标签:value else who 依赖关系 dfs 权重 图片 add 没有
本博客的代码的思想和图片参考:好大学慕课浙江大学陈越老师、何钦铭老师的《数据结构》
拓扑排序
首先我们来举个例子说明:计算机专业的排课
课程号 课程名称预修课程
C1 程序设计基础无
C2 离散数学无
C3 数据结构 C1, C2
C4 微积分(一) 无
C5 微积分(二) C4
C6 线性代数 C5
C7 算法分析与设计 C3
C8 逻辑与计算机设计基础无
C9 计算机组成 C8
C10 操作系统 C7, C9
C11 编译原理 C7, C9
C12 数据库 C7
C13 计算理论 C2
C14 计算机网络 C10
C15 数值分析 C6
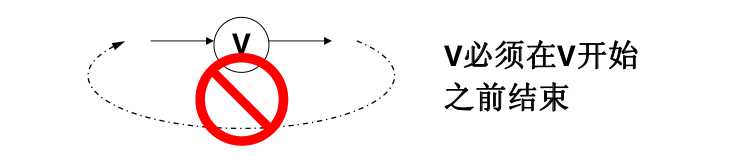
1.拓扑序:如果图中从V到W有一条有向路径,则V一定排在W之前。满足此条件的顶点序列称为一个拓扑序。
2.获得一个拓扑序的过程就是拓扑排序
3.AOV如果有合理的拓扑序,则必定是有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graph, DAG)
如果在一个图中有环路,那么,他的拓扑排序是木有的,因为下面的理论是不可能的。
首先我们需要根据给的关系表构建一张有向图,在有向图中,我们可以吧课程编号设置为顶点,如果该课程有直接的预修课程,我们让直接的预修课程指向该课程。下面是上面的计算机排课的有向图表示。
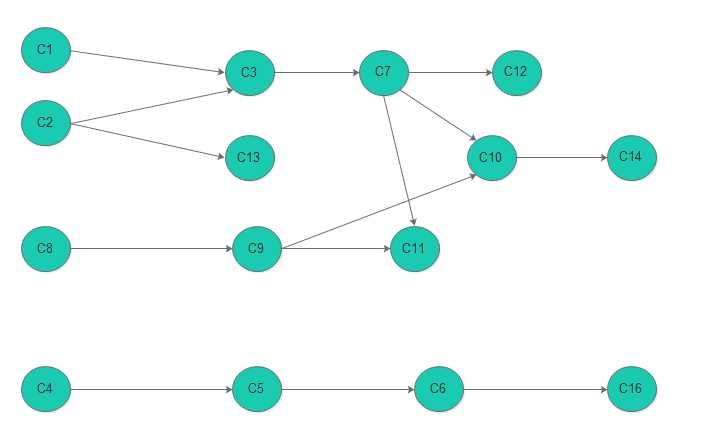
我们先找出图中没有入度的顶点并进行打印(记录),在初始情况下,有C1 C2 C8 C4 可以记录,然后在记录完以后,我们删除刚才记录和顶点和边。依次的记录或者输出输出如下
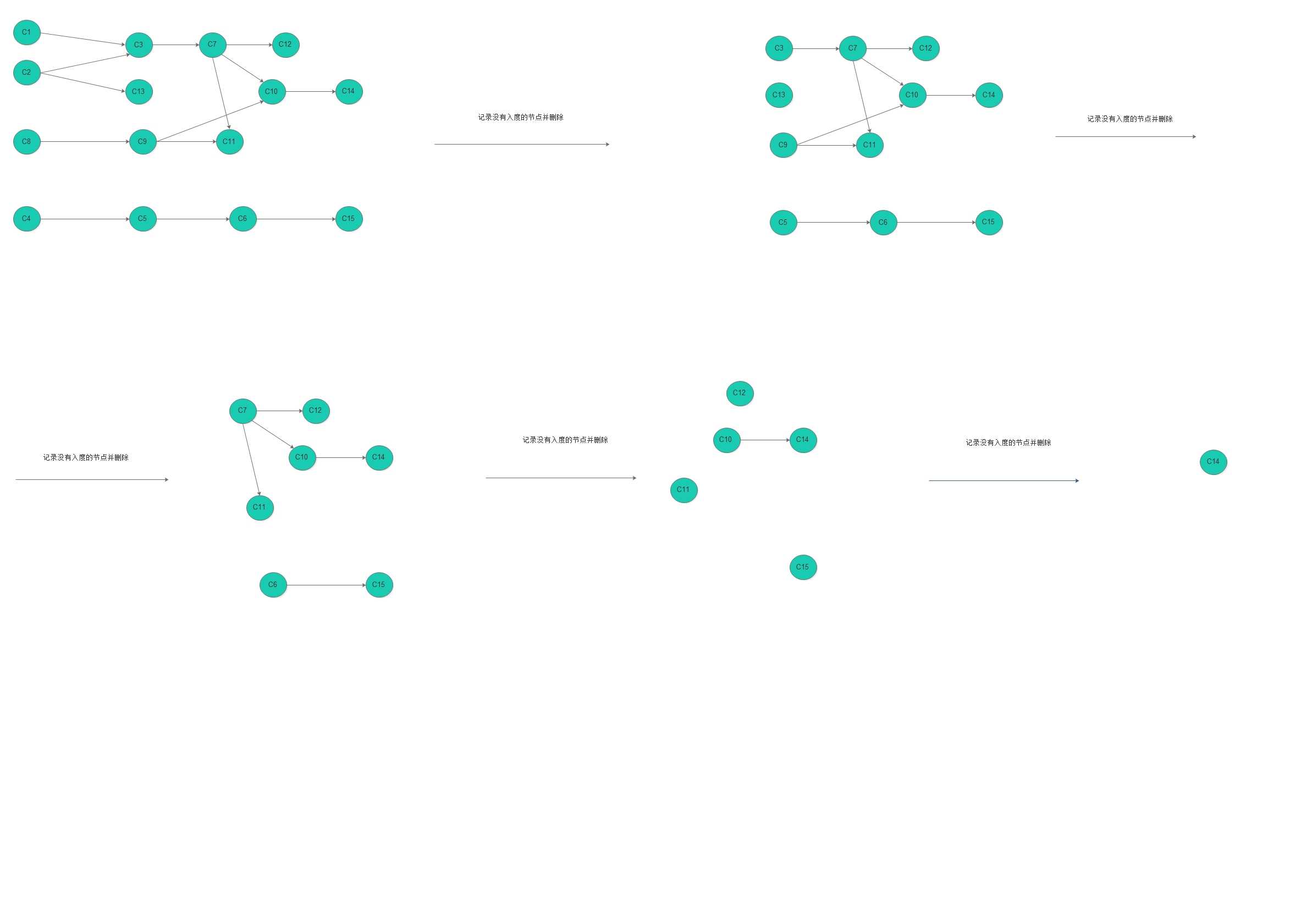

C1 C2 C8 C4
C3 C13 C9 C5
C7 C6
C12 C10 C11 C15
C14
void TopSort()
{
for ( cnt = 0; cnt < |V|; cnt++ ) {
V = 未输出的入度为0的顶点; /* O(|V|) */
if ( 这样的V不存在 ) {
Error ( “图中有回路” );
break;
}
输出V,或者记录V的输出序号;
for ( V 的每个邻接点 W )
Indegree[W]––;
}
}
上面的伪代码的介绍:
1.当还没有输出(记录)到V个顶点时,就退出了,表示图有回路
2.如何实现删除已经记录的顶点--->对V进行一次记录,更新其邻接点的入度减一
3.如何实现“未输出的入度为0的顶点”如果每次都对所有的顶点进行以此遍历,那么次算法的时间复杂度为T=O(v^2),这可以不是一个非常好的算法,如何进行改进
我们可以建立一个容器,在开始或者每次入度减一时,检查是否有节点的入度变为0,如果有,就把该节点放入一个容器里面。这样这部操作就可以变成一个常数。
下面是改进以后的伪代码:
void TopSort()
{
for ( 图中每个顶点 V )
If ( Indegree[V]==0 )
Enqueue( V, Q );
while ( !IsEmpty(Q) ) {
V = Dequeue( Q );
输出V,或者记录V的输出序号; cnt++;
for ( V 的每个邻接点 W )
if ( ––Indegree[W]==0 )
Enqueue( W, Q );
}
if ( cnt != |V| )
Error( “图中有回路” );
}
改进后的算法时间复杂的为T=O(V+E)
此算法还可以用来检查有向无环图DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph)
AOE(Activity On Edge)网络:一般用于安排项目的工序
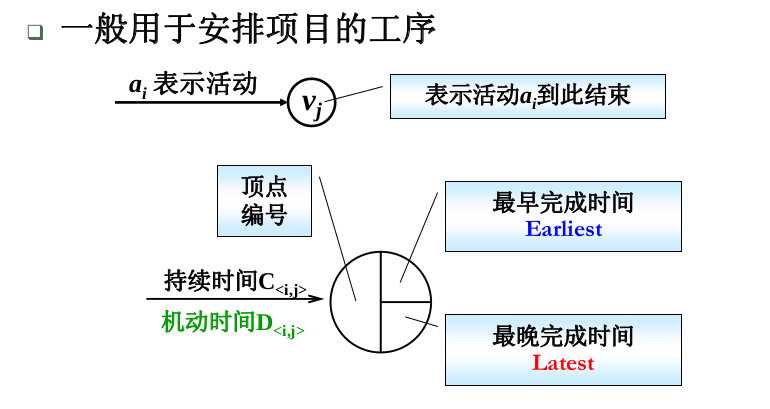
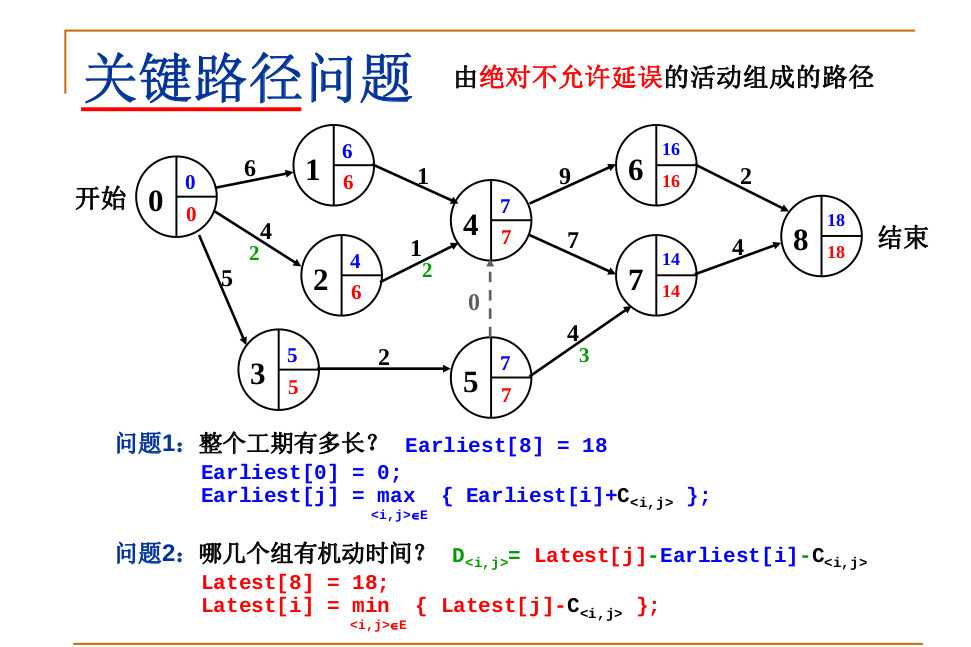
上面的说的都是理论,让我们来做一下练习吧
Given the relations of all the activities of a project, you are supposed to find the earliest completion time of the project.
Each
input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line
containing two positive integers N (≤100), the number of activity
check points (hence it is assumed that the check points are numbered
from 0 to N?1), and M, the number of activities. Then M lines
follow, each gives the description of an activity. For the i-th
activity, three non-negative numbers are given: S[i],
E[i], and L[i],
where S[i] is the index of the starting
check point, E[i] of the ending check
point, and L[i] the lasting time of the
activity. The numbers in a line are separated by a space.
For each test case, if the scheduling is possible, print in a line its earliest completion time; or simply output "Impossible".
9 120 1 60 2 40 3 51 4 12 4 13 5 25 4 04 6 94 7 75 7 46 8 27 8 4
18
4 50 1 10 2 22 1 31 3 43 2 5
Impossible
时间限制:400ms
内存限制:64MB
代码长度限制:16kB
判题程序:系统默认
作者:陈越
单位:浙江大学
这道题目解决的求一个工程的最早完成时间,是拓扑排序的一个变形。根据我们上面关键路径的理论知识,我们知道,最早完成时间是上一个节点的最早完成时间+持续时间中的最大值。那么我们先在原来的图的节点中添加一个字段来存储earliest,然后初始化earliest为0.在从队列中取出元素时,我们对其邻接点的earliest进行判断,让邻接点的earliest等于父节点+持续时间的最大值,并进行更新。如果最后所有的顶点都记录完毕,我们返回true,否则返回false(图有回路). 剩下的工作就是根据返回值输出所有顶点中earliest的最大值或者Impossible。弄清楚拓扑排序以后,这道题目还是很简单的。
拓扑排序的源代码:

1 /* 2 * topSort.c 3 * 4 * Created on: 2017年5月17日 5 * Author: ygh 6 */ 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <stdlib.h> 9 10 #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 10001 /*define the max number of the vertex*/ 11 #define INFINITY 65535 /*define double byte no negitive integer max number is 65535*/ 12 #define ERROR -1 13 14 typedef int vertex; /*define the data type of the vertex*/ 15 typedef int weightType; /*define the data type of the weight*/ 16 typedef char dataType; /*define the data type of the vertex value*/ 17 18 /*define the data structure of the Edge*/ 19 typedef struct eNode *ptrToENode; 20 typedef struct eNode { 21 vertex v1, v2; /*two vertex between the edge <v1,v2>*/ 22 weightType weight; /*the value of the edge‘s weight */ 23 }; 24 typedef ptrToENode edge; 25 26 /*==================A adjacent link to describe a graph=========================================*/ 27 /*define the data structure adjacent table node*/ 28 typedef struct adjNode *ptrToAdjNode; 29 typedef struct adjNode { 30 vertex adjVerx; /*the index of the vertex*/ 31 weightType weight; /*the value of the weight*/ 32 ptrToAdjNode next; /*the point to point the next node*/ 33 }; 34 35 /*define the data structure of the adjacent head*/ 36 typedef struct vNode *ptrToVNode; 37 typedef struct vNode { 38 ptrToAdjNode head; /*the point to point the adjacent table node*/ 39 dataType data; /*the space to store the name of the vertex,but some time the vertex has no names*/ 40 } adjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; 41 42 /*define the data structure of graph*/ 43 typedef struct gLNode *ptrTogLNode; 44 typedef struct gLNode { 45 int vertex_number; /*the number of the vertex*/ 46 int edge_nunber; /*the number of the edge*/ 47 adjList g; /*adjacent table*/ 48 }; 49 typedef ptrTogLNode adjacentTableGraph; /*a graph show by adjacent table*/ 50 51 /* 52 create a graph given the vertex number. 53 @param vertexNum The verter number of the graph 54 @return a graph with vertex but no any egdgs 55 */ 56 adjacentTableGraph createLGraph(int vertexNum) { 57 adjacentTableGraph graph; 58 59 vertex v; 60 graph = (adjacentTableGraph) malloc(sizeof(struct gLNode)); 61 graph->vertex_number = vertexNum; 62 graph->edge_nunber = 0; 63 /*initialize the adjacent table*/ 64 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 65 graph->g[v].head = NULL; 66 } 67 return graph; 68 } 69 70 /* 71 insert a edge to graph.We will distinct oriented graph and undirected graph 72 The e->v1 and e->v2 are the vertexs‘ indexs in the adjacent table 73 @param graph The graph you want to insert edge 74 @param e The edge you want to insert the graph 75 @param isOriented Whether the graph is oriented graph.If the graph is oriented 76 we will set adjacent table graph[v1]->head=v2 and set graph[v1].head=v2 77 otherwise we only set graph[v1].head=v2 78 */ 79 void insertEdgeToLink(adjacentTableGraph graph, edge e, int isOriented) { 80 /*build node<v1,v2>*/ 81 ptrToAdjNode newNode; 82 newNode = (ptrToAdjNode) malloc(sizeof(struct adjNode)); 83 newNode->adjVerx = e->v2; 84 newNode->weight = e->weight; 85 newNode->next = graph->g[e->v1].head; 86 graph->g[e->v1].head = newNode; 87 /*if the graph is directed graph*/ 88 if (!isOriented) { 89 newNode = (ptrToAdjNode) malloc(sizeof(struct adjNode)); 90 newNode->adjVerx = e->v1; 91 newNode->weight = e->weight; 92 newNode->next = graph->g[e->v2].head; 93 graph->g[e->v2].head = newNode; 94 } 95 } 96 97 /* 98 build a graph stored by adjacent table 99 */ 100 adjacentTableGraph buildLGraph(int isOrdered) { 101 adjacentTableGraph graph; 102 edge e; 103 vertex i; 104 int vertex_num; 105 106 scanf("%d", &vertex_num); 107 graph = createLGraph(vertex_num); 108 scanf("%d", &(graph->edge_nunber)); 109 if (graph->edge_nunber) { 110 e = (edge) malloc(sizeof(struct eNode)); 111 for (i = 0; i < graph->edge_nunber; i++) { 112 scanf("%d %d", &e->v1, &e->v2); 113 e->v1--; 114 e->v2--; 115 e->weight = 1; 116 insertEdgeToLink(graph, e, isOrdered); 117 } 118 } 119 120 return graph; 121 } 122 123 /*==============================define a queue=====================================================*/ 124 /*define a list to store the element in the queue*/ 125 typedef vertex elementType; 126 typedef struct node3 *pList; 127 typedef struct node3 { 128 elementType element; 129 struct node3 *next; 130 }; 131 132 /*define a queue to point the list*/ 133 typedef struct node4 *pQueue; 134 typedef struct node4 { 135 pList front; /*the front point to point the head of the list*/ 136 pList rear; /*the rear point to point the rear of of the list*/ 137 }; 138 139 /*create a empty list to store the queue element*/ 140 pList createEmptyList() { 141 pList list; 142 list = (pList) malloc(sizeof(struct node3)); 143 list->next = NULL; 144 return list; 145 } 146 /*create a empty queye*/ 147 pQueue createEmptyQueue() { 148 pQueue queue = (pQueue) malloc(sizeof(struct node4)); 149 queue->front = NULL; 150 queue->rear = NULL; 151 return queue; 152 } 153 154 /* 155 Wether the queue is empty 156 @param queue The queue need to adjust 157 @return If the queue is null,return 1 otherwise return 0 158 */ 159 int isQueueEmpty(pQueue queue) { 160 return (queue->front == NULL); 161 } 162 163 /* 164 Add a element to a queue,If the queue is null,we will create a new queue 165 @parama queue The queue we will add elememt to 166 @prama element The element we will add to queue 167 */ 168 void addQueue(pQueue queue, elementType element) { 169 if (isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 170 pList list = createEmptyList(); 171 list->element = element; 172 queue->front = queue->rear = list; 173 } else { 174 pList newNode = (pList) malloc(sizeof(struct node3)); 175 newNode->element = element; 176 newNode->next = queue->rear->next; 177 queue->rear->next = newNode; 178 queue->rear = newNode; 179 } 180 } 181 182 /* 183 delete a element from a queue 184 @param queue The queue will be deleted a element 185 @return The element has been deleted 186 */ 187 elementType deleteEleFromQueue(pQueue queue) { 188 if (isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 189 printf("the queue is empty,don‘t allow to delete elemet from it!"); 190 return -1; 191 } else { 192 pList oldNode = queue->front; 193 elementType element = oldNode->element; 194 if (queue->front == queue->rear) { 195 queue->rear = queue->front = NULL; 196 } else { 197 queue->front = queue->front->next; 198 } 199 free(oldNode); 200 return element; 201 } 202 } 203 204 /* 205 * Top sort algorithms thoughts: 206 * 1.we first initialize all vertex in-degree is zero,then we according to 207 * the graph to set the each vertex in-degree. 208 * 2.find zero in-degree vertex and put it in queue. 209 * 3.get a vertex from a queue and record its index 210 * 4.get the all adjacent vertex of the vertex and let them in-degree decrement,at this moment,if 211 * some vertex has decrease into zero,we put them into queue. 212 * 5.Execute this operation until the queue is empty 213 * 214 * @param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 215 * @param topOrder A <code>vertex</code> array to store the index of the 216 * vertex about the top queue 217 * @return If the graph is no circle,indicate the top sort is correct 1 will be return 218 * otherwise will return 0 219 */ 220 int topSort(adjacentTableGraph graph, vertex topOrder[]) { 221 vertex v; 222 ptrToAdjNode w; 223 int indegree[MAX_VERTEX_NUM], vertexConter = 0; 224 /* 225 * Create a queue to store the vertex whose in-degree is zero 226 */ 227 pQueue queue = createEmptyQueue(); 228 /* 229 * Initialize topOrder 230 */ 231 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 232 indegree[v] = 0; 233 } 234 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 235 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 236 indegree[w->adjVerx]++; 237 } 238 } 239 240 /* 241 * Add in-degree vertex to queue 242 */ 243 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 244 if (indegree[v] == 0) { 245 addQueue(queue, v); 246 } 247 } 248 while (!isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 249 v = deleteEleFromQueue(queue); 250 /* 251 * Record the vertex of top sort 252 */ 253 topOrder[vertexConter++] = v; 254 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 255 if (--indegree[w->adjVerx] == 0) { 256 addQueue(queue, w->adjVerx); 257 } 258 } 259 } 260 261 /* 262 *Adjust whether all vertexes have been recorded 263 */ 264 if (vertexConter == graph->vertex_number) { 265 return 1; 266 } else { 267 return 0; 268 } 269 } 270 271 /* 272 * Print the index of the vertex of the top sort 273 */ 274 void printTopSort(int topSort[], int length) { 275 int i; 276 printf("topSort:"); 277 for (i = 0; i < length; i++) { 278 printf("%d ", topSort[i] + 1); 279 } 280 } 281 282 int main() { 283 adjacentTableGraph graph = buildLGraph(1); 284 vertex topOrder[graph->vertex_number]; 285 int bool = topSort(graph, topOrder); 286 if (bool) { 287 printTopSort(topOrder, graph->vertex_number); 288 } else { 289 printf("the grap has a circle"); 290 } 291 return 0; 292 }
测试数据和结果:
15 14
1 3
2 3
2 13
3 7
7 12
7 10
7 11
8 9
9 11
9 10
10 14
4 5
5 6
6 15
result:
topSort:1 2 4 8 13 3 5 9 7 6 11 10 12 15 14
How Long Does It Take的源代码

1 /* 2 * take.c 3 * 4 * Created on: 2017年5月17日 5 * Author: ygh 6 */ 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <stdlib.h> 9 10 #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 101 /*define the max number of the vertex*/ 11 #define INFINITY 65535 /*define double byte no negitive integer max number is 65535*/ 12 #define ERROR -1 13 14 typedef int vertex; /*define the data type of the vertex*/ 15 typedef int weightType; /*define the data type of the weight*/ 16 typedef char dataType; /*define the data type of the vertex value*/ 17 18 /*define the data structure of the Edge*/ 19 typedef struct eNode *ptrToENode; 20 typedef struct eNode { 21 vertex v1, v2; /*two vertex between the edge <v1,v2>*/ 22 weightType weight; /*the value of the edge‘s weight */ 23 }; 24 typedef ptrToENode edge; 25 26 /*==================A adjacent link to describe a graph=========================================*/ 27 /*define the data structure adjacent table node*/ 28 typedef struct adjNode *ptrToAdjNode; 29 typedef struct adjNode { 30 vertex adjVerx; /*the index of the vertex*/ 31 weightType weight; /*the value of the weight*/ 32 ptrToAdjNode next; /*the point to point the next node*/ 33 }; 34 35 /*define the data structure of the adjacent head*/ 36 typedef struct vNode *ptrToVNode; 37 typedef struct vNode { 38 ptrToAdjNode head; /*the point to point the adjacent table node*/ 39 dataType data; /*the space to store the name of the vertex,but some time the vertex has no names*/ 40 weightType earliest; /*The earliest data of the project*/ 41 } adjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; 42 43 /*define the data structure of graph*/ 44 typedef struct gLNode *ptrTogLNode; 45 typedef struct gLNode { 46 int vertex_number; /*the number of the vertex*/ 47 int edge_nunber; /*the number of the edge*/ 48 adjList g; /*adjacent table*/ 49 }; 50 typedef ptrTogLNode adjacentTableGraph; /*a graph show by adjacent table*/ 51 52 /* 53 create a graph given the vertex number. 54 @param vertexNum The verter number of the graph 55 @return a graph with vertex but no any egdgs 56 */ 57 adjacentTableGraph createLGraph(int vertexNum) { 58 adjacentTableGraph graph; 59 60 vertex v; 61 graph = (adjacentTableGraph) malloc(sizeof(struct gLNode)); 62 graph->vertex_number = vertexNum; 63 graph->edge_nunber = 0; 64 /*initialize the adjacent table*/ 65 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 66 graph->g[v].head = NULL; 67 graph->g[v].earliest = 0; 68 } 69 return graph; 70 } 71 72 /* 73 insert a edge to graph.We will distinct oriented graph and undirected graph 74 The e->v1 and e->v2 are the vertexs‘ indexs in the adjacent table 75 @param graph The graph you want to insert edge 76 @param e The edge you want to insert the graph 77 @param isOriented Whether the graph is oriented graph.If the graph is oriented 78 we will set adjacent table graph[v1]->head=v2 and set graph[v1].head=v2 79 otherwise we only set graph[v1].head=v2 80 */ 81 void insertEdgeToLink(adjacentTableGraph graph, edge e, int isOriented) { 82 /*build node<v1,v2>*/ 83 ptrToAdjNode newNode; 84 newNode = (ptrToAdjNode) malloc(sizeof(struct adjNode)); 85 newNode->adjVerx = e->v2; 86 newNode->weight = e->weight; 87 newNode->next = graph->g[e->v1].head; 88 graph->g[e->v1].head = newNode; 89 /*if the graph is directed graph*/ 90 if (!isOriented) { 91 newNode = (ptrToAdjNode) malloc(sizeof(struct adjNode)); 92 newNode->adjVerx = e->v1; 93 newNode->weight = e->weight; 94 newNode->next = graph->g[e->v2].head; 95 graph->g[e->v2].head = newNode; 96 } 97 } 98 99 /* 100 build a graph stored by adjacent table 101 */ 102 adjacentTableGraph buildLGraph(int isOrdered) { 103 adjacentTableGraph graph; 104 edge e; 105 vertex i; 106 int vertex_num; 107 108 scanf("%d", &vertex_num); 109 graph = createLGraph(vertex_num); 110 scanf("%d", &(graph->edge_nunber)); 111 if (graph->edge_nunber) { 112 e = (edge) malloc(sizeof(struct eNode)); 113 for (i = 0; i < graph->edge_nunber; i++) { 114 scanf("%d %d %d", &e->v1, &e->v2, &e->weight); 115 insertEdgeToLink(graph, e, isOrdered); 116 } 117 } 118 119 return graph; 120 } 121 122 /*==============================define a queue=====================================================*/ 123 /*define a list to store the element in the queue*/ 124 typedef vertex elementType; 125 typedef struct node3 *pList; 126 typedef struct node3 { 127 elementType element; 128 struct node3 *next; 129 }; 130 131 /*define a queue to point the list*/ 132 typedef struct node4 *pQueue; 133 typedef struct node4 { 134 pList front; /*the front point to point the head of the list*/ 135 pList rear; /*the rear point to point the rear of of the list*/ 136 }; 137 138 /*create a empty list to store the queue element*/ 139 pList createEmptyList() { 140 pList list; 141 list = (pList) malloc(sizeof(struct node3)); 142 list->next = NULL; 143 return list; 144 } 145 /*create a empty queye*/ 146 pQueue createEmptyQueue() { 147 pQueue queue = (pQueue) malloc(sizeof(struct node4)); 148 queue->front = NULL; 149 queue->rear = NULL; 150 return queue; 151 } 152 153 /* 154 Wether the queue is empty 155 @param queue The queue need to adjust 156 @return If the queue is null,return 1 otherwise return 0 157 */ 158 int isQueueEmpty(pQueue queue) { 159 return (queue->front == NULL); 160 } 161 162 /* 163 Add a element to a queue,If the queue is null,we will create a new queue 164 @parama queue The queue we will add elememt to 165 @prama element The element we will add to queue 166 */ 167 void addQueue(pQueue queue, elementType element) { 168 if (isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 169 pList list = createEmptyList(); 170 list->element = element; 171 queue->front = queue->rear = list; 172 } else { 173 pList newNode = (pList) malloc(sizeof(struct node3)); 174 newNode->element = element; 175 newNode->next = queue->rear->next; 176 queue->rear->next = newNode; 177 queue->rear = newNode; 178 } 179 } 180 181 /* 182 delete a element from a queue 183 @param queue The queue will be deleted a element 184 @return The element has been deleted 185 */ 186 elementType deleteEleFromQueue(pQueue queue) { 187 if (isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 188 printf("the queue is empty,don‘t allow to delete elemet from it!"); 189 return -1; 190 } else { 191 pList oldNode = queue->front; 192 elementType element = oldNode->element; 193 if (queue->front == queue->rear) { 194 queue->rear = queue->front = NULL; 195 } else { 196 queue->front = queue->front->next; 197 } 198 free(oldNode); 199 return element; 200 } 201 } 202 203 /* 204 * We solve this problem by top sort,but we need to update the adjacent 205 * vertex earliest value at decreasing the adjacent vertex in-degree,the 206 * earliest the max value of parent‘s earliest value add the weight(last time). 207 * The vertex which has no in-degree will set earliest to 0 at first time 208 * 209 * Top sort algorithms thoughts: 210 * 1.we first initialize all vertex in-degree is zero,then we according to 211 * the graph to set the each vertex in-degree. 212 * 2.find zero in-degree vertex and put it in queue. 213 * 3.get a vertex from a queue and record its index 214 * 4.get the all adjacent vertex of the vertex and let them in-degree decrement,at this moment,if 215 * some vertex has decrease into zero,we put them into queue. 216 * 5.Execute this operation until the queue is empty 217 * 218 * @param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 219 * @param topOrder A <code>vertex</code> array to store the index of the 220 * vertex about the top queue 221 * @return If the graph is no circle,indicate the top sort is correct 1 will be return 222 * otherwise will return 0 223 */ 224 int getEarliestDate(adjacentTableGraph graph, vertex topOrder[]) { 225 vertex v; 226 ptrToAdjNode w; 227 int indegree[MAX_VERTEX_NUM], vertexConter = 0; 228 /* 229 * Create a queue to store the vertex whose in-degree is zero 230 */ 231 pQueue queue = createEmptyQueue(); 232 /* 233 * Initialize topOrder 234 */ 235 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 236 indegree[v] = 0; 237 } 238 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 239 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 240 indegree[w->adjVerx]++; 241 } 242 } 243 244 /* 245 * Add in-degree vertex to queue 246 */ 247 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 248 if (indegree[v] == 0) { 249 addQueue(queue, v); 250 graph->g[v].earliest = 0; 251 } 252 } 253 while (!isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 254 v = deleteEleFromQueue(queue); 255 /* 256 * Record the vertex of top sort 257 */ 258 topOrder[vertexConter++] = v; 259 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 260 /* 261 * Update the adjacent vertex‘s earliest 262 */ 263 if ((graph->g[v].earliest + w->weight) 264 > (graph->g[w->adjVerx].earliest)) { 265 graph->g[w->adjVerx].earliest = graph->g[v].earliest 266 + w->weight; 267 } 268 if (--indegree[w->adjVerx] == 0) { 269 addQueue(queue, w->adjVerx); 270 } 271 } 272 } 273 274 /* 275 *Adjust whether all vertexes have been recorded 276 */ 277 if (vertexConter == graph->vertex_number) { 278 return 1; 279 } else { 280 return 0; 281 } 282 } 283 284 /* 285 * Get the earliest max value from all vertex.we search each vertex and find the max earliest 286 * and return 287 * @param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 288 */ 289 int getEarliestTime(adjacentTableGraph graph) { 290 weightType maxTime = -1; 291 vertex v; 292 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 293 if (graph->g[v].earliest > maxTime) { 294 maxTime = graph->g[v].earliest; 295 } 296 } 297 return maxTime; 298 } 299 300 int main() { 301 adjacentTableGraph graph = buildLGraph(1); 302 vertex topOrder[graph->vertex_number]; 303 int bool = getEarliestDate(graph, topOrder); 304 if (bool) { 305 printf("%d\n", getEarliestTime(graph)); 306 } else { 307 printf("Impossible"); 308 } 309 return 0; 310 }
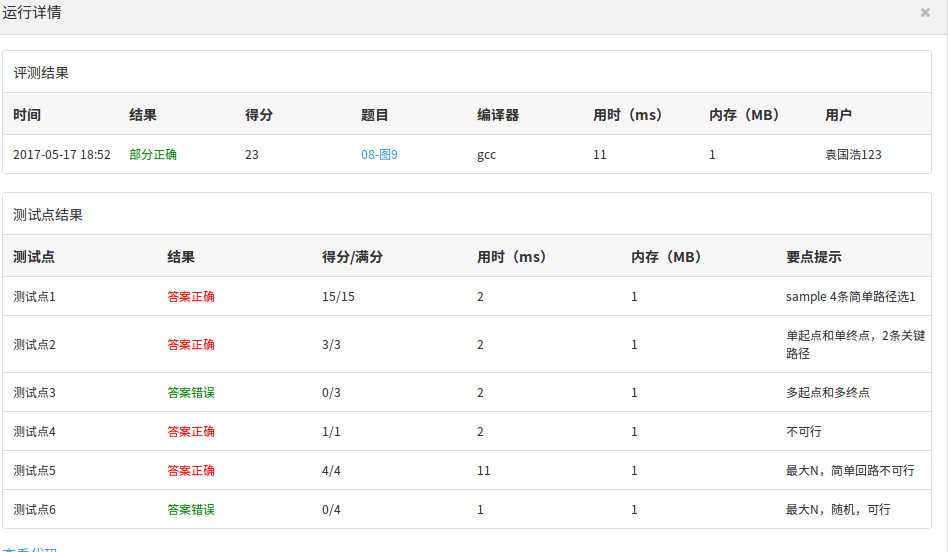
还有一道练习题满分30分,我得了23分,主体算法应该是对的,某些细节方面估计还有点问题
假定一个工程项目由一组子任务构成,子任务之间有的可以并行执行,有的必须在完成了其它一些子任务后才能执行。“任务调度”包括一组子任务、以及每个子任务可以执行所依赖的子任务集。
比如完成一个专业的所有课程学习和毕业设计可以看成一个本科生要完成的一项工程,各门课程可以看成是子任务。有些课程可以同时开设,比如英语和C程序设计,它们没有必须先修哪门的约束;有些课程则不可以同时开设,因为它们有先后的依赖关系,比如C程序设计和数据结构两门课,必须先学习前者。
但是需要注意的是,对一组子任务,并不是任意的任务调度都是一个可行的方案。比如方案中存在“子任务A依赖于子任务B,子任务B依赖于子任务C,子任务C又依赖于子任务A”,那么这三个任务哪个都不能先执行,这就是一个不可行的方案。
任务调度问题中,如果还给出了完成每个子任务需要的时间,则我们可以算出完成整个工程需要的最短时间。在这些子任务中,有些任务即使推迟几天完成,也不会影响全局的工期;但是有些任务必须准时完成,否则整个项目的工期就要因此延误,这种任务就叫“关键活动”。
请编写程序判定一个给定的工程项目的任务调度是否可行;如果该调度方案可行,则计算完成整个工程项目需要的最短时间,并输出所有的关键活动。
输入第1行给出两个正整数N(≤100)和M,其中N是任务交接点(即衔接相互依赖的两个子任务的节点,例如:若任务2要在任务1完成后才开始,则两任务之间必有一个交接点)的数量。交接点按1~N编号,M是子任务的数量,依次编号为1~M。随后M行,每行给出了3个正整数,分别是该任务开始和完成涉及的交接点编号以及该任务所需的时间,整数间用空格分隔。
如果任务调度不可行,则输出0;否则第1行输出完成整个工程项目需要的时间,第2行开始输出所有关键活动,每个关键活动占一行,按格式“V->W”输出,其中V和W为该任务开始和完成涉及的交接点编号。关键活动输出的顺序规则是:任务开始的交接点编号小者优先,起点编号相同时,与输入时任务的顺序相反。
7 81 2 41 3 32 4 53 4 34 5 14 6 65 7 56 7 2
171->22->44->66->7
1.先按照5.1问题计算出每个节点的earliest,并找出最大值,这样就计算出17
2.由于需要输入关键路径,而关键路径的计算和latest有关,我们必须先计算出latest。
3.我们知道,最后完工的顶点出度为0,并且他的earliest等于latest,所以我们先初始化出度为0的latest,让其等于earliest。然后我们找其父节点,让父节点的latest为子节点的latest减去权重(持续时间),去所有子节点中的最小值。这样我们可以成功的计算出每个节点的latest。然后如何判断是关键节点呢。
4.判断是否为关键节点,如果子节点的latest-父节点的earliest-连接边的权重==0
那么这条边为关键路径,否则不是,进行对应的输出即可。
下面是我的代码,没有通过全部测试点,如果你知道原因,可以在下面评论告诉我哦

1 /* 2 * keyPath.c 3 * 4 * Created on: 2017年5月17日 5 * Author: ygh 6 */ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include <stdlib.h> 10 11 #define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 100 /*define the max number of the vertex*/ 12 #define INFINITY 65535 /*define double byte no negitive integer max number is 65535*/ 13 #define ERROR -1 14 15 typedef int vertex; /*define the data type of the vertex*/ 16 typedef int weightType; /*define the data type of the weight*/ 17 typedef char dataType; /*define the data type of the vertex value*/ 18 19 vertex inputOrder[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; 20 /*define the data structure of the Edge*/ 21 typedef struct eNode *ptrToENode; 22 typedef struct eNode { 23 vertex v1, v2; /*two vertex between the edge <v1,v2>*/ 24 weightType weight; /*the value of the edge‘s weight */ 25 }; 26 typedef ptrToENode edge; 27 28 /*==================A adjacent link to describe a graph=========================================*/ 29 /*define the data structure adjacent table node*/ 30 typedef struct adjNode *ptrToAdjNode; 31 typedef struct adjNode { 32 vertex adjVerx; /*the index of the vertex*/ 33 weightType weight; /*the value of the weight*/ 34 ptrToAdjNode next; /*the point to point the next node*/ 35 }; 36 37 /*define the data structure of the adjacent head*/ 38 typedef struct vNode *ptrToVNode; 39 typedef struct vNode { 40 ptrToAdjNode head; /*the point to point the adjacent table node*/ 41 dataType data; /*the space to store the name of the vertex,but some time the vertex has no names*/ 42 weightType earliest; /*The earliest data of the project*/ 43 weightType latest; /*The latest time*/ 44 } adjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; 45 46 /*define the data structure of graph*/ 47 typedef struct gLNode *ptrTogLNode; 48 typedef struct gLNode { 49 int vertex_number; /*the number of the vertex*/ 50 int edge_nunber; /*the number of the edge*/ 51 adjList g; /*adjacent table*/ 52 }; 53 typedef ptrTogLNode adjacentTableGraph; /*a graph show by adjacent table*/ 54 55 /* 56 create a graph given the vertex number. 57 @param vertexNum The verter number of the graph 58 @return a graph with vertex but no any egdgs 59 */ 60 adjacentTableGraph createLGraph(int vertexNum) { 61 adjacentTableGraph graph; 62 63 vertex v; 64 graph = (adjacentTableGraph) malloc(sizeof(struct gLNode)); 65 graph->vertex_number = vertexNum; 66 graph->edge_nunber = 0; 67 /*initialize the adjacent table*/ 68 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 69 graph->g[v].head = NULL; 70 graph->g[v].earliest = 0; 71 graph->g[v].latest = INFINITY; 72 } 73 return graph; 74 } 75 76 /* 77 insert a edge to graph.We will distinct oriented graph and undirected graph 78 The e->v1 and e->v2 are the vertexs‘ indexs in the adjacent table 79 @param graph The graph you want to insert edge 80 @param e The edge you want to insert the graph 81 @param isOriented Whether the graph is oriented graph.If the graph is oriented 82 we will set adjacent table graph[v1]->head=v2 and set graph[v1].head=v2 83 otherwise we only set graph[v1].head=v2 84 */ 85 void insertEdgeToLink(adjacentTableGraph graph, edge e, int isOriented) { 86 /*build node<v1,v2>*/ 87 ptrToAdjNode newNode; 88 newNode = (ptrToAdjNode) malloc(sizeof(struct adjNode)); 89 newNode->adjVerx = e->v2; 90 newNode->weight = e->weight; 91 newNode->next = graph->g[e->v1].head; 92 graph->g[e->v1].head = newNode; 93 /*if the graph is directed graph*/ 94 if (!isOriented) { 95 newNode = (ptrToAdjNode) malloc(sizeof(struct adjNode)); 96 newNode->adjVerx = e->v1; 97 newNode->weight = e->weight; 98 newNode->next = graph->g[e->v2].head; 99 graph->g[e->v2].head = newNode; 100 } 101 } 102 103 /* 104 build a graph stored by adjacent table 105 */ 106 adjacentTableGraph buildLGraph(int isOrdered) { 107 adjacentTableGraph graph; 108 edge e; 109 vertex i; 110 int vertex_num; 111 112 scanf("%d", &vertex_num); 113 graph = createLGraph(vertex_num); 114 scanf("%d", &(graph->edge_nunber)); 115 if (graph->edge_nunber) { 116 e = (edge) malloc(sizeof(struct eNode)); 117 for (i = 0; i < graph->edge_nunber; i++) { 118 scanf("%d %d %d", &e->v1, &e->v2, &e->weight); 119 e->v1--; 120 e->v2--; 121 insertEdgeToLink(graph, e, isOrdered); 122 } 123 } 124 125 return graph; 126 } 127 128 /*==============================define a queue=====================================================*/ 129 /*define a list to store the element in the queue*/ 130 typedef vertex elementType; 131 typedef struct node3 *pList; 132 typedef struct node3 { 133 elementType element; 134 struct node3 *next; 135 }; 136 137 /*define a queue to point the list*/ 138 typedef struct node4 *pQueue; 139 typedef struct node4 { 140 pList front; /*the front point to point the head of the list*/ 141 pList rear; /*the rear point to point the rear of of the list*/ 142 }; 143 144 /*create a empty list to store the queue element*/ 145 pList createEmptyList() { 146 pList list; 147 list = (pList) malloc(sizeof(struct node3)); 148 list->next = NULL; 149 return list; 150 } 151 /*create a empty queye*/ 152 pQueue createEmptyQueue() { 153 pQueue queue = (pQueue) malloc(sizeof(struct node4)); 154 queue->front = NULL; 155 queue->rear = NULL; 156 return queue; 157 } 158 159 /* 160 Wether the queue is empty 161 @param queue The queue need to adjust 162 @return If the queue is null,return 1 otherwise return 0 163 */ 164 int isQueueEmpty(pQueue queue) { 165 return (queue->front == NULL); 166 } 167 168 /* 169 Add a element to a queue,If the queue is null,we will create a new queue 170 @parama queue The queue we will add elememt to 171 @prama element The element we will add to queue 172 */ 173 void addQueue(pQueue queue, elementType element) { 174 if (isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 175 pList list = createEmptyList(); 176 list->element = element; 177 queue->front = queue->rear = list; 178 } else { 179 pList newNode = (pList) malloc(sizeof(struct node3)); 180 newNode->element = element; 181 newNode->next = queue->rear->next; 182 queue->rear->next = newNode; 183 queue->rear = newNode; 184 } 185 } 186 187 /* 188 delete a element from a queue 189 @param queue The queue will be deleted a element 190 @return The element has been deleted 191 */ 192 elementType deleteEleFromQueue(pQueue queue) { 193 if (isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 194 printf("the queue is empty,don‘t allow to delete elemet from it!"); 195 return -1; 196 } else { 197 pList oldNode = queue->front; 198 elementType element = oldNode->element; 199 if (queue->front == queue->rear) { 200 queue->rear = queue->front = NULL; 201 } else { 202 queue->front = queue->front->next; 203 } 204 free(oldNode); 205 return element; 206 } 207 } 208 209 /* 210 * We solve this problem by top sort,but we need to update the adjacent 211 * vertex earliest value at decreasing the adjacent vertex in-degree,the 212 * earliest the max value of parent‘s earliest value add the weight(last time). 213 * The vertex which has no in-degree will set earliest to 0 at first time 214 * 215 * Top sort algorithms thoughts: 216 * 1.we first initialize all vertex in-degree is zero,then we according to 217 * the graph to set the each vertex in-degree. 218 * 2.find zero in-degree vertex and put it in queue. 219 * 3.get a vertex from a queue and record its index 220 * 4.get the all adjacent vertex of the vertex and let them in-degree decrement,at this moment,if 221 * some vertex has decrease into zero,we put them into queue. 222 * 5.Execute this operation until the queue is empty 223 * 224 * @param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 225 * @param topOrder A <code>vertex</code> array to store the index of the 226 * vertex about the top queue 227 * @return If the graph is no circle,indicate the top sort is correct 1 will be return 228 * otherwise will return 0 229 */ 230 int getEarliestDate(adjacentTableGraph graph, vertex topOrder[]) { 231 vertex v; 232 ptrToAdjNode w; 233 int indegree[MAX_VERTEX_NUM], vertexConter = 0; 234 /* 235 * Create a queue to store the vertex whose in-degree is zero 236 */ 237 pQueue queue = createEmptyQueue(); 238 /* 239 * Initialize topOrder 240 */ 241 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 242 indegree[v] = 0; 243 } 244 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 245 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 246 indegree[w->adjVerx]++; 247 } 248 } 249 250 /* 251 * Add in-degree vertex to queue 252 */ 253 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 254 if (indegree[v] == 0) { 255 addQueue(queue, v); 256 graph->g[v].earliest = 0; 257 } 258 } 259 while (!isQueueEmpty(queue)) { 260 v = deleteEleFromQueue(queue); 261 /* 262 * Record the vertex of top sort 263 */ 264 topOrder[vertexConter++] = v; 265 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 266 if ((graph->g[v].earliest + w->weight) 267 > (graph->g[w->adjVerx].earliest)) { 268 graph->g[w->adjVerx].earliest = graph->g[v].earliest 269 + w->weight; 270 } 271 if (--indegree[w->adjVerx] == 0) { 272 addQueue(queue, w->adjVerx); 273 } 274 } 275 } 276 277 /* 278 *Adjust whether all vertexes have been recorded 279 */ 280 if (vertexConter == graph->vertex_number) { 281 return 1; 282 } else { 283 return 0; 284 } 285 } 286 287 /* 288 * You know ,we need to let these vertex whose out-degree is zero 289 * latest equal earliest.These whose out-degree is zero is the vertex which 290 * the project‘s finish vertex 291 * @param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 292 */ 293 void initLatest(adjacentTableGraph graph) { 294 vertex v; 295 ptrToAdjNode w; 296 vertex outdegree[graph->vertex_number]; 297 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 298 outdegree[v] = 0; 299 } 300 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 301 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 302 outdegree[v]++; 303 } 304 } 305 /* 306 *find out-degree vertex and set them latest equal earliest 307 */ 308 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 309 if (outdegree[v] == 0) { 310 graph->g[v].latest = graph->g[v].earliest; 311 } 312 } 313 } 314 315 /* 316 * Calculate the the latest by the earliest and the top sort result 317 * From the class,we can know the latest value is minimal value amount the child vertex‘s latest 318 * minus the weight(we use the weight as the lasting time).Before caller this method,we have 319 * initialize the terminal vertex latest value.You can see the method above. 320 *@param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 321 *@param topOrder a <code>vertex</code> array to store the top sort result 322 * 323 */ 324 void calculateTheLatest(adjacentTableGraph graph, vertex topOrder[]) { 325 int length = graph->vertex_number, i; 326 ptrToAdjNode w; 327 vertex v; 328 for (i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { 329 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 330 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 331 if (w->adjVerx == topOrder[i]) { 332 if (graph->g[v].latest 333 > (graph->g[topOrder[i]].latest - w->weight)) { 334 graph->g[v].latest = graph->g[topOrder[i]].latest 335 - w->weight; 336 } 337 338 } 339 } 340 } 341 } 342 } 343 344 /* 345 * Print the key path,we know when child vertex‘s latest minus parent vertex‘s earliest 346 * and minus the weight(we use the weight as the lasting time),if the result is equal zero 347 * indicating this is key path.we print them. 348 *@param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 349 */ 350 void recordKeyActivity(adjacentTableGraph graph) { 351 vertex v; 352 ptrToAdjNode w; 353 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 354 for (w = graph->g[v].head; w; w = w->next) { 355 if (graph->g[w->adjVerx].latest - graph->g[v].earliest 356 == w->weight) { 357 printf("%d->%d\n", v + 1, w->adjVerx + 1); 358 } 359 } 360 } 361 } 362 363 /* 364 * Get the earliest max value from all vertex.we search each vertex and find the max earliest 365 * and return 366 * @param grap A graph which use adjacent list is used to store the vertex 367 */ 368 int getEarliestTime(adjacentTableGraph graph) { 369 weightType maxTime = -1; 370 vertex v; 371 for (v = 0; v < graph->vertex_number; v++) { 372 if (graph->g[v].earliest > maxTime) { 373 maxTime = graph->g[v].earliest; 374 } 375 } 376 return maxTime; 377 } 378 379 /* 380 * Access graph vertex by the index of the vertex 381 */ 382 void visit(adjacentTableGraph graph, vertex v) { 383 printf("%d %d %d\n", v, graph->g[v].earliest, graph->g[v].latest); 384 } 385 386 /* 387 Depth first search a graph 388 @param graph The graph need to search 389 @param startPoint The fisrt point we start search the graph 390 @paran int *visited The array we use to tag the vertex we has accessed. 391 */ 392 void DFS(adjacentTableGraph graph, vertex startPoint, int *visited) { 393 ptrToAdjNode p; 394 visit(graph, startPoint); 395 visited[startPoint] = 1; 396 for (p = graph->g[startPoint].head; p; p = p->next) { 397 if (visited[p->adjVerx] == 0) { 398 DFS(graph, p->adjVerx, visited); 399 } 400 } 401 } 402 403 /* 404 * Fill a array with value 405 * @param arr The array need to be filled 406 * @param length The length of the array 407 * @param filledValue The value the array will be filled 408 */ 409 void fullArray(int *arr, int length, int filledValue) { 410 int i; 411 for (i = 0; i < length; i++) { 412 arr[i] = filledValue; 413 } 414 } 415 416 int main() { 417 adjacentTableGraph graph = buildLGraph(1); 418 vertex topOrder[graph->vertex_number]; 419 vertex keyActivities[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; 420 int bool = getEarliestDate(graph, topOrder); 421 if (bool) { 422 printf("%d\n", getEarliestTime(graph)); 423 } else { 424 printf("0\n"); 425 } 426 initLatest(graph); 427 calculateTheLatest(graph, topOrder); 428 recordKeyActivity(graph); 429 return 0; 430 }
PTA的测试结果图:
标签:value else who 依赖关系 dfs 权重 图片 add 没有
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yghjava/p/6869332.html