标签:格式化 for 递归 创建 ini lap 程序 方法 closed
提笔写初体验总不知道从何说起,直接聊PHP中的函数、PHP网络技术、数据库操作、PHP模板等感觉又不是初体验。最后还是决定从PHP的面向对象、PHP的魔术方法、PHP的反射、PHP中的异常和错误这4个方面简单介绍一下。
这里我们就不给面向对象下定义了,不过我们还是要说一下类和对象的。类是对象的抽象组织,对象是类的具体存在。接下来我们就拿PHP为例,来探讨一下对象的“形”与“本”的问题。
在PHP中,每个类的定义都是以关键字class开头,后面是类名和一对花括号,括号中包含类成员和方法的定义。如下是一个简单类的定义:

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function sayHello(){ echo "My name is $this->name and I am $this->age years old. I am a $this->sex.\r\n"; echo self::$information; echo "<br>"; } } $person = new Person(); $person->name = ‘Lisi‘; $person->sayHello(); echo serialize($person); //输出结果如下: //My name is Lisi and I am 23 years old. I am a male. I come from the earth //O:6:"Person":3:{s:4:"name";s:4:"Lisi";s:11:"Personage";i:23;s:11:"Personsex";s:4:"male";}
当把类对象序列化输出时,可以看出类对象在存储时类似于数组的形式。那么类对象与数组从本质上又有什么区别与联系呢?接下来从对象“本”来分析一下PHP对对象的底层实现。如下是PHP源码中对变量的定义:

#变量定义 typedef struct _zval_struct zeal; //存储变量的类型 struct _zval_struct { /* Variable information */ zvalue_value value; /* 存储变量的值 */ zend_uint refcount; /* 变量引用数 */ zend_uchar type; /* 变量类型 */ zend_uchar is_ref; /* 变量是否被引用 */ }; typedef union _zvalue_value { long lval; /* 长整型 */ double dval; /* double型 */ struct { char *val; int len; } str; /* String型 */ HashTable *ht; /* array型 */ zend_object_value obj; /* 对象型 */ } zvalue_value; #对象底层实现 typedef struct _zend_object { zend_class_entry *ce; //类入口,存储该对象的类结构,相当于类指针 HashTable *properties; //对象属性组成的HashTable HashTable *guards; /* 阻止递归调用 */ } zend_object; typedef struct _zend_guard { zend_bool in_get; zend_bool in_set; zend_bool in_unset; zend_bool in_isset; zend_bool dummy; /* sizeof(zend_guard) must not be equal to sizeof(void*) */ } zend_guard; //由于zend_class_entry源码较多且复杂,因此此处省略。
通过上面的代码我们也对PHP如何存储对象有了初步的认识,那对象与数组又是什么关系呢?通过PHP的源码可得,zvalue_object结构中有一个HashTable的类型,它就是存储数组的。PHP对象的结构体中不仅有HashTable(用于存储类对象特有的属性),而且还有对象所属类的入口等,如下是PHP对象的组成:
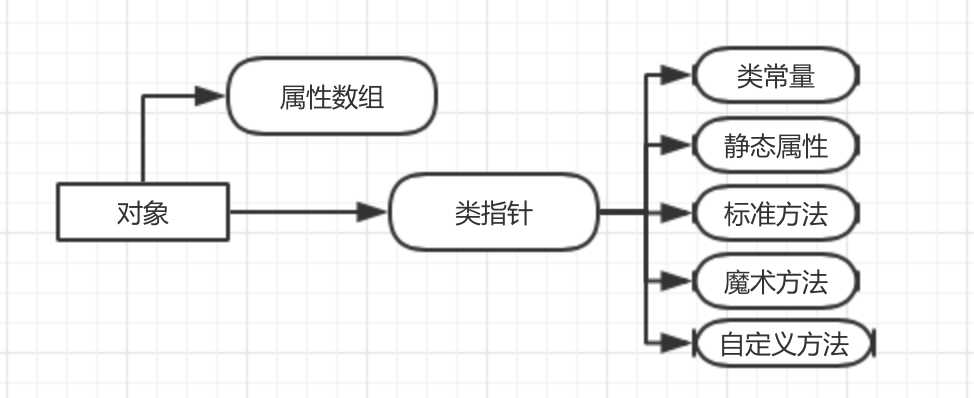 其中PHP源码中zend_class_entry结构体中存储的就是类的指针,该结构体中包含类常量、静态属性、标准方法、魔术方法、自定义方法等。而属性数组存储的是类对象的属性。接下来我们还是以如上的Person类为例,谈一谈对象与数组:
其中PHP源码中zend_class_entry结构体中存储的就是类的指针,该结构体中包含类常量、静态属性、标准方法、魔术方法、自定义方法等。而属性数组存储的是类对象的属性。接下来我们还是以如上的Person类为例,谈一谈对象与数组:
class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } } $person = new Person(); $person_arr = array("name"=>"zhangsan", "age"=>"23", "sex"=>"male"); echo serialize($person); echo "<br>"; //输出对象序列化结果并换行符 echo serialize($person_arr); echo "<br>"; //输出数组序列化结果并换行 $object = (object)$person_arr; //将数组转化为对象 echo serialize($object); //输出数组序转化为对象的序列化结果 /*输出结果如下: O:6:"Person":3:{s:4:"name";s:8:"zhangsan";s:11:"Personage";i:23;s:11:"Personsex";s:4:"male";} a:3:{s:4:"name";s:8:"zhangsan";s:3:"age";s:2:"23";s:3:"sex";s:4:"male";} O:8:"stdClass":3:{s:4:"name";s:8:"zhangsan";s:3:"age";s:2:"23";s:3:"sex";s:4:"male";} 结果解释如下: O代表的是对象,a代表的是数组, O后的数字(6和8)代表该对象所属类名的长度,紧挨在数字后面的就是类名 类名后面的数字为类对象属性的个数,如上有3个,分别为name,age,sex 大括号中的为对象或数组的属性名和属性值的键值对,其中s代表字符串 最后需要说明的是当把数组转化为对象时,因为没有与数组转换成对象对应的类,因此PHP中一个称为"孤儿"的类stdClass类就会收留这个对象 */
可能细心的你在对象组成的那张图中看到了魔术方法,但是上一节中并没有对zend_class_entry中的内容做任何介绍。那么什么又是魔术方法呢?魔术方法就是以两个下划线“__”开头、具有一些特殊作用的方法。其实如上的Person类中,我们不经意间就使用了魔术方法__construct(),这个魔术方法就是构造方法。用于在创建类对象时对属性进行赋值。接下来我们将介绍几个常见的魔术方法让大家对魔术方法有个初步了解。

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function __sleep() { // TODO: Implement __sleep() method return array("name","age"); //该方法指定仅序列化对象的name和age属性 } public function __wakeup() { // TODO: Implement __wakeup() method. var_dump($this->name); //打印输出对象的name属性的值 var_dump($this->sex); //打印输出对象的sex属性的值,由于sex没有被序列化,因此输出null } } $serResult = serialize(new Person()); //序列化一个Person类对象,该方法完成前先调用Person类的__sleep() echo $serResult; echo "<br>"; //输出对象序列化结果并换行符 $unSerResult = unserialize($serResult); //将序列化结果反序列化,该方法完成前调用Person类的__wakeup方法 echo $unSerResult->name; echo "<br>"; //由反序列化得到的Person类对象调用对象的name属性 echo var_dump($unSerResult); echo "<br>"; //输出反序列化得到的Person类对象 /*输出结果如下: O:6:"Person":2:{s:4:"name";s:8:"zhangsan";s:11:"Personage";i:23;} string(8) "zhangsan" NULL zhangsan object(Person)#1 (3) { ["name"]=> string(8) "zhangsan" ["age":"Person":private]=> int(23) ["sex":"Person":private]=> NULL } */

1 class Person { 2 public $name; 3 private $age; 4 private $sex; 5 public static $information = "I come from the earth"; 6 public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { 7 $this->sex = $sex; 8 $this->age = $age; 9 $this->name = $name; 10 } 11 public function __destruct() { 12 // TODO: Implement __destruct() method. 13 echo "The object will be destructed"; 14 } 15 } 16 17 $person = new Person(); 18 unset($person); //unset()方法释放$person对象 19 echo $person->name; //该行试图打印$person对象的name属性值,由于$person对象已经被销毁了,因此该行会报错 20 /* 21 输出结果如下: 22 The object will be destructed 23 Notice: Undefined variable: person in /Users/zhangshilei/PhpstormProjects/untitled/demo/Person.php on line 19 24 25 Notice: Trying to get property of non-object in /Users/zhangshilei/PhpstormProjects/untitled/demo/Person.php on line 19 26 */

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function __get($field) { // TODO: Implement __get() method. echo "the get method is executed<br>"; return $this->$field; } public function __set($key, $value) { // TODO: Implement __set() method. echo "The set method is executed<br>"; $this->$key = $value; } } $person = new Person(); $person->name="Lisi"; echo $person->name; echo "<br>"; $person->age = 25; //age作为$person的私有属性,如果没有__set()方法此句会报错 echo $person->age; //没有__get()方法,此句会报错,如果__get()方法中没有return语句,该句没有返回值 /*输出结果如下: Lisi The set method is executed the get method is executed 25 结果解释如下: 不知道大家注意到了没有,设置公有属性name的值没有调用__set()方法,读取公有属性name的值没有调用__get()方法 只有在设置和读取私有属性age的值才调用了__get()和__set()方法 */

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function __call($name, $arguments) { // TODO: Implement __call() method. echo "被调用方法的名称为:$name<br>"; echo "传入该方法的参数为:", var_dump($arguments),"<br>"; } public static function __callStatic($name, $arguments) { // TODO: Implement __callStatic() method. echo "被调用静态方法的名称为:$name<br>"; echo "传入该方法的参数为:", var_dump($arguments),"<br>"; } } $person = new Person(); $person->shopping("clothes","fruit","snack"); Person::travel("Beijing","Pair","London","Prussia"); /* 输出结果为: 被调用方法的名称为:shopping 传入该方法的参数为:array(3) { [0]=> string(7) "clothes" [1]=> string(5) "fruit" [2]=> string(5) "snack" } 被调用静态方法的名称为:travel 传入该方法的参数为:array(4) { [0]=> string(7) "Beijing" [1]=> string(4) "Pair" [2]=> string(6) "London" [3]=> string(7) "Prussia" } */

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function __toString() { // TODO: Implement __toString() method. return "My name is $this->name.<br> I am $this->age years old and I am a $this->sex."; } } $person = new Person(); echo $person; /* 输出结果如下: My name is zhangsan. I am 23 years old and I am a male. */
关于PHP的魔术方法我们就简单介绍到这里,由上我们可以看出从构造方法上,PHP相比于还稍有欠缺,但PHP中有__set()和__get(),使得动态增加对象的属性字段变得更加方便,而对于Java来说要实现类似的效果,就不得不借助反射API或直接修改编译后字节码的方式实现了。Java中有反射机制,那么PHP中呢?接下来让我们来看一看PHP中的反射实现。
反射,直观的理解就是根据到达地找到出发地和来源。比如给出一个对象就可以找到对象所属的类、拥有哪些方法。反射可以在PHP运行状态中,扩展分析PHP程序,导出或提取出关于类、方法、属性、参数等的详细信息,这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为反射API。

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function __sleep() { // TODO: Implement __sleep() method return array("name","age"); //该方法指定仅序列化对象的name和age属性 } public function __wakeup() { // TODO: Implement __wakeup() method. var_dump($this->name); //打印输出对象的name属性的值 var_dump($this->sex); //打印输出对象的sex属性的值,由于sex没有被序列化,因此输出null } public function __destruct() { // TODO: Implement __destruct() method. echo "The object will be destructed"; } public function __get($field) { // TODO: Implement __get() method. echo "the get method is executed<br>"; return $this->$field; } public function __set($key, $value) { // TODO: Implement __set() method. echo "The set method is executed<br>"; $this->$key = $value; } public function __call($name, $arguments) { // TODO: Implement __call() method. echo "被调用方法的名称为:$name<br>"; echo "传入该方法的参数为:", var_dump($arguments),"<br>"; } public static function __callStatic($name, $arguments) { // TODO: Implement __callStatic() method. echo "被调用方法的名称为:$name<br>"; echo "传入该方法的参数为:", var_dump($arguments),"<br>"; } public function __toString() { // TODO: Implement __toString() method. return "My name is $this->name.<br> I am $this->age years old and I am a $this->sex."; } public function sayHello($other){ echo "My name is $this->name, nice to meet you $other"; } } $person = new Person(); $reflect = new ReflectionObject($person); $props = $reflect->getProperties(); //获取对象的属性列表(所有属性) foreach ($props as $prop){ //打印类中属性列表 echo $prop->getName(),"\r"; } echo "<br>"; $methods = $reflect->getMethods(); //获取类的方法列表 foreach ($methods as $method){ echo $method->getName(),"\r"; } echo "<br>"; //返回对象属性的关联数组 var_dump(get_object_vars($person)); echo "<br>"; //返回类的公有属性的关联数组 var_dump(get_class_vars(get_class($person))); echo "<br>"; //获取类的方法名组成的数组 var_dump(get_class_methods(get_class($person))); /*输出结果如下: name age sex information __construct __sleep __wakeup __destruct __get __set __call __callStatic __toString sayHello array(1) { ["name"]=> string(8) "zhangsan" } array(2) { ["name"]=> NULL ["information"]=> string(21) "I come from the earth" } array(10) { [0]=> string(11) "__construct" [1]=> string(7) "__sleep" [2]=> string(8) "__wakeup" [3]=> string(10) "__destruct" [4]=> string(5) "__get" [5]=> string(5) "__set" [6]=> string(6) "__call" [7]=> string(12) "__callStatic" [8]=> string(10) "__toString" [9]=> string(8) "sayHello" } */
如上代码中介绍的是通过对象获取类的方法和属性字段,而反射不仅仅可以用于类和对象,还可以用于函数、扩展模块、异常等。既然反射可以探知类的内部结构,那么就可以利用反射机制实现插件的功能,也可以利用反射机制实现动态代理。接下来举个简单的例子看看如何通过反射机制实现动态代理。

class Person { public $name; private $age; private $sex; public static $information = "I come from the earth"; public function __construct($name="zhangsan", $age=23, $sex="male") { $this->sex = $sex; $this->age = $age; $this->name = $name; } public function sayHello($other){ echo "My name is $this->name, nice to meet you ".implode("",$other)."<br>"; } } class Dynamicproxy{ private $target; public function __construct($className) { //为动态代理传入类名称,则自动生成类对象 $this->target = new $className(); } public function __call($name, $arguments) { // TODO: Implement __call() method. $reflect = new ReflectionObject($this->target); if($method = $reflect->getMethod($name)){ //获取名称为$name的类方法 if($method->isPublic() && !$method->isAbstract()){ echo "Before the method ".$method->getName()." we should do something<br>"; $method->invoke($this->target,$arguments); echo "After the method ".$method->getName()." we should do something<br>"; } } } } $objProxy = new Dynamicproxy("Person"); $objProxy->sayHello("Janny"); /* 输出结果如下: Before the method sayHello we should do something My name is zhangsan, nice to meet you Janny After the method sayHello we should do something */
如上的代码中真正实现sayHello()动作的是Person类中的sayHello()方法,而Dynamicproxy仅是一个代理类,其中并没有定义sayHello()方法,而是通过__call()方法动态调用类Person的sayHello()方法。在DynamicProxy类中可以做sayHello()方法的前后拦截,并且可以动态的改变类中的方法和属性。很多时候,善用反射可以保持代码的优雅和简洁,但反射也会破坏类的封装性,因为反射可以使本不应该暴露的方法或属性被强制暴露了出来。
在语言级别通常有许多错误处理模式,但这些模式往往建立在约定俗称的基础上,也就是错误都是可预知的。不同的语言对异常和错误的定义也是不一样的,在PHP中,遇到任何自身错误都会触发一个错误,而不是抛出异常。也就是说PHP一旦遇到非正常代码,通常都会触发错误,而不是抛出异常。因此如果想使用异常处理不可预料的问题,是办不到的。比如,想在文件不存在或数据库无法建立连接时触发异常,是不可行的。PHP会把这些作为错误抛出,而不是作为异常捕获。还是回到PHP的错误处理上,PHP中的错误级别大致分为以下几类:

function showError(){ $date = ‘2017-06-05‘; if(ereg("([0-9]{4})-([0-9]{1,2})-([0-9]{1,2})",$date,$regs)){ //deprecated级别错误 echo $regs[3].$regs[2].$regs[1]; }else{ echo "Invalid date format: $date"; } if($value > 5){ //notice级别的错误 echo "It is amazing, the variable $value is not init",PHP_EOL; } $a = array(‘o‘=>2,4,6,8); echo $a[o]; //notice级别的错误 $sum = array_sum($a,3); //warning级别的错误,传入参数不正确 echo fun(); //fetal error echo "the code is after fetal error"; //该句不执行 //echo "prase error:",$55; } showError();
接下来我们看一看针对上边介绍的各个级别的错误PHP是如何处理的。PHP中提供了set_error_handler()函数来处理错误,当然该函数也不是可以托管所有种类的错误,如E_ERROR、E_PARSE、E_CORE_ERROR等错误,这些错误会以原始的方式显示。当然也可以通过restore_error_handler()取消接管:

function DivisionError($errno, $errmsg, $errfile, $errline){ // 获取当前错误时间 $dt = date("Y-m-d H:i:s (T)"); $errortype = array ( E_ERROR => ‘Error‘, E_WARNING => ‘Warning‘, E_PARSE => ‘Parsing Error‘, E_NOTICE => ‘Notice‘, E_CORE_ERROR => ‘Core Error‘, E_CORE_WARNING => ‘Core Warning‘, E_COMPILE_ERROR => ‘Compile Error‘, E_COMPILE_WARNING => ‘Compile Warning‘, E_USER_ERROR => ‘User Error‘, E_USER_WARNING => ‘User Warning‘, E_USER_NOTICE => ‘User Notice‘, E_STRICT => ‘Runtime Notice‘, E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR => ‘Catchable Fatal Error‘ ); $user_errors = array(E_USER_ERROR, E_USER_WARNING, E_USER_NOTICE); $err = "错误时间".$dt."<br>"; $err .= "错误等级".$errno ."<br>"; $err .= "错误等级名称" . $errortype[$errno] . "<br>"; $err .= "错误消息" . $errmsg . "<br>"; $err .= "错误发生所在文件" . $errfile . "<br>"; $err .= "错误所在行" . $errline . "<br>"; echo $err; } set_error_handler("DivisionError"); //当抛出错误时,直接交给DivisionError处理 function showError(){ $date = ‘2017-06-05‘; if(ereg("([0-9]{4})-([0-9]{1,2})-([0-9]{1,2})",$date,$regs)){ //deprecated级别错误 echo $regs[1].$regs[2].$regs[3]; }else{ echo "Invalid date format: $date"; } if($value > 5){ //notice级别的错误 echo "It is amazing, the variable $value is not init",PHP_EOL; } $a = array(‘o‘=>2,4,6,8); echo $a[o]; //notice级别的错误 $sum = array_sum($a,3); echo fun(); //fetal error echo "the code is after fetal error"; //该句不执行 //echo "prase error:",$55; } showError();
如上这种“曲折迂回”的处理方式也存在问题:必须依靠程序员自己来掌控对异常的处理,对于异常高发区、敏感区,如果处理不好就会出现业务数据不一致的问题,但是优点就是可以获得程序运行的上下文信息,以进行针对性补救。
对于代码中存在的异常,需要认为的进行抛出,接下来我们通过自定义一个异常类来处理抛出的异常,

class DivisionException extends Exception{ //自定义异常处理类 public function __toString(){ //覆写父类的__toString(),规定输出格式 $errorMessage = ‘错误发生于文件‘.$this->getFile().‘第‘.$this->getLine().‘行<br>‘ .‘错误原因为‘.$this->getMessage(); return $errorMessage; } } class Calculate { private $num1; private $num2; private $operater; public function __construct($num1, $num2, $operater) { $this->operater = $operater; $this->num1 = $num1; $this->num2 = $num2; } public function getResult() { try { if ($this->operater == "+") { return $this->num1 + $this->num2; } else if ($this->operater == "-") { return $this->num1 - $this->num2; } else if ($this->operater == "*") { return $this->num1 * $this->num2; } else { if($this->num2 == 0){ //如果除数为0则抛出异常 throw new DivisionException("除数不能为0"); } return $this->num1 / $this->num2; } } catch (DivisionException $exception){ echo $exception; } } } $calculate = new Calculate(10,0,"/"); echo $calculate->getResult(); /** 输出结果如下: 错误发生于文件/Users/zhangshilei/PhpstormProjects/untitled/demo/Person.php第98行 错误原因为除数不能为0 */
初体验就为大家介绍到这里吧,以后有机会在深入的去了解PHP函数、PHP与网络、PHP与数据库等等的内容吧。
标签:格式化 for 递归 创建 ini lap 程序 方法 closed
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhanglei93/p/6922596.html