标签:ring 规范 设计 方便 targe jar包 难度 学习路线 javamail
Spring第一天:IOC容器(Bean管理),Spring与Web项目整合
Spring第二天:AOP(面向切面编程),Spring的JDBC模板
Spring第三天:Spring的事务管理,SSH整合开发
Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java开发框架,由Rod Johnson 在其著作Expert One-On-One J2EE Development and Design中阐述的部分理念和原型衍生而来。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件,同时为 J2EE 应用程序开发提供集成的框架。Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。然而,Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。Spring的核心是控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
EE开发分成三层结构:
WEB层:Spring MVC
业务层:Bean管理:(Spring IOC)
持久层:Spring的JDBC模板,ORM模板用于整合其他的持久层框架
相关书籍:
Expert One-to-One J2EE Design and Development:J2EE的设计和开发(2002.EJB)
Expert One-to-One J2EE Development without EJB:J2EE不使用EJB的开发(@interface21)
Spring 3.X 和 Spring4.X
http://repo.spring.io/webapp/search/artifact/?0&q=spring-framework
解压(Spring目录结构)
docs:API和开发规范
libs:jar包和源码
schema:约束
IOC:Inverse of Control,控制反转,将对象的创建权反转给Spring
Spring IOC的核心内容:

引入jar包(符合上述IOC开发相关的jar包就行了,再加上日志记录相关两个jar包):
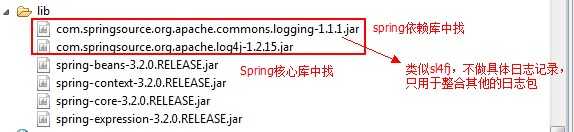
注:hibernate中的Slf4j包不做具体的日志记录,只是用于整合其他日志jar包。
首先在src目录下创建Spring的配置文件:applicationContext.xml。
然后引入spring的约束(spring-framework-3.2.0.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html\xsd-config.html的最下面copy)。
最后完成bean配置。
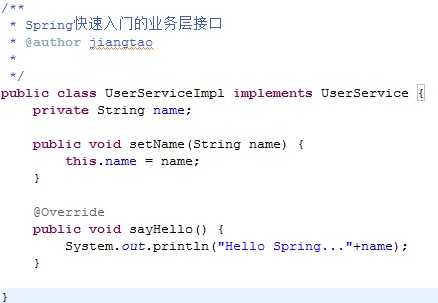
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- Spring的快速入门=================== --> <bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.spring.demo1.UserServiceImpl"> <!--属性依赖注入--> <property name="name" value="老王(XML)"/> </bean> </beans>
新建SpringDemo1类:
@Test /** * 传统方式开发: */ public void demo1(){ UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); // 手动设置: userService.setName("老王"); userService.sayHello(); } @Test /** * Spring框架开发: */ public void demo2(){ // 使用Spring的工厂: ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // 通过工厂获得类: UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService"); userService.sayHello(); }
IOC:控制反转,将对象的创建权反转给Spring。
DI:依赖注入,必须将对象的创建权交给Spring,将对象所依赖的属性注入进来.
依赖(A依赖B):
public class A{ private B b; public void setB(B b){ this.b = b; } }
继承:is a
聚合:has a。又分松散聚合关系与紧密聚合关系。
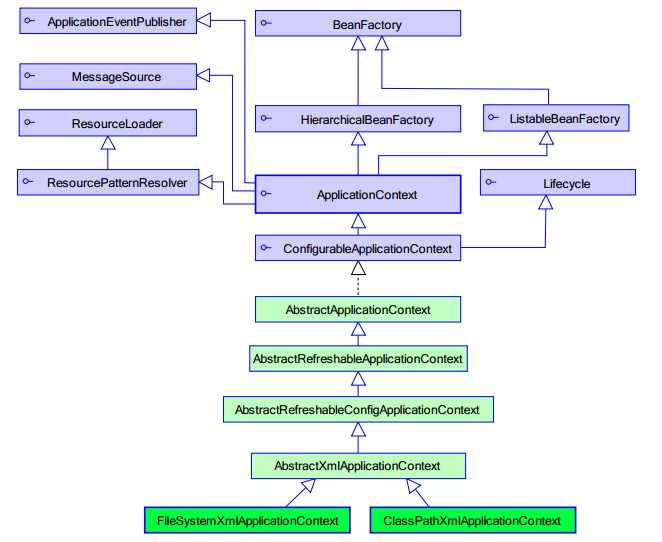
ApplicatioContext接口有两个实现类:
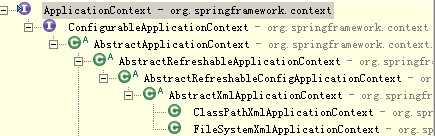
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径下Spring的配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载本地磁盘下Spring的配置文件
/** * Spring框架开发:读取本地磁盘配置文件 */ public void demo3(){ // 使用Spring的工厂: ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("C:\\applicationContext.xml"); // 通过工厂获得类: UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService"); userService.sayHello(); }
关闭工厂的方法只有其子类中才有:
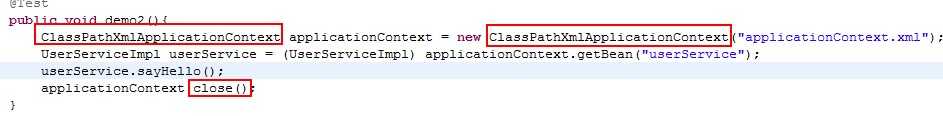
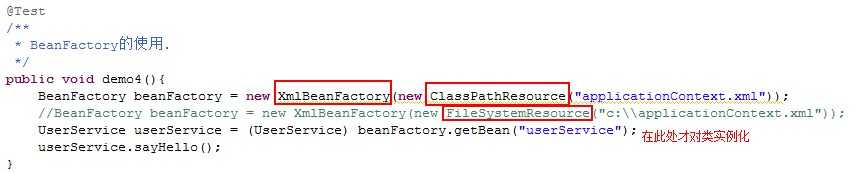
ApplicationContext:在加载applicationContext.xml时就会创建类的实例
BeanFactory:是在调用getBean方法时才会生成类的实例
Spring(一):概述,IOC(Bean管理),整合Web项目,整合JUnit单元测试
标签:ring 规范 设计 方便 targe jar包 难度 学习路线 javamail
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/crxdb/p/6828546.html