标签:java
之前我们实现了迭代器模式,很多编程语言实际上已经内置了迭代器类,比如Java就为我们实现了迭代器Iterator。我们首先来看Iterator中的源码。
通过JDK源码我们发现Iterator是一个接口,包含三个方法:hasNext、next、remove。

1 package java.util; 2 3 public interface Iterator<E> { 4 5 /** 6 *如果迭代器中还有元素则返回true 7 */ 8 boolean hasNext(); 9 10 /**11 *返回迭代器中的下一个元素12 */13 E next();14 15 /**16 *通过迭代器删除处于集合中最底层的元素17 */18 void remove();19 }
Iterator是一个接口,那如何来创建一个实例呢?要记住,迭代器和集合类的关系非常紧密,我们可以通过集合类来创建一个Iterator实例,ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector都有对它的实现。我们来看ArrayList是如何创建一个Iterator迭代器实例的。在此之前我们先来看看集合和迭代器之间的继承关系。
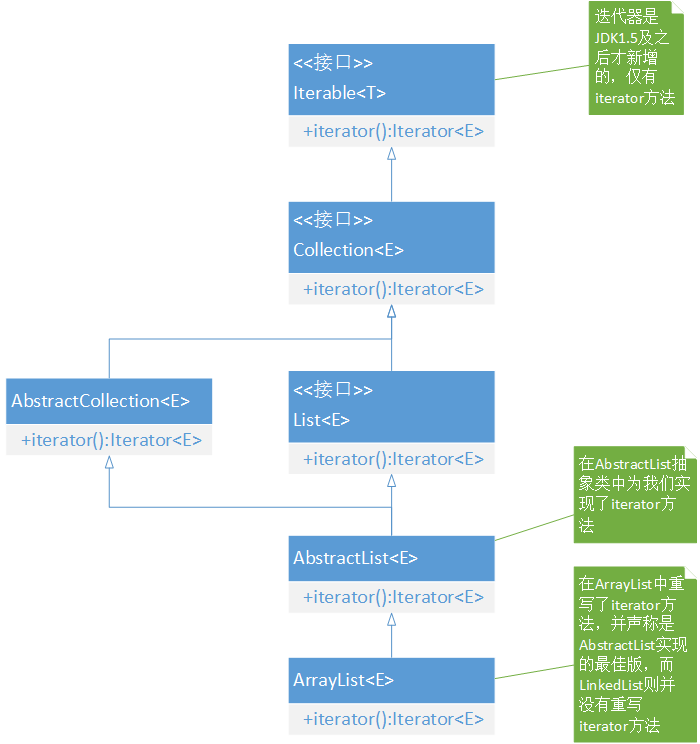
由于集合的关系相对来说比较复杂,在此我们主要看注释部分,通过阅读源代码会发现ArrayList覆写了AbstractList抽象类中的iterator方法并声称效果更佳,而LinkedList则没有覆写,由此可判断ArrayList的iterator方法比LinkedList中的iterator方法更为高效。
我们直接看ArrayList里中实现的iterator方法。
1 public Iterator<E> iterator() {2 return new Itr();3 }从代码来看它返回类一个Itr的对象实例,顺着代码看看这个Itr类是什么。

1 private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { 2 int cursor; // 返回下一个元素的索引 3 int lastRet = -1; // 返回最后一个元素的索引;如果没有则返回-1 4 int expectedModCount = modCount; 5 6 public boolean hasNext() { 7 return cursor != size; 8 } 9 10 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")11 public E next() {12 checkForComodification();13 int i = cursor;14 if (i >= size)15 throw new NoSuchElementException();16 Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;17 if (i >= elementData.length)18 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();19 cursor = i + 1;20 return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];21 }22 23 public void remove() {24 if (lastRet < 0)25 throw new IllegalStateException();26 checkForComodification();27 28 try {29 ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);30 cursor = lastRet;31 lastRet = -1;32 expectedModCount = modCount;33 } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {34 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();35 }36 }37 38 final void checkForComodification() {39 if (modCount != expectedModCount)40 throw new ConcurrentModificationException();41 }42 }
原来Itr它是一个私有的内部类,实现Iterator接口。
我们来一行一行读。在第3行中有一个modCount变量。跟踪这个变量,发现这个变量有点意思:
protected transient int modCount = 0;
发现有一个“transient”关键字,查阅资料发现这个关键字的意思是:表示一个域不是该对象序列化的一部分。意思是在对象被序列化时不包括这个变量,至于为什么要这么做呢,我们可以留下一个疑问。(JDk源码注释中是这么说的:The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing List should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator has detected concurrent modification.英语太次只能读懂最后一句:如果这个期望是可见性的,那么这个迭代器会检测到有一个并发的修改。猜测是和并发多线程相关。)
hasnext的实现较为简单:
1 public boolean hasNext() {2 return cursor != size; //下一个元素的索引是否等于ArrayList的大小3 }next的实现:

public E next() {
checkForComodification(); //检查是否并发修改 int i = cursor; if (i >= size) throw new NoSuchElementException(); //索引大于ArrayList大小抛出异常
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; //后面实际是在取ArrayList中的数据 if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
在next方法中我们看到有一个checkForCommodification方法:
final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}看来这个modCount变量确实是和并发相关,如果expectedModCount和modCount这两个值不同,则抛出当前正在并发修改的异常。
最后我们来看remove方法的实现:

public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) //这个地方格外注意,不能在未调用next时直接调用remove方法,必须在remove调用前调用next方法,将通过cursor索引值将其值赋给lastRet throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification(); try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
在remove方法中我们要格外注意,在第一句是检测lastRet是否小于0,我们初始化了lastRet变量-1的值,这意味着,如果我们如果创建完Iterator实例后直接调用remove方法会抛出一个IllegalStateException异常,那怎么才能正确调用呢?那就是在调用remove方法前先调用next方法,此时lastReturn通过cursor索引被赋值,这个时候才能正确使用remove方法。同时它也会调用checkForCommodification方法做并发修改检测。其实我们可以看到JDK源码之所以写到好,是因为它每个方法都做了很多的检测,以确保在尽量多的场景下准确无误地运行。今天关于Java的迭代器就通过JDK源码简单介绍,通过对源码的阅读能够加深我们的理解,这还只是简单的阅读,并没有做很深的理解。最后,我们以为一个Iterator的例子结尾。

1 package day_29_iterator; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 import java.util.List; 6 7 /** 8 * @author turbo 9 *10 * 2016年9月29日11 */12 public class Main {13 14 /**15 * @param args16 */17 public static void main(String[] args) {18 List list = new ArrayList();19 list.add(1);20 list.add(2);21 Iterator iterator = list.iterator();22 while (iterator.hasNext()){23 System.out.println(iterator.next());24 }25 }26 27 }
标签:java
原文地址:http://12953214.blog.51cto.com/12943214/1942290