标签:jdbc threadlocal jdbcutil 依赖注入 深入浅出
JDBC6.0最终版。
数据访问层Dao
业务逻辑层service
我们在Dao层中封装了对表的常用操作,增删改查。
我们在Util里封装了JDBCUtil工具类解决冗余问题。
现在我们有一个银行转账问题:
1.根据卡号,密码,先查询
2.转出账户再余额足够的情况下,减去转出资金。
3转入账户添加转入资金。
对于2,3步骤我们因当把他们看作是一个事务,事务的原子性,一致性,隔离性。要求
要么一起成功,要么一起不成功。当然从现实考虑,也确实应当这样,如果在2,3步骤之间失败了
就回退。
这整个转账逻辑,我们可以称之为业务。所以针对软件的三层结构。我们把这部分称为-----业务层(service)
在service层调用Dao层的方法。
而在service层里的连接对象和Dao层里的连接对象不是同一个对象,这就会造成混乱,打破事务的一致性。
从而导致,转出钱减去了,转入账户没加钱。
Service方法中的事务控制失败。
原因:service控制事务时过的conn和DAO访问数据库使用的conn时两个不同对象
解决:
保证service和Dao使用同一个conn对象
1:通过参数传递。
2:每个线程对象有一个Map属性,可以存储数据
在service获得conn,将conn放入当前Thread对象,在DAO访问数据库时取时,从Thread取出conn
ThreadLocal简介及使用:
操作当前线程对象中的一小块空间。
1创建ThreadLocal对象 ThreadLocal<Connection> tdl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
2tdl.set(conn);将conn添加到当前线程。
3tdl.get();获得当前线程中的数据
4tdl.remove()移除当前线程里的数据
话不多说我们来看代码有三个文件 JDBC_Util3.java JDBC_Dao3.java JDBC_Service.java
JDBC_Util3.java
public class JDBC_Util3 {
private static final Properties prop = new Properties();
private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> tdl = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
static{
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = JDBC_Util3.class.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
prop.load(is);
String driverName = prop.getProperty("driverName");
Class.forName(driverName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//返回链接
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
Connection conn = null;
conn = tdl.get();//获得当前线程连接
if(conn == null){
//说明当前线程没有conn
String user = prop.getProperty("user");
String password = prop.getProperty("password");
String url = prop.getProperty("url");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//将当 conn存入线程
tdl.set(conn);
}
return conn;
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
public static void release(ResultSet rs,Statement stm,Connection conn){
try {
if(rs!=null){rs.close();}
if(stm!=null){stm.close();}
if(conn!=null){
conn.close();
tdl.remove();//移除当前线程对象中的conn
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JDBC_Dao3.java
public class JDBC_Dao3 {
/ /更新账户
public void upDateAccount(Account toAcc) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
try {
conn = JDBC_Util3.getConnection();
String sql = "update account set card_id=?,"
+ "password=?,balance=?,phone=? where card_id=?";
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstm.setString(1, toAcc.getCardId());
pstm.setString(2, toAcc.getPassword());
pstm.setDouble(3, toAcc.getBalance());
pstm.setString(4, toAcc.getPhone());
pstm.setString(5, toAcc.getCardId());
int i = pstm.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBC_Util.release(null, pstm, null);
}
}
// 查询账户
public Account queryAccount(Integer toCardId) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Account acc = null;
try {
conn = JDBC_Util3.getConnection();
stm = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from account where card_id = "
+ toCardId;
System.out.println(sql);
rs = stm.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
acc = new Account();
acc.setCardId(rs.getString("card_id"));
acc.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
acc.setBalance(rs.getDouble("balance"));
acc.setPhone(rs.getString("phone"));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
JDBC_Util.release(rs, stm, null);
}
return acc;
}
}
JDBC_Service.java
public class JDBC_Service {
public void transfer(Integer fromCardId,String password,
Integer toCardId,Double money){
Connection conn = null;
try{
conn = JDBC_Util2.getConnection();
//事务自动提交关闭
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
JDBC_Dao3 dao = new JDBC_Dao3();
//验证卡号是否存在
Account fromAcc = dao.queryAccount(fromCardId);
if(fromAcc == null){
throw new RuntimeException("卡号不存在");
}
//验证密码是否正确
if(null==password||!password.equals(fromAcc.getPassword())){
throw new RuntimeException("密码错误");
}
//验证余额
if(fromAcc.getBalance()<money){
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
//转出账户更新
fromAcc.setBalance(fromAcc.getBalance()-money);
dao.upDateAccount(fromAcc);
Account toAcc = dao.queryAccount(toCardId);
//验证到账卡号
if(toAcc ==null){
throw new RuntimeException("到账卡号不存在");
}
//转入账户更新
toAcc.setBalance(toAcc.getBalance()+money);
dao.upDateAccount(toAcc);
//提交事务
conn.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}finally{
JDBC_Util.release(null, null, conn);
}
}
}
最后main函数测试
JDBC_Service sv = new JDBC_Service();
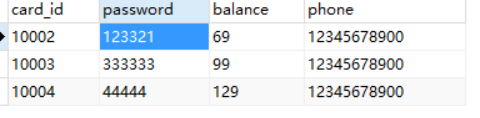
sv.transfer(10002, "123321", 10004, 30.00);
转账成功
10002 -30 10004 +30
=========================华丽丽的终结===========================
总结:虽然由于快节奏的开发,编程速度的追求,越爱越多的MVC框架出现,比如持久层的hibernate,
mybatis等等,他们对Dao层的支持都很强大,既 快速,又简便。但是他们的底层同样是使用了JDBC,
为了追求高速简便,我们可以不使用JDBC,但一定要了解JDBC。了解JDBC也有助于学习其他持久层框架。
以上就是我对JDBC全部心得。
限于文章篇幅原因,这里仅仅介绍冰山一角。由于笔者的水平有限,编写时间也很仓促,
文中难免会出现一些错误或者不准确的地方,不妥之处恳请读者批评指正。
本文出自 “心有猛虎,细嗅蔷薇” 博客,转载请与作者联系!
标签:jdbc threadlocal jdbcutil 依赖注入 深入浅出
原文地址:http://zhangdongxu.blog.51cto.com/12029530/1921710