标签:fileread 种类 amp out little 对象 编码 dwr 清空
Java输入输出流总结
一、介绍
流是数据源或数据目标的输入或输出设备的抽象表示。支持流输入和输出的主要包是java.io,但是也有其他的包,比如java.nio.file。java.io包支持两种类型的流——包含二进制数据的字节流和包含字符数据的字符流。
当写数据到字节流中时,数据会以字节序列的形式写到流中,与它们在内存中的形式完全一样,在这个过程中不会发生数据转换。即java.io包中的InputStream和OutputStream的派生类,通常用来读取二进制数据,如图像和声音。
将字符串作为字符数据读入流时,默认Unicode字符会首先被自动转化成主机的本地字符表示,之后再写到流中。包括Reader和Writer类。字符流用于存储和提取文本,也可以使用字符流读取由非java程序创建的文本文件。
但是,Read和Write并不是取代InputStream和OutputStream,有时,你还必须同时使用"基于byte的类"和"基于字符的类"。为此,它还提供了两个"适配器(adapter)"类。InputStreamReader负责将InputStream转化成Reader,而OutputStreamWriter则将OutputStream转化成Writer。
二、字节流
包java.io中的两个类InputStream和OutputStream,java基于他们对流I/O操作提供支持。InputStream和OutputStream都是抽象类,无法创建实例,但是可以用于派生具有更加实际输入输出功能的类。这两个类都实现了Closeable接口,而Closeable接口只声明了方法close()——关闭流并且释放流对象保存的所有资源。
1、InputStream类
InputStream包含三个read()方法用于从流中读取数据:
public abstract int read(); 抽象方法,以int类型返回流中可用的下一个字节。读取到末尾,返回-1。
public int read(byte[] array); 该方法从流中读取字节填充到数组array的连续元素中,最大读取长度为array.length个字节。读取到末尾,返回-1。
public int read(byte[] array, int offset, int length); 该方法从流中读取length长度的字节填充到数组array中,将array[offset]作为存放起始位置。读取到末尾,返回-1。
public int available(); 返回输入流中可以读取的字节数。注意:若输入阻塞,当前线程将被挂起,如果InputStream对象调用这个方法的话,它只会返回0,这个方法必须由继承InputStream类的子类对象调用才有用。
public long skip(long n); 忽略输入流中的n个字节,返回值是实际忽略的字节数, 跳过一些字节再读取。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
InputStream类的派生类结构:

2、OutputStream类
OutputStream提供了3个write()方法来输出数据,和InputStream相对应:
public abstract void write(int b); 先将int转换成byte类型,把低字节写入到输出流中。
public void write(byte[] array); 将数组array中的字节写到输出流。
public void write(byte[] array, int offset, int length); 将数组array中从array[offset]开始的length个字节写到输出流。
public void flush(); 将数据缓冲区中数据全部输出,并清空缓冲区。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
OutputStream类的派生类结构:

3、FileInputStream类
FileInputStream类是InputStream类的子类,用来处理以文件作为数据输入源的数据流。
使用方法:
方式1:
File fin=new File("d:/abc.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(fin);
方式2:
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream("d: /abc.txt");
方式3:
构造函数将 FileDescriptor()对象作为其参数。
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor();
FileInputStream f2=new FileInputStream(fd);
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
4、FileOutputStream类
FileOutputStream类用来处理以文件作为数据输出目的数据流;一个表示文件名的字符串,也可以是File或FileDescriptor对象。
创建一个文件流对象方法:
方式1:
File f=new File("d:/abc.txt");
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream (f);
方式2:
FileOutputStream out=new
FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt");
方式3:构造函数将 FileDescriptor()对象作为其参数。
FileDescriptor() fd=new FileDescriptor();
FileOutputStream f2=new FileOutputStream(fd);
方式4:构造函数将文件名作为其第一参数,将布尔值作为第二参数。
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("d:/abc.txt",true);
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
使用过程:
(1)生成文件流对象(对文件读操作时应该为FileInputStream类,而文件写应该为FileOutputStream类);
(2)调用FileInputStream或FileOutputStream类中的功能函数如read()、write(int b)等)读写文件内容;
(3)关闭文件close()。
注意:
(1)文件中写数据时,若文件已经存在,则覆盖存在的文件;
(2)的读/写操作结束时,应调用close方法关闭流。
例子:利用FileInputStream读取一个文件,并存入缓存中,然后通过FileOutputStream写到一个新的文件
1 import java.io.*; 2 2 3 3 public class FileStreamDemo { 4 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 5 5 6 6 //创建两个文件,face.gif是已经存在文件,newFace.gif是新创建的文件 7 7 File inFile = new File("1.gif"); 8 8 File outFile = new File("new1.gif"); 9 9 10 10 //创建流文件读入与写出类 11 11 FileInputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(inFile); 12 12 FileOutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream(outFile); 13 13 14 14 //通过available方法取得流的最大字符数 15 15 byte[] b = new byte[inStream.available()]; 16 16 inStream.read(b); //读入流,保存在byte数组 17 17 outStream.write(b); //写出流,保存在文件newFace.gif中 18 18 19 19 inStream.close(); 20 20 outStream.close(); 21 21 } 22 22 }
5、File类
File类与InputStream / OutputStream类同属于一个包,它不允许访问文件内容。
File类主要用于命名文件、查询文件属性和处理文件目录。
6、从一个流构造另一个流
java的流类提供了结构化方法,如,底层流和高层过滤流。而高层流不是从输入设备读取,而是从其他流读取。同样高层输出流也不是写入输出设备,而是写入其他流。
使用"分层对象(layered objects)",为单个对象动态地,透明地添加功能的做法,被称为Decorator Pattern。Decorator模式要求所有包覆在原始对象之外的对象,都必须具有与之完全相同的接口。这使得decorator的用法变得非常的透明--无论对象是否被decorate过,传给它的消息总是相同的。这也是Java I/O类库要有"filter(过滤器)"类的原因:抽象的"filter"类是所有decorator的基类。Decorator模式常用于如下的情形:如果用继承来解决各种需求的话,类的数量会多到不切实际的地步。Java的I/O类库需要提供很多功能的组合,于是decorator模式就有了用武之地。
为InputStream和OutputStream定义decorator类接口的类,分别是FilterInputStream和FilterOutputStream。
FilterInputStream的种类:
DataInputStream:与DataOutputStream配合使用,这样你就能以一种"可携带的方式(portable fashion)"从流里读取primitives了(int,char,long等)
BufferedInputStream:用这个类来解决"每次要用数据的时候都要进行物理读取"的问题。意思是"用缓冲区"。
LineNumberInputStream:跟踪输入流的行号;有getLineNumber( )和setLineNumber(int)方法
PushbackInputStream:有一个"弹压单字节"的缓冲区(has a one byte push-back buffer),这样你就能把最后读到的那个字节再压回去了。
FilterOutputStream的种类:
DataOutputStream:与DataInputStream配合使用,这样你就可以用一种"可携带的方式(portable fashion)"往流里写primitive了(int, char, long,等)
PrintStream:负责生成带格式的输出(formatted output)。DataOutputStrem负责数据的存储,而PrintStream负责数据的显示。
BufferedOutputStream:用 这个类解决"每次往流里写数据,都要进行物理操作"的问题。也就是说"用缓冲区"。用flush( )清空缓冲区。
7、BufferedInputStream类
BufferedInputStream与BufferedOutputStream可以为InputStream、OutputStream类的对象增加缓冲区功能。构建BufferedInputStream实例时,需要给定一个InputStream类型的实例,实现BufferedInputStream时,实际上最后是实现InputStream实例。同样地,在构建BufferedOutputStream时,也需要给定一个OutputStream实例,实现BufferedOutputStream时,实际上最后是实现OutputStream实例。
BufferedInputStream的数据成员buf是一个位数组,默认为2048字节。当读取数据来源时,例如文件,BufferedInputStream会尽量将buf填满。当使用read()方法时,实际上是先读取buf中的数据,而不是直接对数据来源作读取。当buf中的数据不足时,BufferedInputStream才会再实现给定的InputStream对象的read()方法,从指定的装置中提取数据。
方式1:
File srcFile = new File(args[0]);
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
创建 BufferedInputStream 并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。创建一个内部缓冲区数组并将其存储在 buf 中。
方式2:
File srcFile = new File(args[0]);
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile),1024);
创建具有指定缓冲区大小的 BufferedInputStream,并保存其参数,即输入流 in,以便将来使用。创建一个长度为 size 的内部缓冲区数组并将其存储在 buf 中。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
8、BufferedOutputStream类
BufferedOutputStream的数据成员buf是一个位数组,默认为512字节。当使用write()方法写入数据时,实际上会先将数据写至buf中,当buf已满时才会实现给定的OutputStream对象的write()方法,将buf数据写至目的地,而不是每次都对目的地作写入的动作。
方式1:
File desFile = new File(args[1]);
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(desFile));
创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将数据写入指定的基础输出流。
方式2:
File desFile = new File(args[1]);
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(desFile),1024);
创建一个新的缓冲输出流,以将具有指定缓冲区大小的数据写入指定的基础输出流。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
例子:使用BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream复制BuffferedStreamDemo.java的内容至BufferedStreamDemo.txt文件并显示输出
1 import java.io.*; 2 2 3 3 public class BufferedStreamDemo { 4 4 5 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 6 try{ 7 7 byte[] data=new byte[1]; 8 8 9 9 File srcFile=new File("BufferedStreamDemo.java"); 10 10 File desFile=new File("BufferedStreamDemo.txt");//声明两个文件实例 11 11 12 12 BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));//实例化BufferedInputStream 13 13 BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(desFile));//实例化BufferedOutputStream 14 14 15 15 System.out.println("复制文件: "+srcFile.length()+"字节"); 16 16 //将从BufferedStreamDemo.java文件读取的字节写到data,然后再写到BufferedStreamDemo.txt 17 17 while(bufferedInputStream.read(data)!=-1){ 18 18 bufferedOutputStream.write(data); 19 19 } 20 20 21 21 //将缓冲区中的数据全部写出 22 22 bufferedOutputStream.flush(); 23 23 24 24 System.out.println("复制完成"); 25 25 26 26 //显示输出BufferedStreamDemo.txt文件的内容 27 27 bufferedInputStream =new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("BufferedStreamDemo.txt"))); 28 28 while(bufferedInputStream.read(data)!=-1){ 29 29 String str=new String(data); 30 30 System.out.print(str); 31 31 } 32 32 33 33 bufferedInputStream.close(); 34 34 bufferedOutputStream.close(); 35 35 36 36 }catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ 37 37 System.out.println("using: java useFileStream src des"); 38 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 39 }catch(IOException e){ 40 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 41 } 42 42 } 43 43 }
9、DataInputStream类
DataInputStream和DataOutputStream可提供一些对Java基本数据类型写入的方法,像读写int、double和boolean等的方法。由于Java的数据类型大小是规定好的,在写入或读出这些基本数据类型时,就不用担心不同平台间数据大小不同的问题。
有时没有必要存储整个对象的信息,而只是要存储一个对象的成员数据,成员数据的类型假设都是Java的基本数据类型,这样的需求不必使用到与Object输入、输出相关的流对象,可以使用DataInputStream、DataOutputStream来写入或读出数据。
DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(args[0]));
方法:
public String readUTF(); 读入一个已使用UTF-8修改版格式编码的字符串
public String readLine(); 是通过BufferedReader.readLine()实现的。
public boolean readBoolean;
public int readInt();
public byte readByte();
public char readChar(); 等等一系列读取基本数据类型的方法
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
10、DataOutputStream类
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(args[0]));
方法:
public void writeBoolean(boolean b); 将一个boolean值以1-byte形式写入基本输出流。
public void writeByte(int v); 将一个byte值以1-byte值形式写入到基本输出流中。
public void writeBytes(String s); 将字符串按字节顺序写入到基本输出流中。
public void writeChar(int v); 将一个char值以2-byte形式写入到基本输出流中。先写入高字节。
public void writeInt(int v); 将一个int值以4-byte值形式写入到输出流中先写高字节。
public void writeUTF(String str); 以机器无关的的方式用UTF-8修改版将一个字符串写到基本输出流。该方法先用writeShort写入两个字节表示后面的字节数。
public int size(); 返回written的当前值。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
例子:先用DataOutputStream想文本写入各种类型数据,再用DataInputStream从中读取各种类型数据。
1 import java.io.*; 2 2 3 3 public class DataInputStreamDemo { 4 4 5 5 private static final int LEN = 5; 6 6 7 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 8 // 测试DataOutputStream,将数据写入到输出流中。 9 9 testDataOutputStream() ; 10 10 // 测试DataInputStream,从上面的输出流结果中读取数据。 11 11 testDataInputStream() ; 12 12 } 13 13 14 14 /** 15 15 * DataOutputStream的API测试函数 16 16 */ 17 17 private static void testDataOutputStream() { 18 18 19 19 try { 20 20 File file = new File("file.txt"); 21 21 DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file)); 22 22 23 23 out.writeBoolean(true); 24 24 out.writeByte((byte)0x41); 25 25 out.writeChar((char)0x4243); 26 26 out.writeShort((short)0x4445); 27 27 out.writeInt(0x12345678); 28 28 out.writeLong(0x0FEDCBA987654321L); 29 29 out.writeUTF("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz严12"); 30 30 31 31 out.close(); 32 32 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 33 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 36 } 37 37 } 38 38 /** 39 39 * DataInputStream的API测试函数 40 40 */ 41 41 private static void testDataInputStream() { 42 42 43 43 try { 44 44 File file = new File("file.txt"); 45 45 DataInputStream in = 46 46 new DataInputStream( 47 47 new FileInputStream(file)); 48 48 49 49 System.out.printf("byteToHexString(0x8F):0x%s\n", byteToHexString((byte)0x8F)); 50 50 System.out.printf("charToHexString(0x8FCF):0x%s\n", charToHexString((char)0x8FCF)); 51 51 System.out.printf("readBoolean():%s\n", in.readBoolean()); 52 52 System.out.printf("readByte():0x%s\n", byteToHexString(in.readByte())); 53 53 System.out.printf("readChar():0x%s\n", charToHexString(in.readChar())); 54 54 System.out.printf("readShort():0x%s\n", shortToHexString(in.readShort())); 55 55 System.out.printf("readInt():0x%s\n", Integer.toHexString(in.readInt())); 56 56 System.out.printf("readLong():0x%s\n", Long.toHexString(in.readLong())); 57 57 System.out.printf("readUTF():%s\n", in.readUTF()); 58 58 59 59 in.close(); 60 60 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 61 61 e.printStackTrace(); 62 62 } catch (IOException e) { 63 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 64 } 65 65 } 66 66 67 67 // 打印byte对应的16进制的字符串 68 68 private static String byteToHexString(byte val) { 69 69 return Integer.toHexString(val & 0xff); 70 70 } 71 71 72 72 // 打印char对应的16进制的字符串 73 73 private static String charToHexString(char val) { 74 74 return Integer.toHexString(val); 75 75 } 76 76 77 77 // 打印short对应的16进制的字符串 78 78 private static String shortToHexString(short val) { 79 79 return Integer.toHexString(val & 0xffff); 80 80 } 81 81 }
三、字符流
包java.io中的两个类Reader和Writer,他们是能将字节流以字符流方式进行读写的对象,因此字符流在本质上是以Reader和Writer封装的字节流。Reader和Writer都是抽象类,这两个类都实现了声明close()方法的AutoCloseable接口。
Reader和Writer类以及他们的子类本身都不是流,但是他们提供了一些方法,可用于将底层的流作为字符流读写。因此,通常使用底层的InputStream和OutputStream对象来创建Reader和Writer对象。
1、Reader类
还实现了Readable接口,该接口声明了read()方法,用于将字符读入作为参数传入read()方法的CharBuffer对象。
public int read(); 读取单个字符。
public int read(char[] cbuf); 读取多个字符到字符数组cbuf。
public abstract int read(char[] cbuf,int off,int len); 读取len个字符到字符数组cbuf中,从cbuf[off]开始存放。
public boolean ready(); 这个输入流是否准备好了。
public void reset(); 重置输入流。
public long skip(long n); 跳过n个字符读取。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
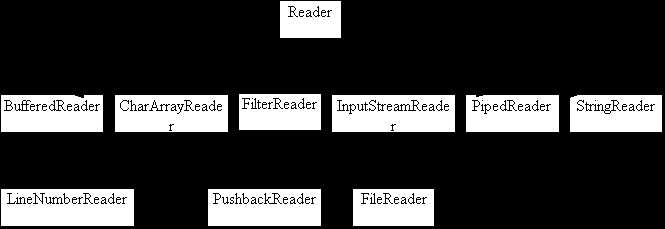
Reader类的派生类结构:
2、Writer类
Writer类实现了Appendable接口,声明了3种版本的append()方法,还有5个write()方法。
public Writer append(char c); 将字符c附加到Writer封装的任意流后面。
public Writer append(CharSequence csq); 将CharSequence类型的参数附加到底层流的后面。
public Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end); 将一个字符序列的子序列附加到底层流的后面。
public void write(int c); 写一个单独的字符。
public void write(String str); 写一个字符串。
public void write(String str, int off, int len); 写一个字符串的子串。
public void write(char[] cbuf); 写一个字符数组。
public abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len); 写一个字符数组的子串。
public abstract void flush(); 将数据缓冲区中数据全部输出,并清空缓冲区。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
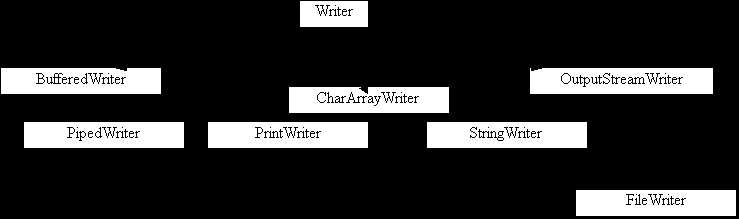
Writer类的派生类结构:
3、InputStreamReader类
若想对InputStream和OutputStream进行字符处理,可以使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter为其加上字符处理的功能,它们分别为Reader和Writer的子类。
举个例子来说,若想要显示纯文本文件的内容,不用费心地自行判断字符编码(例如范例14.15中要费心地自行判断是ASCII英文字母或BIG5中文字),只要将InputStream、OutputStream的实例作为构建InputStreamReader、OutputStreamWriter时的变量,就可以操作InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter来进行文本文件的读取,让它们为您做字符判断与转换的动作。
如果以文件操作为例,则内存中的字符数据需要通过OutputStreamWriter变为字节流才能保存在文件中,读取时需要将读入的字节流通过InputStreamReader变为字符流。过程如下:
写入数据-->内存中的字符数据-->字符流-->OutputStreamWriter-->字节流-->网络传输(或文件保存)
读取数据<--内存中的字符数据<--字符流<--InputStreamReader<--字节流<--网络传输(或文件保存)
构造方法:
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in); 创建一个使用默认字符集的 InputStreamReader。
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName); 创建使用指定字符集的 InputStreamReader。
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs); 创建使用指定字符集的 InputStreamReader。
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec); 创建使用指定字符集解码器的 InputStreamReader。
常用Charset:
|
US-ASCII |
7 位 ASCII 字符,也叫作 ISO646-US、Unicode 字符集的基本拉丁块 |
|
ISO-8859-1 |
ISO 拉丁字母表 No.1,也叫作 ISO-LATIN-1 |
|
UTF-8 |
8 位 UCS 转换格式 |
|
UTF-16BE |
16 位 UCS 转换格式,Big Endian(最低地址存放高位字节)字节顺序 |
|
UTF-16LE |
16 位 UCS 转换格式,Little-endian(最高地址存放低位字节)字节顺序 |
|
UTF-16 |
16 位 UCS 转换格式,字节顺序由可选的字节顺序标记来标识 |
常用方法:
public String getEncoding(); 返回此流使用的字符编码的名称。如果该编码有历史上用过的名称,则返回该名称;否则返回该编码的规范化名称。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
4、OutputStreamWriter类
构造方法:
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out); 创建使用默认字符编码的 OutputStreamWriter。
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName); 创建使用给定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs); 创建使用给定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc); 创建使用给定字符集编码器的 OutputStreamWriter。
常用方法:
public String getEncoding(); 返回此流使用的字符编码的名称。如果该编码具有历史名称,则返回该名称;否则返回该编码的规范化名称。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
例子:从一个文件中用InputStreamReader读取,然后将字节流转换成字符流存在字符串数组;用OutputStreamWriter向另一个文件写入该数组。
1 1 import java.io.*; 2 2 3 3 public class InputStreamReaderDemo { 4 4 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 所有的异常抛出 5 5 File f1 = new File("helpinfo.txt"); 6 6 File f2 = new File("test.txt"); 7 7 Writer out = null; 8 8 Reader in = null; 9 9 out = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(f2));// 通过子类实例化父类对象,字节流变为字符流 10 10 in = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(f1)); 11 11 char c[] = new char[1024]; 12 12 in.read(c); 13 13 System.out.print(c); 14 14 out.write(c); // 使用字符流输出 15 15 in.close(); 16 16 out.close(); 17 17 } 18 18 }
5、FileReader类
FileReader类创建了一个可以读取字符流文件内容的Reader类。
构造方法:
public FileReader(File file); 在给定从中读取数据的 File 的情况下创建一个新 FileReader。
public FileReader(String fileName); 在给定从中读取数据的文件名的情况下创建一个新 FileReader。
public FileReader(FileDescripter fd); 在给定从中读取数据的 FileDescriptor 的情况下创建一个新 FileReader。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
6、FileWriter类
FileWriter类创建一个可以用字符流写文件的Writer类。
构造方法:
public FileWriter(File file); 在给出 File 对象的情况下构造一个FileWriter对象。
public FileWriter(File file, boolean append); 在给出File对象的情况下构造一个FileWriter对象,如果第二个参数为true,则将字节写入文件末尾处,而不是写入文件开始处。
public FileWriter(FileDescripter fd); 构造与某个文件描述符相关联的FileWriter对象。
public FileWriter(String fileName); 在给出文件名的情况下构造一个FileWriter对象。
public FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append); 在给出文件名的情况下构造 FileWriter 对象,如果第二个参数为true,则将字节写入文件末尾处,而不是写入文件开始处。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
例子:从一个文本中读取字符存在数组中,然后再再到另一个文本。
1 1 import java.io.*; 2 2 3 3 public class FileReaderDemo { 4 4 public static void main (String args[ ] ) throws Exception { 5 5 FileReader fr = new FileReader("helpinfo.txt"); 6 6 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("test.txt"); 7 7 char data[]=new char[1024]; 8 8 int num = fr.read(data); 9 9 System.out.println(num); 10 10 fw.write(data); 11 11 fr.close(); 12 12 fw.close(); 13 13 } 14 14 }
7、BufferedReader类
从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而提供字符、数组和行的高效读取。可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者可使用默认的大小。大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。通常,Reader 所作的每个读取请求都会导致对基础字符或字节流进行相应的读取请求。因此,建议用 BufferedReader 包装所有其 read() 操作可能开销很高的 Reader(如 FileReader 和 InputStreamReader)。例如:BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStream(System.in));
构造函数:
public BufferedReader(Reader in); 创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int size); 创建一个使用指定大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
常用方法:
public String readline(); 读取一个文本行,通过下列字符之一即可认为某行已终止:换行 (‘\n‘)、回车 (‘\r‘) 或回车后直接跟着换行。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
8、BufferedWriter类
将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者接受默认的大小。在大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。该类提供了newLine() 方法,它使用平台自己的行分隔符概念,此概念由系统属性line.separetor定义。并非所有平台都使用新行符 (‘\n‘) 来终止各行。因此调用此方法来终止每个输出行要优于直接写入新行符。通常 Writer 将其输出立即发送到基础字符或字节流。除非要求提示输出,否则建议用 BufferedWriter 包装所有其 write() 操作可能开销很高的 Writer(如 FileWriters 和 OutputStreamWriters)。例如,BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("test.txt"));
构造方法:
public BufferedWriter(Writer out); 创建一个使用默认大小输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
public BufferedWriter(Writer out, int size); 创建一个使用指定大小输出缓冲区的新缓冲字符输出流。
常用方法:
public void newline(); 写入一个行分隔符。行分隔符字符串由系统属性line.separetor定义,并且不一定是单个新行 (‘\n‘) 符。
如果发生I/O类型错误,会抛出IOException类型的异常。
例子:从一个文本中读取字符存在数组中,然后再到另一个文本。
import java.io.*; 2 3 public class BufferedReaderDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 BufferedReader br = null; 7 BufferedWriter bw = null; 8 9 String b = null; 10 File file = new File("abc.txt"); 11 if (!file.exists() != false) { 12 try { 13 file.createNewFile(); 14 } catch (IOException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 try { 19 bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); 20 FileReader fr = new FileReader("helpinfo.txt"); 21 br = new BufferedReader(fr); 22 while ((b = br.readLine()) != null) { 23 System.out.println(b); 24 bw.write(b); //输出字符串 25 bw.newLine();//换行 26 bw.flush(); 27 } 28 } catch (Exception e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 }finally { 31 try { 32 br.close(); 33 //bw.close(); 34 } catch (IOException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 }
标签:fileread 种类 amp out little 对象 编码 dwr 清空
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoyihaohaoxuexi/p/6822950.html