标签:类集 读写 receive 过程 port input back round 作用
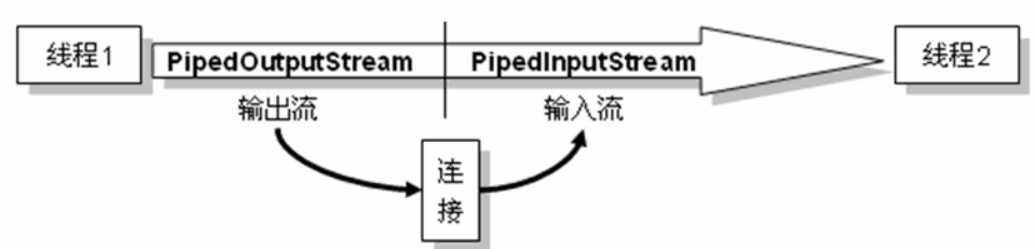
管道流的主要作用是可以进行两个线程间的通讯,分为管道输入流(PipeOutputStream)和管道输出流(PipeInputStream)。
如果要想进行管道输出,则必须把输出流连在输入流之上,在PipeOutputStream上有如下方法用于连接管道。
void connect(PipedInputStream snk) 将此管道输出流连接到接收者。
要想连接输入和输出,必须使用此方法、
PipeOutputStream输出方法:
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len)
将 len 字节从初始偏移量为 off 的指定 byte 数组写入该管道输出流。
PipeInputStream输入方法:读取文件的方法
将连接的PipeOutputStream对象实例的输入流的数据,通过read方法,把内容读取到数组中。
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len)
将最多 len 个数据字节从此管道输入流读入 byte 数组。
实例代码:
package 类集; import java.io.* ; class Send implements Runnable{ // 线程类 private PipedOutputStream pos = null ; // 管道输出流 public Send(){ this.pos = new PipedOutputStream() ; // 实例化输出流 } public void run(){ String str = "Hello World!!!" ; // 要输出的内容 try{ this.pos.write(str.getBytes()) ; }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } try{ this.pos.close() ; }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } } public PipedOutputStream getPos(){ // 得到此线程的管道输出流 return this.pos ; } }; class Receive implements Runnable{ private PipedInputStream pis = null ; // 管道输入流 public Receive(){ this.pis = new PipedInputStream() ; // 实例化输入流 } public void run(){ byte b[] = new byte[1024] ; // 接收内容 int len = 0 ; try{ len = this.pis.read(b) ; // 读取内容 }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } try{ this.pis.close() ; // 关闭 }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } System.out.println("接收的内容为:" + new String(b,0,len)) ;//注意,这里是把读入的数组的数据输出,而不是PipeInputStream实例对象输出, } public PipedInputStream getPis(){ return this.pis ; } }; public class PipedDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ Send s = new Send() ; Receive r = new Receive() ; try{ s.getPos().connect(r.getPis()) ; // 连接管道 }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } new Thread(s).start() ; // 启动线程 new Thread(r).start() ; // 启动线程 } };
PipeInputStream读取文件后,读取的数据都存在了PipeInputStream对象的实例中,且类型为byte。
总结:
开发中很少直接开发多线程程序,本道程序,只是让读者加深读写的操作过程,了解,线程间如何通讯。
标签:类集 读写 receive 过程 port input back round 作用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/alsf/p/6785592.html