标签:round time exce http 之间 block thread ges for
一、为什么要用线程池
1)、降低资源消耗,通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程的创建和销毁造成的消耗。
2)、提高响应速度,当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。
3)、提高线程的可管理性,线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一的分配,调优和监控。
二、注意
1)、需要对线程池原理了如指掌。
三、线程的常见用法
1)、New Thread。
2)、Thread Pool。
四、New Thread 常见用法
new thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
//TODO anything you need
}
})
作为一个严谨的dev来说,new thread 一般是禁止在代码中使用的,new thread 存在许多弊端,例如:
a)、每次new thread 都创建一个线程,性能差。
b)、线程缺乏统一管理,高并发时线程会无限制的新建,相互之间竞争资源,最终会因为占用过大资源导致死机或oom。
c)、缺乏更多扩展功能,如定时执行、定期执行、线程中断。
五、JAVA 线程池
Java 通过Executor 提供四种线程池,分别为:
newCachedThreadPool 创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则创建新线程。
newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列等待。
newScheduledThreadpool 创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
newSingleThreadExecutor 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO)优先级执行。
a)、newCachedThreadPool
创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。
实例代码:
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int index = i;
try {
Thread.sleep(index * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
cachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(index);
}
});
}
但是看到上面代码,大家会不会有个疑问,上面代码反复执行,不是会创建多个线程池么?
是不是应该把线程池做成单例的?
public class CachedThreadPoolProxy {
public static final ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
}
下面我们来做个Test:
@Test public void test() throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) { final int index = i; ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//ThreadPoolProxy.cachedThreadPool; executor.execute(new Runnable() { public void run() { System.out.println(String.format("当前线程:%d", index)); } }); int activeCount = ((ThreadPoolExecutor) executor).getActiveCount(); System.out.println(String.format("当前线程数量:%d", activeCount)); System.out.println(String.format("当前线程hashCode:%s", executor.hashCode())); } }
运行结果:
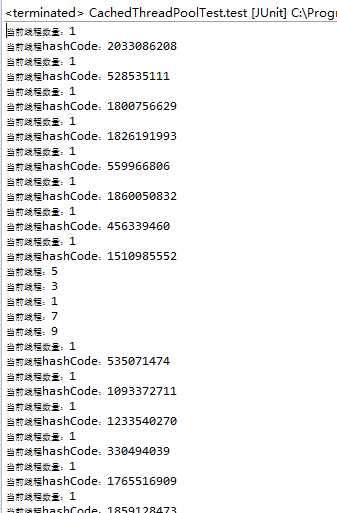
结论:
1、线程池会被多次创建,我们需要把线程池写成单例。
2、线程的执行是无序的。
3、会自动回收空闲线程,无空闲线程时,线程会被不断创建。
b)、newFixedThreadPool
创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
示例代码如下:
@Test
public void test2() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
final int index = i;
ExecutorService executor = ThreadPoolProxy.fixedThreadPool;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(String.format("当前线程:%d", index));
}
});
int activeCount = ((ThreadPoolExecutor) executor).getActiveCount();
int blockCount = ((ThreadPoolExecutor) executor).getQueue().size();
System.out.println(String.format("当前线程数量:%d", activeCount));
System.out.println(String.format("当前线程hashCode:%s", executor.hashCode()));
System.out.println(String.format("当前队列的任务数:%s", blockCount));
}
}
结果示例:

c)、newScheduledThreadPool
创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
延迟执行示例代码如下:
@Test
public void test3() throws InterruptedException {
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);// ThreadPoolProxy.scheduledThreadPool;
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(new Date().getTime());
System.out.println("正在执行。。。。");
}
}, 1, 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
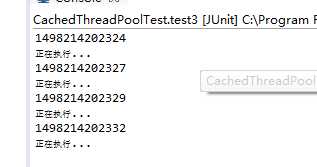
执行上述代码时,发现程序并没有输出,心里当时充满了疑虑,几经测试,发现是因为主线程终止了,schedual 也会停止运行。
@Test
public void test3() throws InterruptedException {
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);// ThreadPoolProxy.scheduledThreadPool;
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(new Date().getTime());
System.out.println("正在执行...");
}
}, 1, 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
Thread.sleep(100000);
}
d)、newSingleThreadExecutor
创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
@Test
public void test4() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executor = ThreadPoolProxy.singleThreadExecutor;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
final int index = i;
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(index);
}
});
}
}
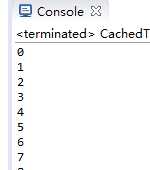
可以看出结果依次输出
PS: 源码
public class ThreadPoolProxy {
public static final ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
public static final ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
public static final ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3);
public static final ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
}
标签:round time exce http 之间 block thread ges for
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaocandou/p/7071335.html