标签:jar text number throw map sys nump 作业 参数
在计算机领域,排序的重要性不用多说。而排序的算法,效率分析等也一直是研究的热点。
本文将给出使用Hadoop分布式方案进行排序的例子,这能极大提高排序的速度,是需要重点掌握的一个案例。
对输入文件中的数据进行排序。
输入文件中的每行内容都是一个数字,要求在输出文件中每行有两个数字,第一个数字代表位次,第二个数字为原始数据。
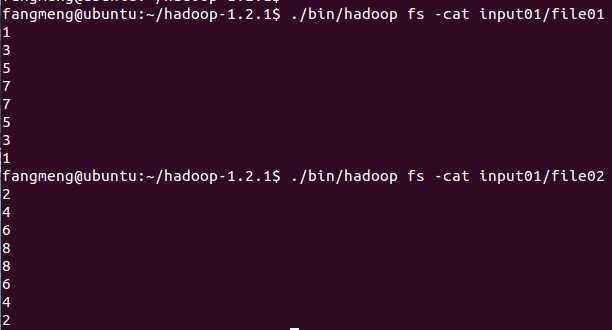
比如文件1包含以下数据:
1
3
5
2
4
6
文件2包含以下数据:
2
4
6
3
1
5
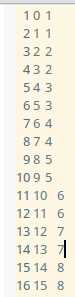
那么输出文件应当为:
1 1
2 1
3 2
4 2
...
表面上看,这是一个非常简单的例子 - Hadoop中存放的键值对本身就是有序的,直接将输入存放进来然后再取出来就完成排序了。
但事实上,直接这样做行不通。为何?因为默认的排序过程是在单个的节点上完成的。也就是说,每个reduce节点收到键值对是在该节点局部有序,而不是在所有reduce节点里全局有序。
解决之道是重写Partition方法,请仔细阅读以下内容:
在shuffle阶段之后(或者说是shuffle最后),将根据map中间输出键值对中的key值来决定将此键值对划分给哪个Partition区间,或者说哪个reduce节点。
可以根据数据的最大最小值将数据划分为多个区间,这样,每个reduce节点就能获取到某个数据段的完整的数据,而且根据hadoop特性,这些数据在单个的reduce节点之内都是有序存放的。
因此每个reduce节点的任务很简单,输出结果就可以了。
至于说位次,只需要在reduce类中声明一个static变量,让这个static变量在不同的reduce调用之间共享就可以了。
要说明的是这里统计的只是数据在每个reduce节点之内的位次,如果要获得全局位次,则需要再遍历一次所有reduce输出文件。时间复杂度仅为O(n)。
1 package org.apache.hadoop.examples; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 //导入各种Hadoop包 6 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 12 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; 13 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 14 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 15 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 16 import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser; 17 18 // 主类 19 public class Sort { 20 21 // Mapper类 22 public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, IntWritable, IntWritable>{ 23 24 // new一个值为1的IntWritable对象 25 private static IntWritable data = new IntWritable(1); 26 27 // 实现map函数 28 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 29 30 // 将切分后的value作为中间输出的key,然后value值为1。 31 String line = value.toString(); 32 data.set(Integer.parseInt(line)); 33 context.write(data, new IntWritable(1)); 34 } 35 } 36 37 // Reducer类 38 public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntWritable, IntWritable, IntWritable, IntWritable> { 39 40 // new一个值为空的IntWritable对象 41 private static IntWritable linenum = new IntWritable(); 42 43 // 实现reduce函数 44 public void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 45 46 // 写入结果键值对 47 for (IntWritable val : values) { 48 context.write(linenum, key); 49 linenum = new IntWritable(linenum.get()+1); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 54 // 重写Partitioner类 55 public static class Partition extends Partitioner <IntWritable, IntWritable> { 56 57 // 重载getPartition方法。下面的三个参数分别为map中间输出的键,值,以及分割区间的个数。 58 public int getPartition(IntWritable key, IntWritable value, int numPartitions) { 59 60 // 依次将键值对分配到各个分割区间 61 int MaxNumber = 65223; 62 int bound = MaxNumber/numPartitions + 1; 63 int keynumber = key.get(); 64 65 for (int i=0; i<numPartitions; i++) { 66 if (keynumber < bound * (i+1) && keynumber >= bound*i) { 67 68 // 返回的 i 就是分配到的区间号 69 return i; 70 } 71 } 72 73 return -1; 74 } 75 } 76 77 // 主函数 78 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 79 80 // 获取配置参数 81 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 82 String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs(); 83 84 // 检查命令语法 85 if (otherArgs.length != 2) { 86 System.err.println("Usage: Dedup <in> <out>"); 87 System.exit(2); 88 } 89 90 // 定义作业对象 91 Job job = new Job(conf, "Sort"); 92 // 注册分布式类 93 job.setJarByClass(Sort.class); 94 // 注册Mapper类 95 job.setMapperClass(Map.class); 96 // 注册Reducer类 97 job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class); 98 // 注册Partition类 99 job.setPartitionerClass(Partition.class); 100 // 注册输出格式类 101 job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); 102 job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); 103 // 设置输入输出路径 104 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0])); 105 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); 106 107 // 运行程序 108 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); 109 } 110 }
输入文件1,2分别为:
1. 掌握Partitioner方法的重写技巧,这是本程序最核心的部分。
2. 熟悉hadoop的key默认有序的性质。
3. 本文采取的是伪分布式,故只有1个reduce节点,体现不出hadoop的优越性。当对海量数据进行排序的时候,它的速度价值才能真正体现出来。
标签:jar text number throw map sys nump 作业 参数
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/muchen/p/6881607.html