标签:math points line cas 示例 draw parameter move 黑白
从官网下载opencv 目录结构如图
在samples中有丰富的示例
应为我的系统中已经安装好opepncv-python,可直接运行
会得到结果:
人脸检测代码如下
#!/usr/bin/env python
‘‘‘
face detection using haar cascades
USAGE:
facedetect.py [--cascade <cascade_fn>] [--nested-cascade <cascade_fn>] [<video_source>]
‘‘‘
# Python 2/3 compatibility
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
import cv2
# local modules
from video import create_capture
from common import clock, draw_str
def detect(img, cascade):
rects = cascade.detectMultiScale(img, scaleFactor=1.3, minNeighbors=4, minSize=(30, 30),
flags=cv2.CASCADE_SCALE_IMAGE)
if len(rects) == 0:
return []
rects[:,2:] += rects[:,:2]
return rects
def draw_rects(img, rects, color):
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in rects:
cv2.rectangle(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
import sys, getopt
print(__doc__)
args, video_src = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], ‘‘, [‘cascade=‘, ‘nested-cascade=‘])
try:
video_src = video_src[0]
except:
video_src = 0
args = dict(args)
cascade_fn = args.get(‘--cascade‘, "../../data/haarcascades/haarcascade_frontalface_alt.xml")
nested_fn = args.get(‘--nested-cascade‘, "../../data/haarcascades/haarcascade_eye.xml")
cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(cascade_fn)
nested = cv2.CascadeClassifier(nested_fn)
cam = create_capture(video_src, fallback=‘synth:bg=../data/lena.jpg:noise=0.05‘)
while True:
ret, img = cam.read()
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = cv2.equalizeHist(gray)
t = clock()
rects = detect(gray, cascade)
vis = img.copy()
draw_rects(vis, rects, (0, 255, 0))
if not nested.empty():
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in rects:
roi = gray[y1:y2, x1:x2]
vis_roi = vis[y1:y2, x1:x2]
subrects = detect(roi.copy(), nested)
draw_rects(vis_roi, subrects, (255, 0, 0))
dt = clock() - t
draw_str(vis, (20, 20), ‘time: %.1f ms‘ % (dt*1000))
cv2.imshow(‘facedetect‘, vis)
if cv2.waitKey(5) == 27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
其中训练好的分类器在
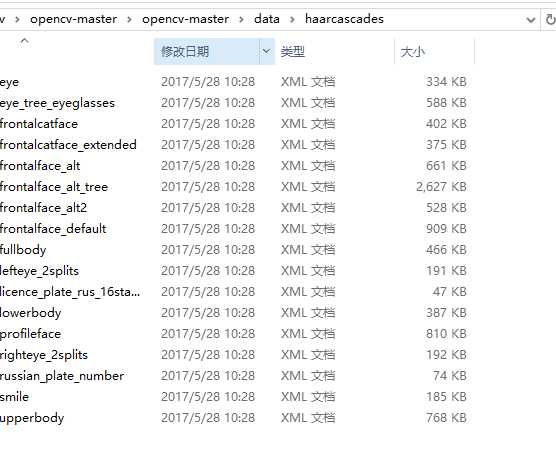
目录下
PS:在树莓派上使用时需要注意,USB接入的摄像头可使用opecv 调用,否则只能用picamera 来调起,
接着时二维码识别
这是资料地址
http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1464566856199.html
上面的这篇博客讲的非常详细和全面,不过没有代码,这里整理了一下方便结合视频的方式检测二维码,
def show(img, code=cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB):
cv_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, code)
while (1):
cv2.imshow(‘ckh‘,img)
key = cv2.waitKey(10)
c = chr(key & 255)
if c in [‘B‘, ‘b‘, chr(27)]:
break
def createLineIterator(P1, P2, img):
"""
Produces and array that consists of the coordinates and intensities of each pixel in a line between two points
Parameters:
-P1: a numpy array that consists of the coordinate of the first point (x,y)
-P2: a numpy array that consists of the coordinate of the second point (x,y)
-img: the image being processed
Returns:
-it: a numpy array that consists of the coordinates and intensities of each pixel in the radii (shape: [numPixels, 3], row = [x,y,intensity])
"""
#define local variables for readability
imageH = img.shape[0]
imageW = img.shape[1]
P1X = P1[0]
P1Y = P1[1]
P2X = P2[0]
P2Y = P2[1]
#difference and absolute difference between points
#used to calculate slope and relative location between points
dX = P2X - P1X
dY = P2Y - P1Y
dXa = np.abs(dX)
dYa = np.abs(dY)
#predefine numpy array for output based on distance between points
itbuffer = np.empty(shape=(np.maximum(dYa,dXa),3),dtype=np.float32)
itbuffer.fill(np.nan)
#Obtain coordinates along the line using a form of Bresenham‘s algorithm
negY = P1Y > P2Y
negX = P1X > P2X
if P1X == P2X: #vertical line segment
itbuffer[:,0] = P1X
if negY:
itbuffer[:,1] = np.arange(P1Y - 1,P1Y - dYa - 1,-1)
else:
itbuffer[:,1] = np.arange(P1Y+1,P1Y+dYa+1)
elif P1Y == P2Y: #horizontal line segment
itbuffer[:,1] = P1Y
if negX:
itbuffer[:,0] = np.arange(P1X-1,P1X-dXa-1,-1)
else:
itbuffer[:,0] = np.arange(P1X+1,P1X+dXa+1)
else: #diagonal line segment
steepSlope = dYa > dXa
if steepSlope:
slope = dX.astype(np.float32)/dY.astype(np.float32)
if negY:
itbuffer[:,1] = np.arange(P1Y-1,P1Y-dYa-1,-1)
else:
itbuffer[:,1] = np.arange(P1Y+1,P1Y+dYa+1)
itbuffer[:,0] = (slope*(itbuffer[:,1]-P1Y)).astype(np.int) + P1X
else:
slope = dY.astype(np.float32)/dX.astype(np.float32)
if negX:
itbuffer[:,0] = np.arange(P1X-1,P1X-dXa-1,-1)
else:
itbuffer[:,0] = np.arange(P1X+1,P1X+dXa+1)
itbuffer[:,1] = (slope*(itbuffer[:,0]-P1X)).astype(np.int) + P1Y
#Remove points outside of image
colX = itbuffer[:,0]
colY = itbuffer[:,1]
itbuffer = itbuffer[(colX >= 0) & (colY >=0) & (colX<imageW) & (colY<imageH)]
#Get intensities from img ndarray
itbuffer[:,2] = img[itbuffer[:,1].astype(np.uint),itbuffer[:,0].astype(np.uint)]
return itbuffer
def isTimingPattern(line):
# 除去开头结尾的白色像素点
while line[0] != 0:
line = line[1:]
while line[-1] != 0:
line = line[:-1]
# 计数连续的黑白像素点
c = []
count = 1
l = line[0]
for p in line[1:]:
if p == l:
count = count + 1
else:
c.append(count)
count = 1
l = p
c.append(count)
# 如果黑白间隔太少,直接排除
if len(c) < 5:
return False
# 计算方差,根据离散程度判断是否是 Timing Pattern
threshold = 5
return np.var(c) < threshold
def cv_distance(P, Q):
return int(np.math.sqrt(pow((P[0] - Q[0]), 2) + pow((P[1] - Q[1]), 2)))
def check(a, b,path):
# 存储 ab 数组里最短的两点的组合
s1_ab = ()
s2_ab = ()
# 存储 ab 数组里最短的两点的距离,用于比较
s1 = np.iinfo(‘i‘).max
s2 = s1
for ai in a:
for bi in b:
d = cv_distance(ai, bi)
if d < s2:
if d < s1:
s1_ab, s2_ab = (ai, bi), s1_ab
s1, s2 = d, s1
else:
s2_ab = (ai, bi)
s2 = d
a1, a2 = s1_ab[0], s2_ab[0]
b1, b2 = s1_ab[1], s2_ab[1]
a1 = (a1[0] + np.int0((a2[0]-a1[0])*1/14), a1[1] + np.int0((a2[1]-a1[1])*1/14))
b1 = (b1[0] + np.int0((b2[0]-b1[0])*1/14), b1[1] + np.int0((b2[1]-b1[1])*1/14))
a2 = (a2[0] + np.int0((a1[0]-a2[0])*1/14), a2[1] + np.int0((a1[1]-a2[1])*1/14))
b2 = (b2[0] + np.int0((b1[0]-b2[0])*1/14), b2[1] + np.int0((b1[1]-b2[1])*1/14))
img = cv2.imread(path)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
th, bi_img = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 将最短的两个线画出来
#cv2.line(draw_img, a1, b1, (0,0,255), 3)
#cv2.line(draw_img, a2, b2, (0,0,255), 3)
lit1 = createLineIterator(a1,b1,bi_img)
lit2 = createLineIterator(a2,b2,bi_img)
if isTimingPattern(lit1[:,2]):
return True
elif isTimingPattern(lit2[:,2]):
return True
else:
return False
def RunImg(path):
img = cv2.imread(path)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_gb = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_gray, (5, 5), 0)
edges = cv2.Canny(img_gray, 100, 200)
img_fc, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(edges, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
hierarchy = hierarchy[0]
found = []
for i in range(len(contours)):
k = i
c = 0
while hierarchy[k][2] != -1:
k = hierarchy[k][2]
c = c + 1 # count hierarchy
if c >= 5:
found.append(i) # store index
# 对图像进行二值化
th, bi_img = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 100, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
draw_img = img.copy()
boxes = []
for i in found:
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[i])
box = np.int0(cv2.boxPoints(rect))
# cv2.drawContours(draw_img,[box], 0, (0,0,255), 2)
# box = map(tuple, box)
box = [tuple(x) for x in box]
boxes.append(box)
# show(draw_img)
# print("Length of Boxes is ",len(boxes))
valid = set()
for i in range(len(boxes)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(boxes)):
if check(boxes[i], boxes[j],path):
valid.add(i)
valid.add(j)
contour_all = []
while len(valid) > 0:
c = contours[found[valid.pop()]]
for sublist in c:
for p in sublist:
contour_all.append(p)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(np.array(contour_all))
box = np.array([cv2.boxPoints(rect)], dtype=np.int0)
cv2.polylines(draw_img, box, True, (0, 0, 255), 3)
show(draw_img)
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
RunImg(‘er.jpg‘)
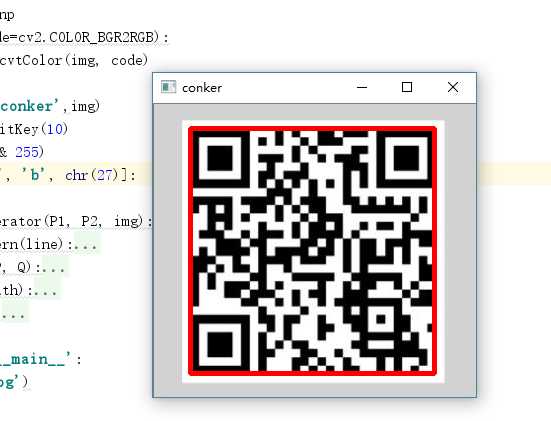
效果很好。
以上
标签:math points line cas 示例 draw parameter move 黑白
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Conker/p/6965106.html