price : 2200
}
];
})
.controller(‘productController‘, function ($scope,productData) {
$scope.productData = productData;
$scope.orderType = ‘id‘;
$scope.order = ‘-‘;
$scope.changeOrder = function(type){
$scope.orderType = type;
if($scope.order === ‘‘){
$scope.order = ‘-‘;
}else{
$scope.order = ‘‘;
}
}
});
?
?
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="user in data | filterAge">
{{user.name}}
{{user.age}}
{{user.city}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [], function ($filterProvider, $provide, $controllerProvider) {
$provide.service(‘Data‘, function () {
return [
{
name: ‘张三‘,
age: ‘20‘,
city: ‘上海‘
},
{
name: ‘李四‘,
age: ‘30‘,
city: ‘北京‘
}
];
});
//第一种实现自定义过滤器的方法。
$filterProvider.register(‘filterAge‘, function () {
return function (obj) {
var newObj = [];
angular.forEach(obj, function (o) {
if (o.age > 20) {
newObj.push(o);
}
});
return newObj;
}
});
$controllerProvider.register(‘firstController‘, function ($scope, Data) {
$scope.data = Data;
})
})
//第二种实现自定义过滤器的方法,是使用模块的快捷方法实现自定义过滤器module.filter
.filter(‘filterCity‘,function(){
return function(obj){
var newObj = [];
angular.forEach(obj, function (o) {
if (o.city === ‘上海‘) {
newObj.push(o);
}
});
return newObj;
}
})
?
?
?
?
?
angular controller
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="secondController">
</div>
<div ng-controller="otherController">
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [], [‘$filterProvider‘, ‘$provide‘, ‘$controllerProvider‘, function (a, b, c) {
console.log(a, b, c);
}])
.factory(‘CustomService‘, [‘$window‘, function (a) {
console.log(a);
}])
// 隐示的依赖注入,js压缩,替换function中的参数,可能会出问题,不推荐这种写法。
.controller(‘firstController‘, function ($scope, CustomService) {
console.log(CustomService);
})
// 显示的依赖注入; 推荐这种写法,写在[] 里面
.controller(‘secondController‘, [‘$scope‘, ‘$filter‘, function (a, b) {
console.log(b(‘json‘)([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]));
}]);
//这种写法不推荐
function otherController(a) {
console.log(a);
}
otherController.$inject = [‘$scope‘];
?
?
?
?
指令和HTML校验
?
校验器 | 格式 | 示例 |
none | namespace-name | ng-bind |
XML | namespace:name | ng:bind |
HTML5 | data-namespace-name | data-ng-bind |
XHTML | x-namespace-name | x-ng-bind |
?
ng-bind这个指令有四种写法
?
指令的执行过程
?
?
?
?
内置事件指令的好处是:在处理完事件之后,帮你去自动的去实现脏检查()
?
?

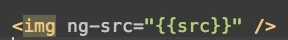
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.red{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<p>{{1+1}}</p>
<p ng-bind="1+1">2</p>
<p ng-bind-template="{{1+1}}"></p>
<!-- $scope.cityArr = [‘上海‘,‘北京‘,‘杭州‘] -->
<ul ng-class="{red:status}" ng-init="cityArr = [‘上海‘,‘北京‘,‘杭州‘]">
<li ng-class-even="‘偶数‘" ng-class-odd="‘奇数‘" ng-repeat="city in cityArr" >
<span>
index:{{$index}}
</span>
<span>
first:{{$first}}
</span>
<span>
middle:{{$middle}}
</span>
<span>
last :{{$last}}
</span>
<span>
{{city}}
</span>
</li>
</ul>
<div ng-include="‘other.html‘">
</div>
<div ng-include src="‘other.html‘">
</div>
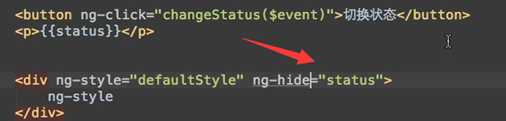
<button ng-click="changeStatus($event)">点击切换</button>
<p>{{status}}</p>
<div ng-style="{color:‘red‘}" ng-hide="status">
你好!!!
</div>
<div ng-style="{color:‘red‘}" ng-show="status">
你好!!!
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.controller(‘firstController‘, function ($scope) {
$scope.status = false;
?
$scope.changeStatus = function (event) {
// 通过element转换成 jquery对象;【angularJs中提供了一些简单的jquery方法】
angular.element(event.target).html(‘切换状态为:‘ + $scope.status);
$scope.status = !$scope.status;
}
$scope.defaultStyle = {
color: ‘red‘,
‘margin-top‘: ‘50px‘
};
$scope.src = ‘http://www.angularjs.org/img/AngularJS-large.png‘;
})
?
?
?
?
?
?
指令的定义
?
?
指令的名字
?
?
指令定义选项
?
?
restrict
?
字母 | 风格 | 示例 |
E | 元素【可以当做标签来使用】 | <my-dir></my-dir> |
C | 样式类 | <span class="my-dir: exp;"></span> |
A | 属性 | <span my-dir="exp"></span> |
M | 注释 | <!-- directive: my-dir exp --> |
?
?
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<custom-tags>1212</custom-tags>
<div class="custom-tags">
</div>
<div custom-tags>
</div>
<!-- directive:custom-tags -->
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [], [‘$compileProvider‘,function ($compileProvider) {
$compileProvider.directive(‘customTags‘,function(){
return {
restrict:‘ECAM‘,
template:‘<div>custom-tags-html</div>‘,
replace:true,
compile:function(){
console.log(1);//打印四次
}
}
});
}])
//.directive(‘‘)
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<script type="text/ng-template" id="customTags2">
<div>
hello {{name}}
</div>
</script>
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<custom-tags></custom-tags>
<custom-tags2></custom-tags2>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.directive(‘customTags‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
templateUrl: ‘tmp/other.html‘,//【引用其他页面,页面内容要用标签包含,不能事纯文本】
replace: true
}
})
.directive(‘customTags2‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
templateUrl: ‘customTags2‘,
replace: true
}
})
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) {
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
}]);
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<custom-tags>原始数据</custom-tags>
<div custom-tags2 custom-tags3>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.directive(‘customTags‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
template:‘<div>新数据 <span ng-transclude></span></div>‘,
replace: true,
transclude:true
}
})
.directive(‘customTags2‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
template:‘<div>2</div>‘,
replace: true,
priority:-1
}
})
.directive(‘customTags3‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
template:‘<div>3</div>‘,
replace: true,
priority: 0,
// 小于0的 directive 都不会执行
terminal:true
}
})
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) {
$scope.name = ‘张三‘;
}]);
?
?
?
为什么编译的过程要分成compile和link?
?
?
compile和link的使用时机
?
?
compile
?
?
link
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<!--
1. div 转换为dom结构
2. 默认的优先级为0,哪个先定义哪个先使用
-->
<div ng-repeat="user in users" custom-tags="" custom-tags2>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
var i = 0;
var myApp = angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.directive(‘customTags‘,function(){
return {
restrict : ‘ECAM‘,
template : ‘<div>{{user.name}}</div>‘,
replace : true,
//tElement 当前元素的 element,当前元素的jquery对象
//tAttrs 当前元素的一些属性
compile:function(tElement,tAttrs,transclude){//【有了compile之后,定义link就没有用了,因为,compile中也包含了link】
tElement.append(angular.element(‘<div>{{user.name}}{{user.count}}</div>‘));
// 编译阶段...
console.log(‘customTags compile 编译阶段...‘);
return {
// 表示在编译阶段之后,指令连接到子元素之前运行
pre:function preLink(scope,iElement,iAttrs,controller){
console.log(‘customTags preLink..‘)
},
// 表示在所有子元素指令都连接之后才运行
post:function postLink(scope,iElement,iAttrs,controller){
?
iElement.on(‘click‘,function(){
scope.$apply(function(){//【apply方法触发脏检查】
scope.user.name = ‘click after‘;
scope.user.count = ++i;
// 进行一次 脏检查
});
})
?
console.log(‘customTags all child directive link..‘)
}
}
// 可以直接返回 postLink
// return postLink function(){
// console.log(‘compile return fun‘);
//}
},
// 此link表示的就是 postLink【因为在 compile中已经定义了link,故而,这里没有必要再定义】
link:function(){
// iElement.on(‘click‘,function(){
// scope.$apply(function(){
// scope.user.name = ‘click after‘;
// scope.user.count = ++i;
// // 进行一次 脏检查
// });
// })
}
}
})
?
.directive(‘customTags2‘,function(){
return {
restrict : ‘ECAM‘,
replace : true,
compile:function(){
// 编译阶段...
console.log(‘customTags2 compile 编译阶段...‘);
?
return {
// 表示在编译阶段之后,指令连接到子元素之前运行
pre:function preLink(){
console.log(‘customTags2 preLink..‘)
},
// 表示在所有子元素指令都连接之后才运行
post:function postLink(){
console.log(‘customTags2 all child directive link..‘)
}
}
?
}
}
})
.directive(‘customTags3‘,function(){ // return postLink;
return function(){
}
})
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) {
$scope.users = [
{
id:10,
name:‘张三‘
},
{
id:20,
name:‘李四‘
}
];
}]);
?
?
?
?
controller && controllerAs && require
?
选项 | 用法 |
directiveName | 通过驼峰法的命名指定了控制器应该带有哪一条指令,默认会从同一个元素上的指令 |
^directiveName | 在父级查找指令 |
?directiveName | 表示指令是可选的,如果找不到,不需要抛出异常 |
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<div book-list>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.directive(‘bookList‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
controller: function ($scope) {
$scope.books = [
{
name: ‘php‘
},
{
name: ‘javascript‘
},
{
name: ‘java‘
}
];
$scope.addBook = function(){
}
this.addBook = function(){
// ...
}
},
controllerAs:‘bookListController‘,//【相当于给上面的controller起一个别名,在link函数中有引用】
template: ‘<ul><li ng-repeat="book in books">{{book.name}}</li></ul>‘,
replace:true,
link:function(scope,iEelement,iAttrs,bookListController){
iEelement.on(‘click‘,bookListController.addBook)
}
}
})//【这里不要给分号,给了后面就不能.controller了,就不能链式操作了】
//不写全,代码压缩会报错
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) {
// console.log($scope);
}]);
?
?
?
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<div book-list>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.directive(‘bookList‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
controller: function ($scope) {
$scope.books = [
{
name: ‘php‘
},
{
name: ‘javascript‘
},
{
name: ‘java‘
}
];
this.addBook = function(){
$scope.$apply(function(){
$scope.books.push({
name:‘Angularjs‘
})
});
}
},
controllerAs:‘bookListController‘,
template: ‘<div><ul><li ng-repeat="book in books">{{book.name}}</li></ul><book-add></book-add></div>‘,
replace:true
}
})
.directive(‘bookAdd‘,function(){
return {
restrict:‘ECAM‘,
require:‘^bookList‘,//【^directiveName 带有^ 符号,表示在父级查找指令】
template:‘<button type="button">添加</button>‘,
replace:true,
link:function(scope,iElement,iAttrs,bookListController){
iElement.on(‘click‘,bookListController.addBook);
}
}
})
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) { // console.log($scope);
}]);
?
?
?
?
【写的多了自然而然就理解了, angularjs 难点在于指令之间的架构】
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
{{
books
}}
<div book-list books="books" parent-books="books" parent-title="{{title}}">
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
.directive(‘bookList‘, function () {
return {
restrict: ‘ECAM‘,
controller: function ($scope) {
// &books
// $scope.books = $scope.a();
//================================================================
// =books;
// $scope.books = $scope.b;
// $scope.b.push({name:‘nodejs‘});
//================================================================
console.log($scope.c);
},
// scope:true, 创建一个有继承链的独立作用域
/ /scope:false, 不创建作用域,继承父元素的作用域
?
// 当为对象的时候也会创建一个独立的作用域
scope:{
// & 将父元素 books 封装成一个a函数
// a:‘&books‘
//================================================================
// = 双向绑定 b = parentBooks属性对应的父作用域的表达式
// b:‘=parentBooks‘
//================================================================
// @ 只能引用父元素的简单类型的属性
c:‘@parentTitle‘
},
controllerAs:‘bookListController‘,
template: ‘<div><ul><li ng-repeat="book in books">{{book.name}}</li></ul></div>‘,
replace:true
}
})
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) {
console.log($scope);
$scope.books = [
{
name: ‘php‘
},
{
name: ‘javascript‘
},
{
name: ‘java‘
}
];
$scope.title = ‘张三‘;
}]);
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../vendor/bootstrap3/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div class="container">
<div ng-controller="firstController">
<kittencup-group>
<kittencup-collapse ng-repeat="collapse in data" heading="{{collapse.title}}">
{{collapse.content}}
</kittencup-collapse>
</kittencup-group>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
// 数据
.factory(‘Data‘, function () {
return [
{
title: ‘no1‘,
content: ‘no1-content‘
},
{
title: ‘no2‘,
content: ‘no2-content‘
},
{
title: ‘no3‘,
content: ‘no3-content‘
}
];
})
// 控制器
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘,‘Data‘,function ($scope,Data) {
$scope.data = Data;
}])
?
.directive(‘kittencupGroup‘,function(){
return {
restrict:‘E‘,
replace:true,//【该标签不符合w3c 规范,肯定要替换掉它】
template:‘<div class="panel-group" ng-transclude></div>‘,
transclude:true,
controllerAs:‘kittencupGroupContrller‘,
controller:function(){
this.groups = [];
this.closeOtherCollapse = function(nowScope){
angular.forEach(this.groups,function(scope){
if(scope !== nowScope){
scope.isOpen = false;
}
})
}
}
}
})
?
.directive(‘kittencupCollapse‘,function(){
return {
restrict:‘E‘,
replace:true,
require:‘^kittencupGroup‘,
templateUrl:‘app/tmp/kittencupCollapse.html‘,//【因为,模板代码比较长,故而,用另外一个页面】
scope:{
heading:‘@‘
},
link:function(scope,element,attrs,kittencupGroupContrller){
scope.isOpen = false;
scope.changeOpen = function(){
scope.isOpen = !scope.isOpen;
kittencupGroupContrller.closeOtherCollapse(scope);
}
kittencupGroupContrller.groups.push(scope);
},
transclude:true
}
})
?
?
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-heading" ng-click="changeOpen()">
<h4 class="panel-title">
<a href="#">
{{heading}}
</a>
</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-collapse" ng-class="{collapse:!isOpen}">
<div class="panel-body" ng-transclude>
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
?
?
?
?
?
value
?
?
run
?
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘,[],[‘$provide‘,function($provide){
console.log(‘config‘);
// $provide.factory
// $provide.service
// $provide.constant
// $provide.value;//【provide中的方法 都会有快捷方法】
?
}])
?
.config(function(APIKEY){
console.log(APIKEY);
console.log(‘config‘);
})
?
// 在config之后controller等其他服务之前,执行此方法。。
.run(function(){
console.log(‘run‘);
})
// 它只是可以注入任何方法
.constant(‘APIKEY‘,‘xxxx‘)
// 只能注入controller...service factory。【在config中无法注入该方法】
.value(‘vension‘,‘1.0.0‘)
?
.controller(‘firstController‘,[‘APIKEY‘,‘vension‘,function(APIKEY,vension){
console.log(APIKEY);
console.log(vension);
console.log(‘controller‘);
}]);
?
?
?
?
input type 扩展
?
?
input 属性
ng-model="data.username" 数据绑定在data.username上
ng-required="true" 值为true 表示必填项
?
?
CSS样式
?
?
Form控制变量
当表单的字段无效,该字段为true
Form名字. 表单名字 获取表单的错误信息
?
?
属性 | 描述 |
$dirty | 表单有填写记录 |
$valid | 字段内容合法的 |
$invalid | 字段内容是非法的 |
$pristine | 表单没有填写记录 |
?
?
?
From 方法
?
?
ng-model
?
?
ngModel 里的属性
?
?
XHR和服务器端的通信
?
$http
?
?
$http短名方法
?
?
$http 配置对象
?
?
responseType
?
?
?
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../vendor/bootstrap3/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp" style="margin-top: 100px;">
<form name="myForm" action="kittencup.php" ng-controller="firstController" class="container form-horizontal">
<div class="form-group" ng-class="{‘has-error‘:myForm.username.$dirty && myForm.username.$invalid}">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">用户名</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" autocomplete="off" name="username" ng-pattern="/^[a-zA-Z]{1}/" ng-required="true" ng-minlength="5" ng-maxlength="10" ng-model="data.username" class="form-control" placeholder="用户名">
<div ng-show="myForm.username.$dirty && myForm.username.$error.maxlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
用户名长度不能超过10位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.username.$dirty && myForm.username.$error.minlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
用户名长度不能小于5位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.username.$dirty && myForm.username.$error.pattern" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
用户名必须已英文字母开始
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group" ng-class="{‘has-error‘:myForm.password.$dirty && myForm.password.$invalid}">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">密 码</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" autocomplete="off" name="password" ng-required="true" ng-minlength="5" ng-maxlength="10" ng-model="data.password" class="form-control" placeholder="密码">
<div ng-show="myForm.password.$dirty && myForm.password.$error.maxlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
密码长度不能超过10位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.password.$dirty && myForm.password.$error.minlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
密码长度不能小于5位
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group" ng-class="{‘has-error‘:myForm.passwordConfirm.$dirty && myForm.passwordConfirm.$invalid}">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">确认密码</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="password" autocomplete="off" name="passwordConfirm" ng-required="true" ng-model="data.passwordConfirm" class="form-control" placeholder="确认密码">
<div ng-show="myForm.password.$dirty && myForm.passwordConfirm.$dirty && data.password !== data.passwordConfirm" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
密码和确认密码不一致
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group" ng-class="{‘has-error‘:myForm.email.$dirty && myForm.email.$invalid}">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">邮箱</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" autocomplete="off" name="email" ng-required="true" ng-minlength="5" ng-maxlength="30" ng-model="data.email" class="form-control" placeholder="邮箱">
<div ng-show="myForm.email.$dirty && myForm.email.$error.maxlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
邮箱长度不能超过30位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.email.$dirty && myForm.email.$error.minlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
邮箱长度不能小于5位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.email.$dirty && myForm.email.$error.email" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
邮箱格式不正确
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group" ng-class="{‘has-error‘:myForm.blog.$dirty && myForm.blog.$invalid}">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">博客网址</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="url" autocomplete="off" name="blog" ng-required="true" ng-minlength="5" ng-maxlength="30" ng-model="data.blog" class="form-control" placeholder="博客网址">
<div ng-show="myForm.blog.$dirty && myForm.blog.$error.maxlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
网址长度不能超过30位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.blog.$dirty && myForm.blog.$error.minlength" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
网址长度不能小于5位
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.blog.$dirty && myForm.blog.$error.url" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
网址格式不正确
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group" ng-class="{‘has-error‘:myForm.age.$dirty && myForm.age.$invalid}">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">年龄</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="number" autocomplete="off" name="age" min="10" max="99" ng-required="true" ng-model="data.age" class="form-control" placeholder="年龄">
<div ng-show="myForm.age.$dirty && myForm.age.$error.max" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
年龄不能超过99岁
</div>
<div ng-show="myForm.age.$dirty && myForm.age.$error.min" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
年龄不能小于10岁
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">性别</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<label class="radio-inline">
<input type="radio" ng-required="true" name="sex" ng-model="data.sex" value="1" /> 男
</label>
<label class="radio-inline">
<input type="radio" ng-required="true" name="sex" ng-model="data.sex" value="0" /> 女
</label>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">爱好</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<label class="checkbox-inline" ng-repeat="hobby in hobbies">
<input type="checkbox" ng-model="hobby.checked" name="hobby[]" ng-checked="data.hobbies === undefined ? false : data.hobbies.indexOf(hobby.id) !== -1" ng-click="toggleHobbySelection(hobby.id)"/> {{hobby.name}}
</label>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">出生地</label>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<select class="form-control" ng-change="data.area = false" ng-model="data.province" ng-options="x.id as x.name for x in cities | cityFilter:0"></select>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<select class="form-control" ng-show="data.province" ng-model="data.area" ng-options="x.id as x.name for x in cities | cityFilter:data.province"></select>
</div>
<div class="col-sm-3">
<select class="form-control" ng-required="true" ng-show="data.province && data.area" ng-model="data.city" ng-options="x.id as x.name for x in cities | cityFilter:data.area"></select>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">只能输入偶数</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" name="even" class="form-group" placeholder="偶数" ng-model="data.even" even>
<div ng-show="myForm.even.$error.even" class="alert alert-danger help-block">
数字必须是偶数
</div>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group">
<label class="col-sm-2 control-label">个人介绍</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<custom-text-area ng-model="data.introduct">aaa</custom-text-area>
<custom-text-area ng-model="data.introduct"></custom-text-area>
</div>
</div>
?
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default" ng-disabled="myForm.$invalid || data.hobbies === undefined || data.hobbies.length === 0">注册</button>
<button type="reset" class="btn btn-default" ng-click="reset()">重置</button>
</div>
?
</div>
</form>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../../vendor/angular/angularjs.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
?
?
?
angular.module(‘myApp‘, [])
?
.filter(‘cityFilter‘, function () {
return function (data, parent) {
var filterData = [];
angular.forEach(data, function (obj) {
if (obj.parent === parent) {
filterData.push(obj);
}
})
return filterData;
}
})
.directive(‘even‘,function(){
return {
require : ‘ngModel‘,
link:function(scope,elm,attrs,ngModelController){
ngModelController.$parsers.push(function(viewValue){
if(viewValue % 2 === 0){
ngModelController.$setValidity(‘even‘,true);
}else{
ngModelController.$setValidity(‘even‘,false);
}
return viewValue;
});
?
// ngModelController.$formatters.push(function(modelValue){
// return modelValue + ‘kittencup‘;
// })
}
};
})
?
.directive(‘customTextArea‘,function(){
return {
restrict:‘E‘,
template:‘<div contenteditable="true"></div>‘,
replace:true,
require : ‘ngModel‘,
link:function(scope,elm,attrs,ngModelController){
?
?
// view->model
elm.on(‘keyup‘,function(){
scope.$apply(function(){
ngModelController.$setViewValue(elm.html());
});
})
?
ngModelController.$render = function(){
elm.html(ngModelController.$viewValue);
}
?
}
};
})
?
?
.controller(‘firstController‘, [‘$scope‘, function ($scope) {
?
var that = this;
?
$scope.hobbies = [
{
id: 1,
name: ‘玩游戏‘
},
{
id: 2,
name: ‘写代码‘
},
{
id: 3,
name: ‘睡觉‘
},
];
?
$scope.cities = [
{
name: ‘上海‘,
parent: 0,
id: 1
},
{
name: ‘上海市‘,
parent: 1,
id: 2
},
{
name: ‘徐汇区‘,
parent: 2,
id: 8
},
{
name: ‘长宁区‘,
parent: 2,
id: 3
},
{
name: ‘北京‘,
parent: 0,
id: 4
},
{
name: ‘北京市‘,
parent: 4,
id: 5
},
{
name: ‘东城区‘,
parent: 5,
id: 6
},
{
name: ‘丰台区‘,
parent: 5,
id: 7
},
{
name: ‘浙江‘,
parent: 0,
id: 9
},
{
name: ‘杭州‘,
parent: 9,
id: 100
},
{
name: ‘宁波‘,
parent: 9,
id: 11
},
{
name: ‘西湖区‘,
parent: 100,
id: 12
},
{
name: ‘北仑区?‘,
parent: 11,
id: 13
}
];
?
?
$scope.data = {
hobbies: [1, 2],
city: 3
};
?
?
// 先保留一份默认值
$scope.origData = angular.copy($scope.data);
?
$scope.reset = function(){
?
$scope.data = angular.copy($scope.origData);
that.initCity();
$scope.myForm.$setPristine();
}
?
// 让城市关联使用
this.findCityId = function (parent) {
var parentId;
angular.forEach($scope.cities, function (city) {
if (city.id === parent) {
parentId = city.parent;
return;
}
})
?
return parentId;
}
?
this.initCity = function(){
if ($scope.data.city !== undefined) {
$scope.data.area = this.findCityId($scope.data.city);
$scope.data.province = this.findCityId($scope.data.area);
}
}
?
// 第一次打开页面 需要初始化一下
this.initCity.call(this);
?
$scope.toggleHobbySelection = function (id) {
?
var index = -1;
if ($scope.data.hobbies === undefined) {
$scope.data.hobbies = [];
} else {
index = $scope.data.hobbies.indexOf(id);
}
?
if (index === -1) {
$scope.data.hobbies.push(id);
} else {
$scope.data.hobbies.splice(index, 1);
}
?
}
}]);
?
?
?
?
AngularUI库提供的最有用的库之一便是ui-router。它是一个路由框架,允许你通过状态机
组织接口,而不是简单的URL路由。
?
?
你还要确保在视图中链接这个库:
<scripttype="text/javascript" src="app/bower_components/angular-ui-router/release/angular-ui-router.js"></script>
同时还需要将ui.router作为依赖注入到你的应用中:
angular.module(‘myApp‘, [‘ui.router‘]);
现在,不同于内置的ngRoute服务,由于ui-router基于状态工作,而不是简单的url,因此
你可以将它嵌套在视图中。
在处理ngRoute服务时我们不再使用ng-view,而改为使用ui-view指令。
在ui-router内处理路由和状态时,我们主要关心的是应用程序处在哪个状态以及Web应用
当前处在哪个路由位置。
<div ng-controller="DemoController">
<div ui-view></div>
</div>
和ngRoute一样,定义在任意给定状态内的模板都处在<div ui-view></div>元素内。此外,
每个模板都可以包含自己的ui-view。 这事实上就允许你在路由中嵌套视图。
为了定义路由,你可以使用.config方法,和常见的方式一样,但不是将路由设置在
$routeProvider上,而是将状态设置在$stateProvider上。
.config(function($stateProvider,$urlRouterProvider) {
$stateProvider
.state(‘start‘, {
url: ‘/start‘,
templateUrl: ‘partials/start.html‘
})
});
这一步给状态配置对象分配了一个名为start的状态。这个状态配置对象,或者说这个
stateConfig
stateProvider
.state(‘inbox‘, {
url: ‘/inbox‘,
template: ‘<h1>Welcome to your inbox</h1>‘
});
当用户导航到/inbox时,应用会转换到inbox状态,然后使用模板内容(<h1>Welcome to your
inbox</h1>)填充主要的ui-view指令。
?
?
//当用户导航到url:/main时,使用templateUrl填充ui-view指令。
.state(‘main‘, {
url: ‘/main‘,
controller: "HeaderCtrl",
templateUrl: ‘views/main.html‘
})
和ngRoute一样,你可以给已经注册好的控制器关联一个URL(使用字符串),也可以创建一
个控制器函数作为状态控制器。
如果没有定义模板(使用上述方式之一),就不会创建这个控制器。
?
?
URL可以接受一系列不同的选项,它还可以在url中设置基本的参数,就像在ngRoute中一样:
$stateProvider
.state(‘inbox‘, {
url: ‘/inbox/:inboxId‘,
template: ‘<h1>Welcome to your inbox</h1>‘,
controller: function($scope, $stateParams) {
$scope.inboxId = $stateParams.inboxId;
}
});
?
AngularJs 权威教程 第25章
标签:form 视图 relink namespace 加载 软件 erp ted 实例化
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/weiqinshian/p/6719416.html