Linux Skills
Table of Contents
- 1. How to use ramdisk in Ubuntu and Fedora?
- 2. How to enable ssh server in Ubuntu?
- 3. How to disable CPU in Linux?
- 4. How to disable SELinux in Linux?
- 5. How to deal with the errors in MP3 files in Rythmbox under Ubuntu?
- 6. How to accelerate the ssh connection?
- 7. When something goes wrong in ubuntu ?
- 8. How to umount a filesystem even when it is busy?
- 9. How to sync files without copying the originals when using Cloud Storage?
- 10. How to rename multiple files at a time?
- 11. What is the most amazing ssh option you have encountered?
- 12. When Ubuntu Xsession goes wrong….
- 13. How to change ubuntu Mirror source?
- 14. How to add a new directory to an existing CVS repository?
- 15. How to set up multiple CVSROOT repositories?
- 16. Whether it is possible to copy an existing cvs repository into the new repository?
- 17. How to checkout from a remote repository?
- 18. How to enlarge tmpfs on the go?
- 19. How to rename all the files in a directory to file-1.torrent, file-2.torrent…?
In this post, I will record the daily usage of linux, as well as the ways to resolve the common problems.
1 How to use ramdisk in Ubuntu and Fedora?
In Fedora, the ramdisk is disabled by default, that is, it is compiled into
the kernel, but as a module, which will be loaded into the kernel when
actually used. So, it is necessary to compile the kernel manually to select
the ramdisk as the built-in modules.
In Ubuntu, the ramdisk support is enabled by default, so the steps are easier
compared to Fedora.
Using the following commands to list the ramdisk:
| ls /dev/ram* |
The output will be like:
| /dev/ram0 /dev/ram10 /dev/ram12 /dev/ram14 /dev/ram2 /dev/ram4 /dev/ram6 /dev/ram8 |
| /dev/ram1 /dev/ram11 /dev/ram13 /dev/ram15 /dev/ram3 /dev/ram5 /dev/ram7 /dev/ram9 |
Format the ramdisk as an ext4fs:
| mkfs.ext4 /dev/ram1 |
Then mount it:
| sudo mount /dev/ram1 /mnt |
2 How to enable ssh server in Ubuntu?
By default, Ubuntu doesn‘t install the ssh server, so the following command
will fail:
| ssh localhost |
| ssh: connect to host localhost port 22: Connection refused |
Using the following command to install the ssh-server:
| sudo apt-get install openssh-server |
Then all things will go well.
3 How to disable CPU in Linux?
It is easy to do with real root user:
| echo 0 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuX/online |
The CPU status can be checked by:
| cat /proc/cpuinfo |
To re-enable the CPU:
| echo 1 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuX/online |
4 How to disable SELinux in Linux?
The SELinux has some negative effect on the self-defined filesystem, so it is
necessary to disable it, using the following command:
| sestatus | \\ |
will list the status of the SELinux,
| SELinux status: enabled |
| SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux |
| SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux |
| Loaded policy name: targeted |
| Current mode: enforcing |
| Mode from config file: enforcing |
| Policy MLS status: enabled |
| Policy deny_unknown status: allowed |
| Max kernel policy version: 28 |
To change the status of SELinux, modify the configure file in:
| /etc/selinux/config | \\ |
5 How to deal with the errors in MP3 files in Rythmbox under Ubuntu?
The easiest way is as follows:
| sudo gedit /etc/profile |
Add the following two lines to the end of the file:
| export PATH=$PATH GST_ID3_TAG_ENCODING=GBK:UTF-8:GB18030 |
| export PATH=$PATH GST_ID3V2_TAG_ENCODING=GBK:UTF-8:GB18030 |
This enables the Chinese characters to be recoginized by the system.
6 How to accelerate the ssh connection?
I am working on a project which has something to do with a remote server, and
I have to ssh to that server, but the server is Fedora and my os is Ubuntu,
and it turns out it takes a long time to resove the host/server IP, the
solution to this problem is:
| ssh -o GSSAPIAuthentication=no user@yourserver |
7 When something goes wrong in ubuntu ?
Afer a failed attempt to upgrade the Ubuntu13.10 to Ubuntu 14.04, the system
shows a popup window everytime the system boots, the title of the window is
"System Program Problem Detected". The following method can be used to solve
the problem:
| sudo rm /var/crush/* |
This command will delete the crushed software of the system so that the reporting utility won‘t work, thus eliminating the annoying message.
8 How to umount a filesystem even when it is busy?
Recently, a project requires frequently mounting and testing a filesystem,
and it is very likely that the newly-mounted filesystem will crash for all
kinds of reasons, and after the accident, it is no longer possible to umount
the filesystem in a normal way. The error message from the OS is as follows:
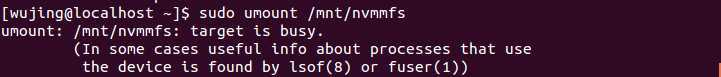
With the -l option of umount, the result can be seen as follows:
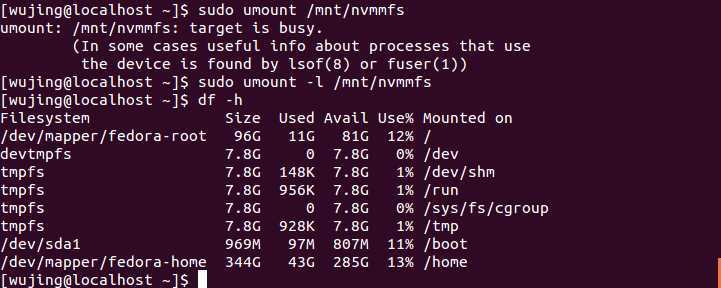
9 How to sync files without copying the originals when using Cloud Storage?
When using CloudDrive, it is likely that the software may only allow you to
synchronize the files or folders under a specific folder, if you have many
other directories to synchronize, you have to copy files, but there is a
simple way to achieve the same goal without copying files—the symbolic
link.
In Linux,the following command can be used to create a symbolic link to
another directory:
| ln -s target-folder link-name |
\
In windows, use the following command:
| mklink /J link-name target-folder |
10 How to rename multiple files at a time?
- Add extention to all the files in a directory:
\
for f in *;do mv "$f" "$f.png";done - Rename:
\
rename ‘s/old-name/new-name/‘ files
11 What is the most amazing ssh option you have encountered?
The first useful option of ssh is the GSSAPIAuthentication=no, which accelerates the connection startup time. Another useful option is the X11 forwarding, with the -X option, you can use the X11 application from the localhost.(Especially for emacs).
12 When Ubuntu Xsession goes wrong….
The problem I encountered is like this:
When I want to logout the xsession of ubuntu, it fails to close all the
running application and return back to the login screen, so I start a
terminal by ALT+CRTL+F1, from which I did a reboot. After the system booted,
I typed my password to my account, but it returned back to the login session
again, and the process continued.
There was some error messages in ~/.xsession-error file, and the mode bits of ~/.xauthority file has changed to root only, so the correct way to deal with the problem is use the following command:
| sudo chmod +x 777 .Xauthority |
13 How to change ubuntu Mirror source?
Copy the existing source configure file to the desired machine,the file is:
| /etc/apt/sources.list |
14 How to add a new directory to an existing CVS repository?
I have a working copy of a cvs-controlled repository, and after I added some
new directories, I failed to add the files in the directories to the version
control system, because the CVS complains that the node corresponding to the
new directory does not exist, the simplest method to solve this problem is the
cvs add command:
| cvs add newdirectory |
Then, in emacs, just type c-x v v, all things will be handled by the smart emacs…
15 How to set up multiple CVSROOT repositories?
The repositories I use on my machine is not under cloud back-up, so I just
want to backup my repositories to my cloud, so I followed the following steps:
- Create and init the new repository but override the existing CVSROOT
environment:
cvs -d /home/wujing/KuaiPan/myrepos init - To make sure that the proper CVSROOT directory is correctly setup, ls the
directory;
- Import the project files into the new CVS repository:
cvs -d /home/wujing/KuaiPan/myrepos import -m "start papers backup" memory_contention wujing start In the above command, the files in the source files in the project directory will be copied into the CVS/memory_contention directory.
- Backup the original files and checkout the versioned files from the cvs
repository:
cvs -d /home/wujing/KuaiPan/myrepos co memory_contention Be sure to specify the correct cvsroot with the -d option.
Note:Be careful about the current working directory when using import and checkout command.
16 Whether it is possible to copy an existing cvs repository into the new repository?
I tried to copy the entire directory and checkout from the new repository, it works fine, which means that the CVSROOT repository can be migrated easily.
17 How to checkout from a remote repository?
I am working with multiple computers, and I want to keep the source files be
synchronized among all of them, and these source files are under cvs control
in my localhost, so just do a checkout from the remote computer with the
following command:
| cvs -d :ext:wujing@172.31.8.22:/home/wujing/myrepos co shell |
Make sure that the ssh connection is enabled in the remote host.
When I am trying to commit the changes to the remote host, the emacs complains
about the missing ssh-askpass file, the right way to solve this problem is to
use password-less ssh connection, the detailed steps are as follows:
Suppose my working host1‘s IP is 172.31.8.22, the working host2‘s ip is
172.20.161.56, and the repository is located in host1, so when I ssh to
host2 from host1 and want to commit the changes to host1, host2 must have
access to host1 without password, do the following configuration:
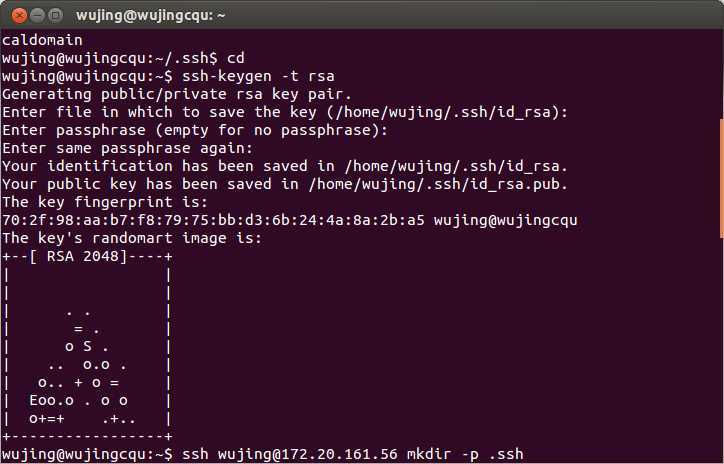
17.1 Create Authentication SSH-Kegen Keys on host1
The screen-shot is as follows:
17.2 Create .ssh Directory on host2
Using the following command:

17.3 Upload Generated Public Keys to host2
Command:

17.4 Set Permissions on host2
Command:

OK, that‘s it, the connection can now operate without password.
18 How to enlarge tmpfs on the go?
Recently, I am frequently downloading/uploading data from a BT site, and I want to cause little traffic to my disk so I just download the movie to my Ubuntu /run/shm directory, the problem is that the default size of this partition is half the size of system memory, which is 4G in my case, and the following command can be used to enlarge this tmpfs:
| sudo mount -o remount,size=5G tmpfs run/shm |
19 How to rename all the files in a directory to file-1.torrent, file-2.torrent…?
Sometimes the filenames of *.torrent files (haha, that‘s it, you probably got it!) may be invalid coding, the following script can rename all of them:
| ls | cat -n | while read n f; do mv "$f" "file-$n.torrent";done |
The cat -n adds number to the output of ls, which can act as a running index to the files, and the second line of the ls | cat -n output is the original filename, so the read n f command reads exactly all the information necessary to finish the renaming, and the do… done does the renaming.
