标签:启动 length test 缓存 mat img ret atom 控制
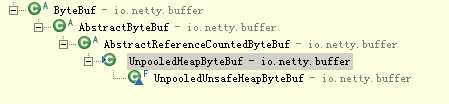
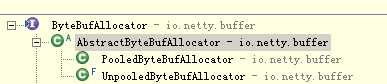
每种ByteBuf都有相应的分配器ByteBufAllocator,类似工厂模式。我们先学习UnpooledHeapByteBuf与其对应的分配器UnpooledByteBufAllocator
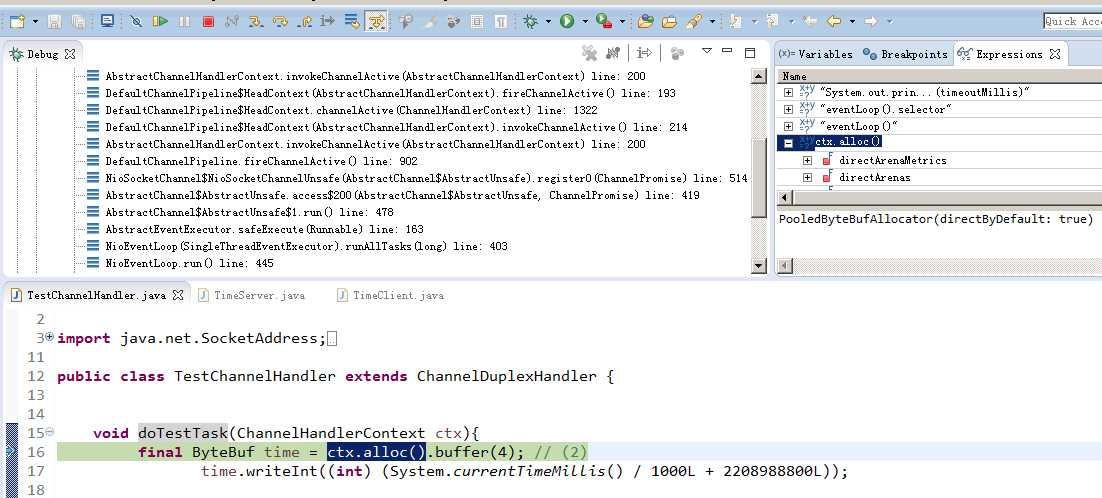
如何知道alloc分配器那是个?
可以从官方下载的TimeServer 例子来学习,本项目已有源码可在 TestChannelHandler.class里断点追踪
从图可以看出netty 4.1.8默认的ByteBufAllocator是PooledByteBufAllocator,可以参过启动参数-Dio.netty.allocator.type unpooled/pooled 设置
细心的读者可以看出分配ByteBuf只有pool跟unpool,但ByteBuf有很多类型,可能出于使用方面考虑,有时不一定设计太死板,太规范反而使学习成本很大
public final class ByteBufUtil { static final ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR; static { String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get( "io.netty.allocator.type", PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled"); allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim(); ByteBufAllocator alloc; if ("unpooled".equals(allocType)) { alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; } else if ("pooled".equals(allocType)) { alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; } else { alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; } DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc; } }
AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf是统计引用总数处理,用到Atomic*技术。
refCnt是从1开始,每引用一次加1,释放引用减1,当refCnt变成1时执行deallocate由子类实现
public abstract class AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf extends AbstractByteBuf { private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf> refCntUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf.class, "refCnt"); private volatile int refCnt = 1; @Override public ByteBuf retain() { return retain0(1); } private ByteBuf retain0(int increment) { for (;;) { int refCnt = this.refCnt; final int nextCnt = refCnt + increment; if (nextCnt <= increment) { throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(refCnt, increment); } if (refCntUpdater.compareAndSet(this, refCnt, nextCnt)) { break; } } return this; } @Override public boolean release() { return release0(1); } private boolean release0(int decrement) { for (;;) { int refCnt = this.refCnt; if (refCnt < decrement) { throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(refCnt, -decrement); } if (refCntUpdater.compareAndSet(this, refCnt, refCnt - decrement)) { if (refCnt == decrement) { deallocate(); return true; } return false; } } } protected abstract void deallocate(); }
对于ByteBuf I/O 操作经常用的是 writeByte(byte[] bytes) readByte(byte[] bytes) 两种
由于ByteBuf支持多种bytes对象,如 OutputStream、GatheringByteChannel、ByteBuffer、ByteBuf等,
我们只拿两三种常用的API来做分析,其它逻辑大同小异
如果读者有印象的话,通常底层只负责流程控制,实现交给应用层/子类处理,AbstractByteBuf.class writeByte/readByte 也是这种处理方式
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { //分配器 private final ByteBufAllocator alloc; //数据 byte[] array; //临时ByteBuffer,用于内部缓存 private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf; private UnpooledHeapByteBuf( ByteBufAllocator alloc, byte[] initialArray, int readerIndex, int writerIndex, int maxCapacity) { //省去部分代码同边界处理 super(maxCapacity); this.alloc = alloc; array = initialArray; this.readerIndex = readerIndex; this.writerIndex = writerIndex; } //获取ByteBuffer容量 @Override public int capacity() { ensureAccessible(); return array.length; } @Override public boolean hasArray() { return true; } //获取原始数据 @Override public byte[] array() { ensureAccessible(); return array; } //扩容/缩容 @Override public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) { ensureAccessible(); //newCapacity参数边界判断 if (newCapacity < 0 || newCapacity > maxCapacity()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("newCapacity: " + newCapacity); } int oldCapacity = array.length; //扩容处理,直接cp到新的array if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) { byte[] newArray = new byte[newCapacity]; System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, array.length); setArray(newArray); } else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) { //减容处理 //这里有两种处理情况 //1.readerIndex > newCapacity 说明还有数据未处理直接将 readerIndex,writerIndex相等 newCapacity //2.否则 writerIndex =Math.min(writerIndex,newCapacity),取最少值,然后直接复制数据 //可以看出netty处理超出readerIndex、writerIndex 限界直接丢弃数据。。。。。。 byte[] newArray = new byte[newCapacity]; int readerIndex = readerIndex(); if (readerIndex < newCapacity) { int writerIndex = writerIndex(); if (writerIndex > newCapacity) { writerIndex = newCapacity this.writerIndex = writerIndex; } System.arraycopy(array, readerIndex, newArray, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex); //System.arraycopy(复制来源数组, 来源组起始坐标, 目标数组, 目标数组起始坐标, 复制数据长度); } else { this.readerIndex = newCapacity; this.writerIndex = newCapacity; } setArray(newArray); } return this; } }
未完侍。。。。。
[编织消息框架][netty源码分析]11 UnpooledHeapByteBuf 与 ByteBufAllocator
标签:启动 length test 缓存 mat img ret atom 控制
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/solq111/p/7099327.html