标签:array body soft and border app type bind except
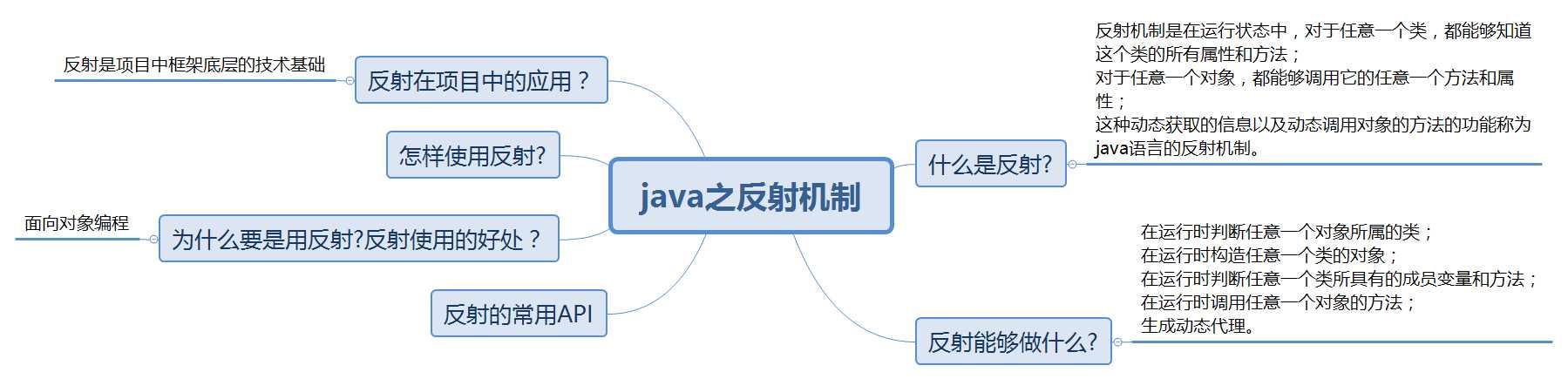
1.反射机制的定义
反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;
对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;
这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
2.反射能做什么
在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类;
在运行时构造任意一个类的对象;
在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法;
在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法;
生成动态代理。
3.反射的常用API
//通过一个对象获得完整的包名和类名 public static void main(String[] args) { ReflectDemo reflectDemo = new ReflectDemo(); System.out.println(reflectDemo.getClass().getName()); /** * 运行结果: * org.xiaowu.reflect.test.ReflectDemo * */ }
//实例化Class类对象
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> class1 = null; Class<?> class2 = null; Class<?> class3 = null; // 一般采用这种形式 class1 = Class.forName("org.xiaowu.reflect.test.ReflectDemo"); class2 = new ReflectDemo().getClass(); class3 = ReflectDemo.class; System.out.println("类名称 " + class1.getName()); System.out.println("类名称 " + class2.getName()); System.out.println("类名称 " + class3.getName()); }
获取一个对象的父类和其实现的方法 package org.xiaowu.reflect.test; import java.io.Serializable; public class ReflectDemo6 implements Serializable { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("org.xiaowu.reflect.test.ReflectDemo6"); // 取得父类 Class<?> parentClass = clazz.getSuperclass(); System.out.println("clazz的父类为:" + parentClass.getName()); // clazz的父类为: java.lang.Object // 获取所有的接口 Class<?> intes[] = clazz.getInterfaces(); System.out.println("clazz实现的接口有:"); for (int i = 0; i < intes.length; i++) { System.out.println((i + 1) + ":" + intes[i].getName()); } // clazz实现的接口有: // 1:java.io.Serializable } }
//获取某个类的全部方法 package org.xiaowu.reflect.test; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Modifier; public class TestReflect1 implements Serializable{ /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("org.xiaowu.reflect.test.TestReflect1"); Method method[] = clazz.getMethods(); for (int i = 0; i < method.length; ++i) { Class<?> returnType = method[i].getReturnType(); Class<?> para[] = method[i].getParameterTypes(); int temp = method[i].getModifiers(); System.out.print(Modifier.toString(temp) + " "); System.out.print(returnType.getName() + " "); System.out.print(method[i].getName() + " "); System.out.print("("); for (int j = 0; j < para.length; ++j) { System.out.print(para[j].getName() + " " + "arg" + j); if (j < para.length - 1) { System.out.print(","); } } Class<?> exce[] = method[i].getExceptionTypes(); if (exce.length > 0) { System.out.print(") throws "); for (int k = 0; k < exce.length; ++k) { System.out.print(exce[k].getName() + " "); if (k < exce.length - 1) { System.out.print(","); } } } else { System.out.print(")"); } System.out.println(); } } }
//通过反射机制调用某个类的方法 package org.xiaowu.reflect.test; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class TestReflect2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("org.xiaowu.reflect.test.TestReflect2"); // 调用TestReflect类中的reflect1方法 Method method = clazz.getMethod("reflect1"); method.invoke(clazz.newInstance()); // Java 反射机制 - 调用某个类的方法1. // 调用TestReflect的reflect2方法 method = clazz.getMethod("reflect2", int.class, String.class); method.invoke(clazz.newInstance(), 20, "张三"); // Java 反射机制 - 调用某个类的方法2. // age -> 20. name -> 张三 } public void reflect1() { System.out.println("Java 反射机制 - 调用某个类的方法1."); } public void reflect2(int age, String name) { System.out.println("Java 反射机制 - 调用某个类的方法2."); System.out.println("age -> " + age + ". name -> " + name); } }
//通过反射机制操作某个类的属性 package org.xiaowu.reflect.test; import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class TestReflect3 { private String proprety = null; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("org.xiaowu.reflect.test.TestReflect3"); Object obj = clazz.newInstance(); // 可以直接对 private 的属性赋值 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("proprety"); field.setAccessible(true); field.set(obj, "Java反射机制"); System.out.println(field.get(obj)); } }
反射机制实现动态代理 package org.xiaowu.reflect.demo; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; //定义项目接口 interface Subject { public String say(String name, int age); } // 定义接口实现类 class RealSubject implements Subject { public String say(String name, int age) { return name + " " + age; } } class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { private Object obj = null; public Object bind(Object obj) { this.obj = obj; return Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj.getClass().getInterfaces(), this); } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object temp = method.invoke(this.obj, args); return temp; } } /** * 在java中有三种类类加载器。 * * 1)Bootstrap ClassLoader 此加载器采用c++编写,一般开发中很少见。 * * 2)Extension ClassLoader 用来进行扩展类的加载,一般对应的是jrelibext目录中的类 * * 3)AppClassLoader 加载classpath指定的类,是最常用的加载器。同时也是java中默认的加载器。 * * 如果想要完成动态代理,首先需要定义一个InvocationHandler接口的子类,已完成代理的具体操作。 * * @author xsoftlab.net * */ public class TestReflect { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { MyInvocationHandler demo = new MyInvocationHandler(); Subject sub = (Subject) demo.bind(new RealSubject()); String info = sub.say("Rollen", 20); System.out.println(info); } }
//反射机制的应用实例 package org.xiaowu.reflect.demo; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; public class TestReflect1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException { ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); Method method = list.getClass().getMethod("add", Object.class); method.invoke(list, "Java反射机制实例。"); System.out.println(list.get(0)); System.out.println(list); } }
//通过反射取得并修改数组的信息 package org.xiaowu.reflect.demo; import java.lang.reflect.Array; public class TestReflect2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] temp = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; Class<?> demo = temp.getClass().getComponentType(); System.out.println("数组类型: " + demo.getName()); System.out.println("数组长度 " + Array.getLength(temp)); System.out.println("数组的第一个元素: " + Array.get(temp, 0)); Array.set(temp, 0, 100); System.out.println("修改之后数组第一个元素为: " + Array.get(temp, 0)); } }
//通过反射机制修改数组的大小 package org.xiaowu.reflect.demo; import java.lang.reflect.Array; public class TestReflect3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { int[] temp = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; int[] newTemp = (int[]) arrayInc(temp, 15); print(newTemp); String[] atr = { "a", "b", "c" }; String[] str1 = (String[]) arrayInc(atr, 8); print(str1); } // 修改数组大小 public static Object arrayInc(Object obj, int len) { Class<?> arr = obj.getClass().getComponentType(); Object newArr = Array.newInstance(arr, len); int co = Array.getLength(obj); System.arraycopy(obj, 0, newArr, 0, co); return newArr; } // 打印 public static void print(Object obj) { Class<?> c = obj.getClass(); if (!c.isArray()) { return; } System.out.println("数组长度为: " + Array.getLength(obj)); for (int i = 0; i < Array.getLength(obj); i++) { System.out.print(Array.get(obj, i) + " "); } System.out.println(); } }
java反射在工厂模式中的应用 package org.xiaowu.reflect.demo; interface fruit { public abstract void eat(); } class Apple implements fruit { public void eat() { System.out.println("Apple"); } } class Orange implements fruit { public void eat() { System.out.println("Orange"); } } class Factory { public static fruit getInstance(String ClassName) { fruit f = null; try { f = (fruit) Class.forName(ClassName).newInstance(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return f; } } /** * 对于普通的工厂模式当我们在添加一个子类的时候,就需要对应的修改工厂类。 当我们添加很多的子类的时候,会很麻烦。 * Java 工厂模式可以参考 * http://baike.xsoftlab.net/view/java-factory-pattern * * 现在我们利用反射机制实现工厂模式,可以在不修改工厂类的情况下添加任意多个子类。 * * 但是有一点仍然很麻烦,就是需要知道完整的包名和类名,这里可以使用properties配置文件来完成。 * * java 读取 properties 配置文件 的方法可以参考 * http://baike.xsoftlab.net/view/java-read-the-properties-configuration-file * * @author xsoftlab.net */ public class TestReflect4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { fruit f = Factory.getInstance("org.xiaowu.reflect.demo.Apple"); if (f != null) { f.eat(); System.out.println("-------------"); } } }
4.为什么要使用反射?使用反射的好处?
这样我们就可以获得类的各种内容,进行了反编译。对于JAVA这种先编译再运行的语言来说,反射机制可以使代码更加灵活,更加容易实现面向对象。
5.怎样使用反射?
|
方法关键字 |
含义 |
|
getDeclaredMethods() |
获取所有的方法 |
|
getReturnType() |
获得方法的放回类型 |
|
getParameterTypes() |
获得方法的传入参数类型 |
|
getDeclaredMethod("方法名",参数类型.class,……) |
获得特定的方法 |
|
|
|
|
构造方法关键字 |
含义 |
|
getDeclaredConstructors() |
获取所有的构造方法 |
|
getDeclaredConstructor(参数类型.class,……) |
获取特定的构造方法 |
|
|
|
|
父类和父接口 |
含义 |
|
getSuperclass() |
获取某类的父类 |
|
getInterfaces() |
获取某类实现的接口 |
6.反射在我们项目中的应用?
配置文件---.properties,称作属性文件。通过反射读取里边的内容。这样代码是固定的,但是配置文件的内容我们可以改,这样使我们的代码灵活了很多!
思维导图:
标签:array body soft and border app type bind except
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mr-wuxiansheng/p/6918130.html