标签:方法重写 over subclass 表复制 例子 font class 实现 表达式
参考copy链接:http://blog.csdn.net/bigconvience/article/details/25025561
在看原型模式,发现要用到clone这个方法,以前和朋友聊过,没怎么看过,刚好要用,就看看了。
源码解释:
/** * Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning * of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general * intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression: * <blockquote> * <pre> * x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote> * will be true, and that the expression: * <blockquote> * <pre> * x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote> * will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements. * While it is typically the case that: * <blockquote> * <pre> * x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote> * will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement. * <p> * By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling * {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except * {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that * {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}. * <p> * By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent * of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence, * it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned * by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means * copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure" * of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these * objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only * primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually * the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone} * need to be modified. * <p> * The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a * specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does * not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a * {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays * are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that * the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]} * is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type. * Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this * object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of * the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the * contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method * performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation. * <p> * The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface * {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object * whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an * exception at run time. * * @return a clone of this instance. * @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object‘s class does not * support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses * that override the {@code clone} method can also * throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot * be cloned. * @see java.lang.Cloneable */ protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
一大串英文我看不怎么懂,都是看别人的博客和翻译文档的。
中文jdk文档:
clone protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException 创建并返回此对象的一个副本。“副本”的准确含义可能依赖于对象的类。这样做的目的是,对于任何对象 x,表达式: x.clone() != x 为 true,表达式: x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass() 也为 true,但这些并非必须要满足的要求。一般情况下: x.clone().equals(x) 为 true,但这并非必须要满足的要求。 按照惯例,返回的对象应该通过调用 super.clone 获得。如果一个类及其所有的超类(Object 除外)都遵守此约定,则 x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()。 按照惯例,此方法返回的对象应该独立于该对象(正被复制的对象)。要获得此独立性,在 super.clone 返回对象之前,有必要对该对象的一个或多个字段进行修改。这通常意味着要复制包含正在被复制对象的内部“深层结构”的所有可变对象,并使用对副本的引用替换对这些对象的引用。如果一个类只包含基本字段或对不变对象的引用,那么通常不需要修改 super.clone 返回的对象中的字段。 Object 类的 clone 方法执行特定的复制操作。首先,如果此对象的类不能实现接口 Cloneable,则会抛出 CloneNotSupportedException。注意,所有的数组都被视为实现接口 Cloneable。否则,此方法会创建此对象的类的一个新实例,并像通过分配那样,严格使用此对象相应字段的内容初始化该对象的所有字段;这些字段的内容没有被自我复制。所以,此方法执行的是该对象的“浅表复制”,而不“深层复制”操作。 Object 类本身不实现接口 Cloneable,所以在类为 Object 的对象上调用 clone 方法将会导致在运行时抛出异常。 返回: 此实例的一个副本。 抛出: CloneNotSupportedException - 如果对象的类不支持 Cloneable 接口,则重写 clone 方法的子类也会抛出此异常,以指示无法复制某个实例。 另请参见: Cloneable
cloneable接口的文档:
public interface Cloneable 此类实现了 Cloneable 接口,以指示 Object.clone() 方法可以合法地对该类实例进行按字段复制。 如果在没有实现 Cloneable 接口的实例上调用 Object 的 clone 方法,则会导致抛出 CloneNotSupportedException 异常。 按照惯例,实现此接口的类应该使用公共方法重写 Object.clone(它是受保护的)。请参阅 Object.clone(),以获得有关重写此方法的详细信息。 注意,此接口不 包含 clone 方法。因此,因为某个对象实现了此接口就克隆它是不可能的。即使 clone 方法是反射性调用的,也无法保证它将获得成功。 从以下版本开始: JDK1.0 另请参见: CloneNotSupportedException, Object.clone()
现在可以知道的是,clone方法就是返回一个原对象的拷贝,默认走的是浅拷贝。克隆的目的是复制对象,但是新的对象是独立于原来的对象的,一般我们克隆出来的对象都在一些属性做了更改,这个时候需要小心一点,如果更改的属性是引用数据类型,可能会影响到原来的对象,如果都是基本数据类型则不怕。使用clone方法的前提是继承Cloneable接口,数组默认实现了Cloneable接口,默认走的是浅拷贝。
那么问题来了,什么是浅拷贝?什么是深拷贝呢?
2.浅克隆(shadow clone)
克隆就是复制一个对象的复本.若只需要复制对象的字段值(对于基本数据类型,如:int,long,float等,则复制值;对于复合数据类型仅复制该字段值,如数组变量则复制地址,对于对象变量则复制对象的reference。
例子:
然后进行测试:
结果为:
克隆前c1: a=100 b=1000
克隆前c1: a=100 b=5
克隆后c2: a=50 b[0]=5
c1和c2的对象模型:
可以看出,基本类型可以使用浅克隆,而对于引用类型,由于引用的是内容相同,所以改变c2实例对象中的属性就会影响到c1。所以引用类型需要使用深克隆。另外,在开发一个不可变类的时候,如果这个不可变类中成员有引用类型,则就需要通过深克隆来达到不可变的目的。
3.深克隆(deep clone)
深克隆与浅克隆的区别在于对复合数据类型的复制。若对象中的某个字段为复合类型,在克隆对象的时候,需要为该字段重新创建一个对象。
例子:
结果为:
克隆前c1: a=100 b=1000
克隆前c1: a=100 b=1000
克隆后c2: a=50 b[0]=5
对象模型:
上面是copy的,自己敲一敲:
两个准备的类:
class Person implements Cloneable{ @Override protected Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return (Person) super.clone(); } String name; int age; Job job; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Job getJob() { return job; } public void setJob(Job job) { this.job = job; } @Override public String toString(){ return "name: " + name + ",age: " + age + ",job: " + job; } } class Job{ String jobName; String address; public String getJobName() { return jobName; } public void setJobName(String jobName) { this.jobName = jobName; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } }
public class CloneTest {
@Test
public void shaowClone() throws Exception{
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setName("guo");
p1.setAge(22);
Job job = new Job();
job.setJobName("IT");
job.setAddress("shanghai");
p1.setJob(job);
Person p2 = p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p2.getJob().setJobName("programmer");
System.out.println(p1.getJob().getJobName());
}
得到结果:
name: guo,age: 22,job: test.Job@4f2410ac
name: guo,age: 22,job: test.Job@4f2410ac
programmer
浅拷贝,就是Object默认的clone方法,完全的copy了这个类,基本数据类型copy了值,引用数据类型copy的是对象的引用,所以如果要对对象进行修改,可以使用深拷贝。
}
所谓的深拷贝,就是自己重写了一下clone方法,将引用变量变成值传递而不是引用传递。
修改的代码;
@Override protected Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Person ectype = (Person) super.clone(); Job tmp = new Job(); tmp.setJobName(ectype.getJob().getJobName()); tmp.setAddress(ectype.getJob().getAddress()); ectype.setJob(tmp); return ectype; }
测试代码:
@Test
public void shaowClone() throws Exception{
Person p1 = new Person();
p1.setName("guo");
p1.setAge(22);
Job job = new Job();
job.setJobName("IT");
job.setAddress("shanghai");
p1.setJob(job);
Person p2 = p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1.toString());
System.out.println(p2.toString());
p2.getJob().setJobName("programmer");
System.out.println(p2.getJob().getJobName());
System.out.println(p1.getJob().getJobName());
}
结果:
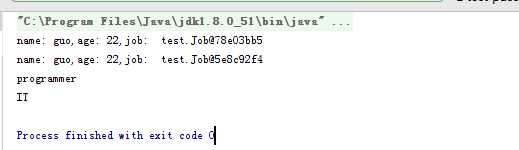
over
标签:方法重写 over subclass 表复制 例子 font class 实现 表达式
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/aigeileshei/p/6863794.html