标签:pre 连接 stream void 分享 ima 定义 情况 include
Microsoft Visual Studio ULtimate 2013 版本:12.0.21055.1 REL
引用变量是一个别名,也就是说,它是某个已存在变量的另一个名字。一旦把引用初始化为某个变量,就可以使用该引用名称或变量名称来指向变量。

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3
4 int main()
5 {
6 int value = 123;
7 int &_value = value;//定义一个引用
8 std::cout << "value 的地址:" << &value << std::endl;
9 std::cout << "_value 的地址:" << &_value << std::endl;
10
11 std::cout << "value :" << value << std::endl;
12 std::cout << "value :" << _value << std::endl;
13 std::cout << "\n";
14 system("pause");
15 }
运行结果:
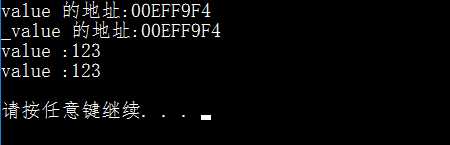
从上述结果可以看出,变量value与其引用变量_value指向了同一块内存,使用引用并未开辟一块新的内存。
1. 不存在空引用。

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3
4 int main()
5 {
6 int value;
7 int &_value = value;
8 std::cout << "value 的地址:" << &value << std::endl;
9 std::cout << "_value 的地址:" << &_value << std::endl;
10
11 std::cout << "value :" << value << std::endl;
12 std::cout << "value :" << _value << std::endl;
13
14 std::cout << "\n";
15 system("pause");
16 }
第一次运行结果:

第二次运行结果:

因为value为空,所以随意指向了一个了一块内存,虽然引用仍起作用,但不存在任何实际意义。(可能因使用的编译器不同,存在不同的情况,但建议不要使用空引用)
2. 一旦引用被初始化为一个对象,就不能被指向到另一个对象

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4
5 int main()
6 {
7 std::string str = "Hello !!!";
8
9 std::string &_str = str;
10 std::cout << "str 的地址:" << &str << std::endl;
11 std::cout << "_str 的地址:" << &_str << std::endl;
12 std::cout << "str :" << str << std::endl;
13 std::cout << "_str :" << _str << std::endl;
14
15 std::cout << std::endl;
16 std::string str_s = "Hello C++ !!!";
17 _str = str_s;
18 std::cout << "str_s 的地址:" << &str_s << std::endl;
19 std::cout << "_str 的地址:" << &_str << std::endl;
20 std::cout << "str_s :" << str_s << std::endl;
21 std::cout << "_str :" << _str << std::endl;
22
23 std::cout << std::endl;
24 std::cout << "str :" << str << std::endl;
25
26 std::cout << "\n";
27 system("pause");
28 }
运行结果:
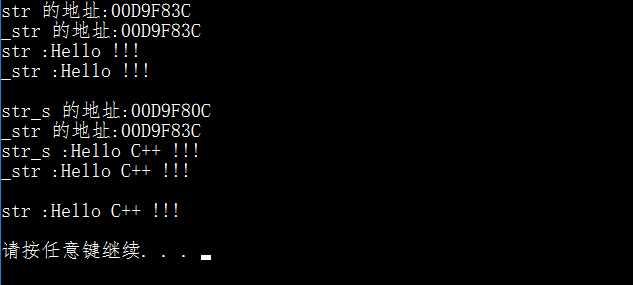
由运行结果可知,当尝试对一个引用变量_str第二次赋值时,实际该引用变量_str并未指向新的变量str_s,而是改变了原变量str的值,因此 一旦引用被初始化为一个对象,就不能被指向到另一个对象。
3. 引用必须在创建时被初始化。

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4 void myString();
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 std::string str = "Hello !!!";
9 std::string &_str;
10 _str = str;
11
12 std::cout << "str 的地址:" << &str << std::endl;
13 std::cout << "_str 的地址:" << &_str << std::endl;
14 std::cout << "str :" << str << std::endl;
15 std::cout << "_str :" << _str << std::endl;
16
17 std::cout << "\n";
18 system("pause");
19 }
运行结果:
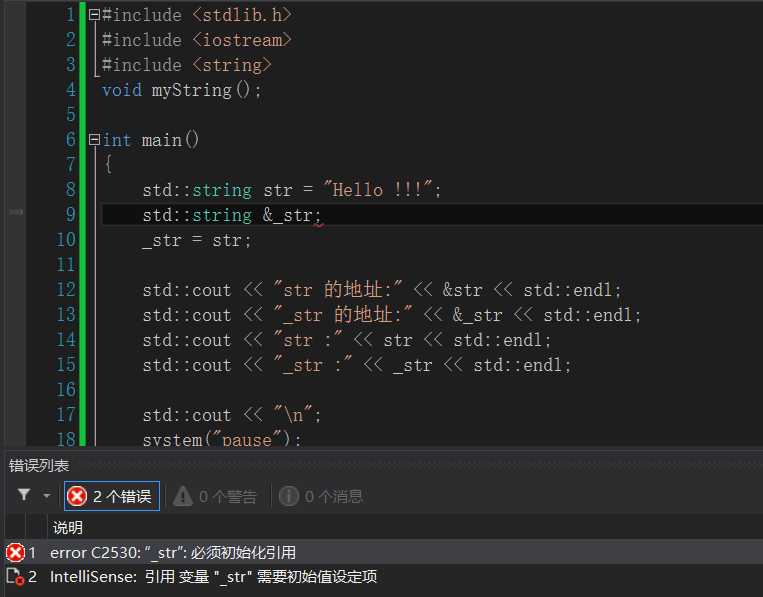
引用必须在创建时被初始化。
1. 把引用作为参数

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4
5 void founcation(std::string str);
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 std::string str = "Hello !!!";
10 std::cout << "主函数 :" << &str << std::endl;
11 founcation(str);
12
13 std::cout << "\n";
14 system("pause");
15 }
16
17 void founcation(std::string str)
18 {
19 std::cout << "函数执行 :" << &str << std::endl;
20 return;
21 }
运行结果:

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4
5 void founcation(const std::string &str);
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 std::string str = "Hello !!!";
10 std::cout << "主函数 :" << &str << std::endl;
11 founcation(str);
12
13 std::cout << "\n";
14 system("pause");
15 }
16
17 void founcation(const std::string &str)
18 {
19 std::cout << "函数执行 :" << &str << std::endl;
20 return;
21 }
运行结果:

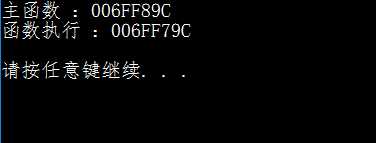
把引用作为参数时,不会在函数调用是创建新的变量,不会开辟新的内存空间。
而不使用引用作为参数则会在函数调用是创建新的变量,开辟一块新的内存空间。
2. 把引用作为返回值

1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4
5 std::string founcation(std::string &str);
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 std::string str = "Hello !!!";
10 std::cout << "主函数 :" << &str << std::endl;
11
12 std::cout << "返回值 :" << &founcation(str) << std::endl;
13
14 std::cout << "\n";
15 system("pause");
16 }
17
18 std::string founcation(std::string &str)
19 {
20 std::cout << "函数执行 :" << &str << std::endl;
21 return str;
22 }
运行结果:


1 #include <stdlib.h>
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4
5 std::string& founcation(std::string &str);
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 std::string str = "Hello !!!";
10 std::cout << "主函数 :" << &str << std::endl;
11
12 std::cout << "返回值 :" << &founcation(str) << std::endl;
13
14 std::cout << "\n";
15 system("pause");
16 }
17
18 std::string& founcation(std::string &str)
19 {
20 std::cout << "函数执行 :" << &str << std::endl;
21 return str;
22 }
运行结果:
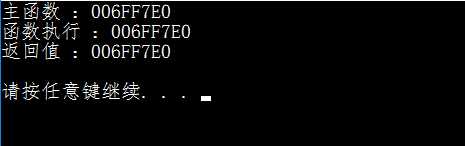
使用引用作为函数返回值,并未开辟新的内存空间,不适用函数作为返回值,则会开辟新的内存空间。
标签:pre 连接 stream void 分享 ima 定义 情况 include
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/QingKeZhiXia/p/7102507.html