标签:strlen swa 部分 header file 另一个 session lib ble
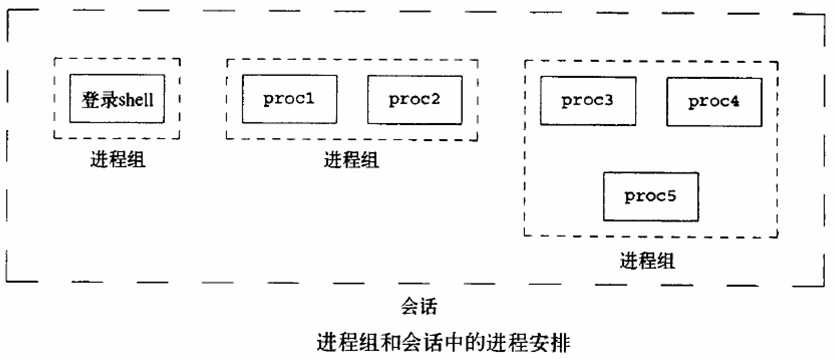
进程组

eg:显示子进程与父进程的进程组id
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 int main() {
6 pid_t pid;
7
8 if ((pid=fork())<0) {
9 printf("fork error!");
10 }else if (pid==0) {
11 printf("The child process PID is %d.\n",getpid());
12 printf("The Group ID is %d.\n",getpgrp());
13 printf("The Group ID is %d.\n",getpgid(0));
14 printf("The Group ID is %d.\n",getpgid(getpid()));
15 exit(0);
16 }
17
18 sleep(3);
19 printf("The parent process PID is %d.\n",getpid());
20 printf("The Group ID is %d.\n",getpgrp());
21
22 return 0;
23 }
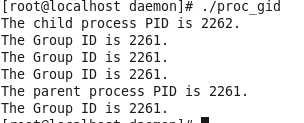
进程组id = 父进程id,即父进程为组长进程

eg:父进程改变自身和子进程的组id
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 int main() {
6 pid_t pid;
7
8 if ((pid=fork())<0) {
9 printf("fork error!");
10 exit(1);
11 }else if (pid==0) {
12 printf("The child process PID is %d.\n",getpid());
13 printf("The Group ID of child is %d.\n",getpgid(0)); // 返回组id
14 sleep(5);
15 printf("The Group ID of child is changed to %d.\n",getpgid(0));
16 exit(0);
17 }
18
19 sleep(1);
20 setpgid(pid,pid); // 改变子进程的组id为子进程本身
21
22 sleep(5);
23 printf("The parent process PID is %d.\n",getpid());
24 printf("The parent of parent process PID is %d.\n",getppid());
25 printf("The Group ID of parent is %d.\n",getpgid(0));
26 setpgid(getpid(),getppid()); // 改变父进程的组id为父进程的父进程
27 printf("The Group ID of parent is changed to %d.\n",getpgid(0));
28
29 return 0;
30 }
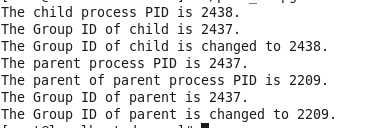


1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 int main() {
6 pid_t pid;
7
8 if ((pid=fork())<0) {
9 printf("fork error!");
10 exit(1);
11 }else if (pid==0) {
12 printf("The child process PID is %d.\n",getpid());
13 printf("The Group ID of child is %d.\n",getpgid(0));
14 printf("The Session ID of child is %d.\n",getsid(0));
15 sleep(10);
16 setsid(); // 子进程非组长进程,故其成为新会话首进程,且成为组长进程。该进程组id即为会话进程
17 printf("Changed:\n");
18 printf("The child process PID is %d.\n",getpid());
19 printf("The Group ID of child is %d.\n",getpgid(0));
20 printf("The Session ID of child is %d.\n",getsid(0));
21 sleep(20);
22 exit(0);
23 }
24
25 return 0;
26 }
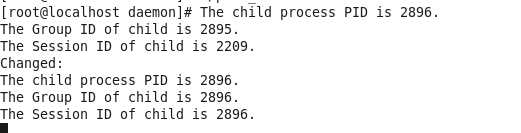
在子进程中调用setsid()后,子进程成为新会话首进程,且成为一个组长进程,其进程组id等于会话id
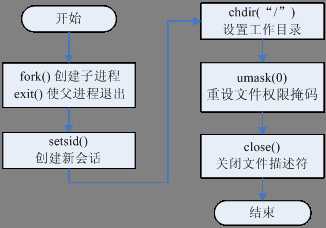
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4 #include <unistd.h>
5 #include <sys/wait.h>
6 #include <sys/types.h>
7 #include <fcntl.h>
8
9 int main() {
10 pid_t pid;
11 int i,fd;
12 char *buf="This is a daemon program.\n";
13
14 if ((pid=fork())<0) {
15 printf("fork error!");
16 exit(1);
17 }else if (pid>0) // fork且退出父进程
18 exit(0);
19
20 setsid(); // 在子进程中创建新会话。
21 chdir("/"); // 设置工作目录为根
22 umask(0); // 设置权限掩码
23 for(i=0;i<getdtablesize();i++) //getdtablesize返回子进程文件描述符表的项数
24 close(i); // 关闭这些不将用到的文件描述符
25
26 while(1) {// 死循环表征它将一直运行
27 // 以读写方式打开"/tmp/daemon.log",返回的文件描述符赋给fd
28 if ((fd=open("/tmp/daemon.log",O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_APPEND,0600))<0) {
29 printf("Open file error!\n");
30 exit(1);
31 }
32 // 将buf写到fd中
33 write(fd,buf,strlen(buf)+1);
34 close(fd);
35 sleep(10);
36 printf("Never output!\n");
37 }
38
39 return 0;
40 }
因为stdout被关掉了,所以“Never ouput!”不会输出。
查看/tmp/daemon.log,说明该程序一直在运行

标签:strlen swa 部分 header file 另一个 session lib ble
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/24zyt/p/6845315.html