标签:概念 var repr 工厂 out ber component display 方法
Netty的线程模型主要是基于React,因为考虑到应用场景的不同所以演化出多种版本。
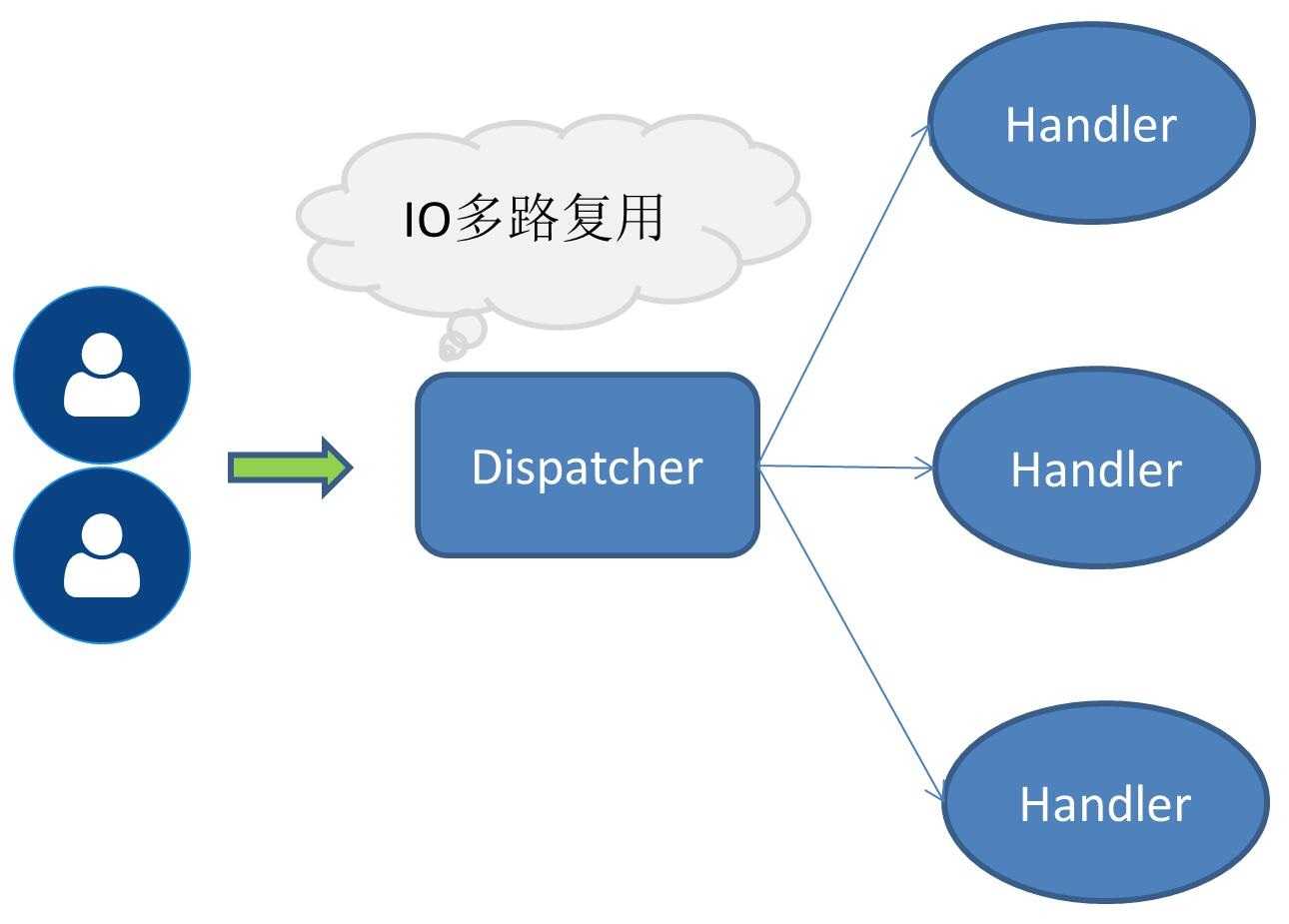
即接收服务请求以及执行IO操作都由一个线程来完成,由于采用的是IO多路复用这类无阻塞IO操作,所以在请求量不大的情况下单线程模式也是可以解决一部分场景问题的。
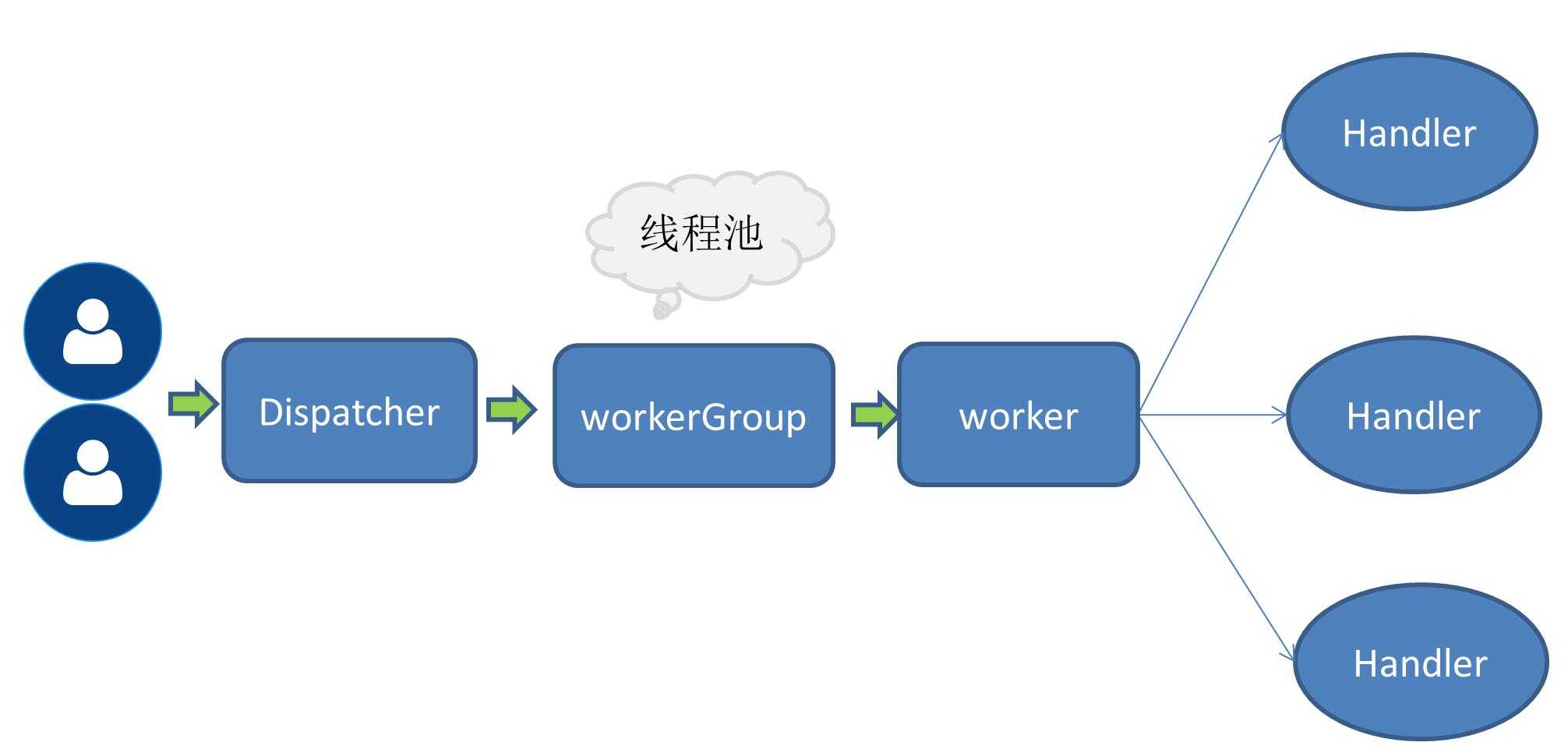
当请求量增大后,原有的一个线程处理所有IO操作变得越来越无法支撑相应的性能指标,所以提到了一个工作线程池的概念,此时接收服务请求还是一个线程,接收请求的线程收到请求后会委托给后面的工作线程池,从线程池中取得一个线程去执行用户请求。
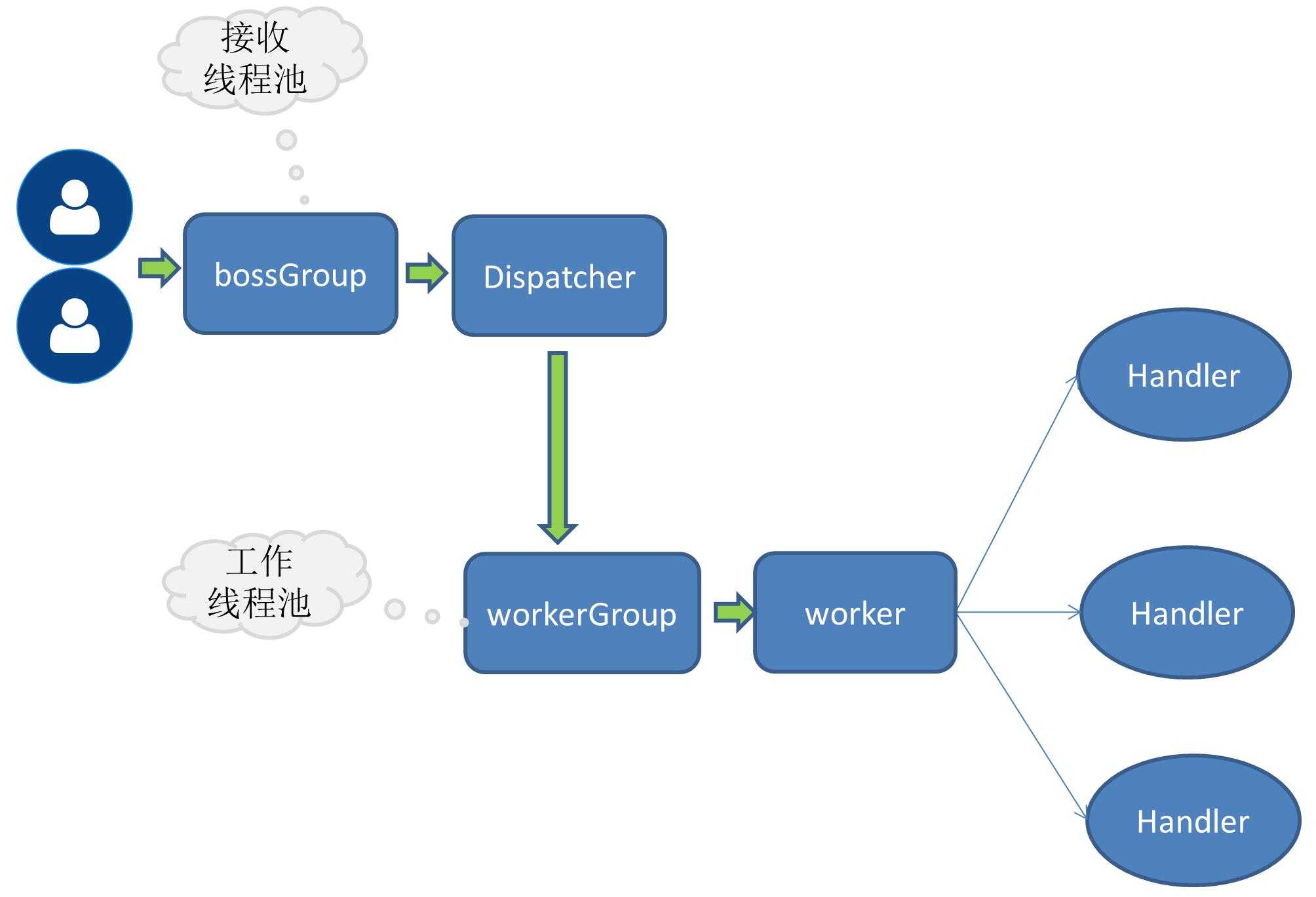
当请求量进一步增大后,单一的接收服务请求的线程无法处理所有客户端的连接,所以将接收服务请求的也扩展成线程池,由多个线程同时负责接收客户端的连接。
上面提到的都是Netty自身的线程模型,伴随着请求量的增长而不断发展出来的优化策略。而RPC请求对应用系统来讲最主要还是业务逻辑的处理,而这类业务有可能是计算密集型的也有可以是IO密集型,像大多数应用都伴随着数据库操作,redis或者是连接其它的网络服务等。如果业务请求中有这类耗时的IO操作,推荐将处理业务请求的任务分配给独立的线程池,否则可能会阻塞netty自身的线程。
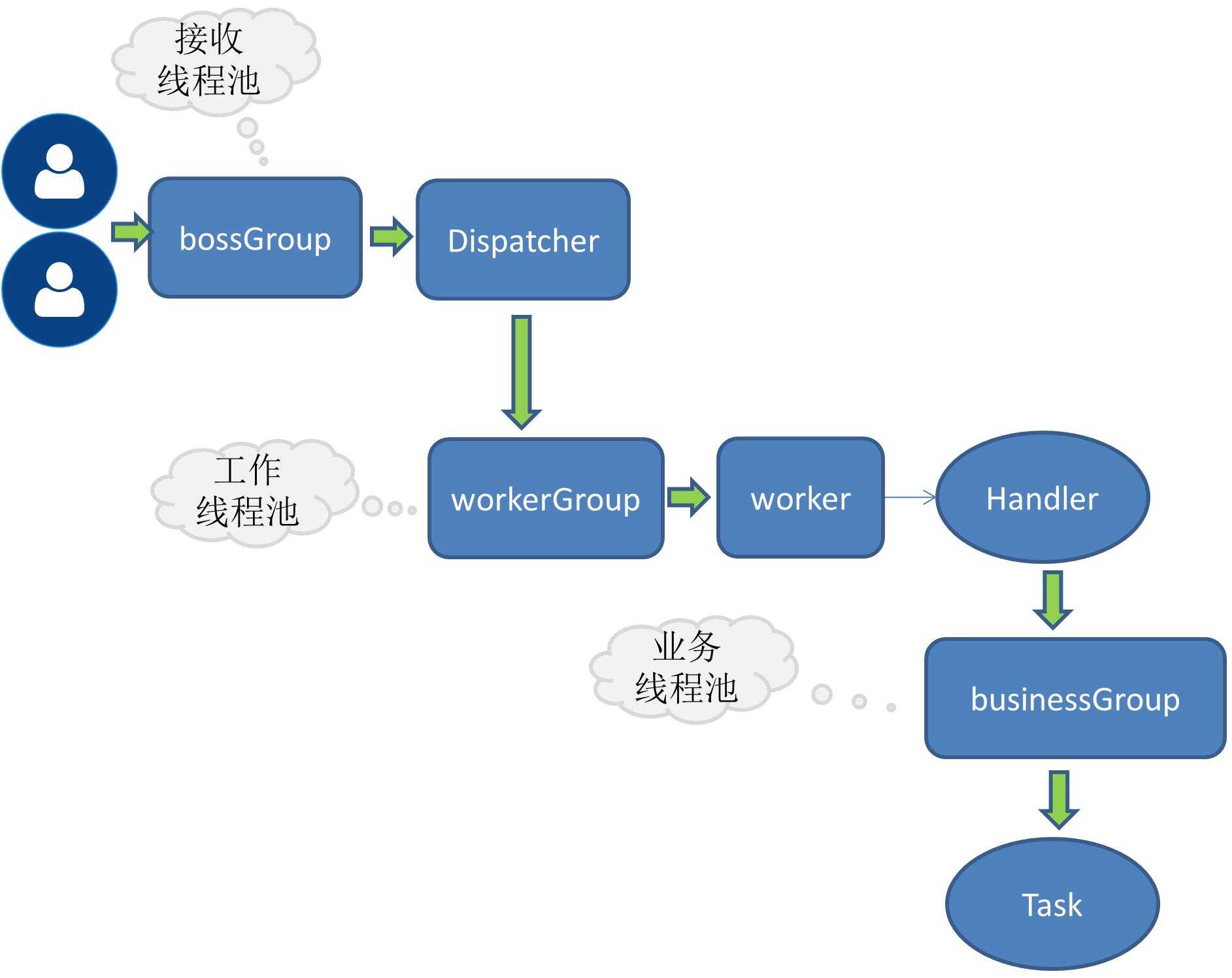
接收请求线程与工作线程分工
目前我实现的RPC是采用多接收多工作线程模式,在服务端是这样绑定端口的:
public void bind(ServiceConfig serviceConfig) {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(this.rpcServerInitializer)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true)
;
try {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(serviceConfig.getHost(),serviceConfig.getPort()).sync();
//...
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RpcException(e);
}
}
finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
boosGroup就是一组用来接收服务请求的
workerGroup就是一组具体负责IO操作的
增加业务线程只需要将handle的操作进一步委派给线程池即可,这里为了扩展所以需要定义接口:
public interface RpcThreadPool {
Executor getExecutor(int threadSize,int queues);
}
参考了dubbo线程池
@Qualifier("fixedRpcThreadPool")
@Component
public class FixedRpcThreadPool implements RpcThreadPool {
private Executor executor;
@Override
public Executor getExecutor(int threadSize,int queues) {
if(null==executor) {
synchronized (this) {
if(null==executor) {
executor= new ThreadPoolExecutor(threadSize, threadSize, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
queues == 0 ? new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>() :
(queues < 0 ? new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()
: new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(queues)),
new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
//...
}
});
}
}
}
return executor;
}
}
小插曲:
记的有一次一朋友突然问java 线程池中的那个coreSize是什么意思?我顿时短路了,因平时也不怎么写多线程,想到平时用的比较多的数据库线程池,里面的参数倒是印象比较深,但就是想不起来有个coreSize。后来才又仔细看了下线程池的一些参数。现在借这个机会又可以多多再看看,以免再次短路。
当有多个线程池实现时,通过线程池名称来动态选择线程池。
@Component
public class RpcThreadPoolFactory {
@Autowired
private Map<String,RpcThreadPool> rpcThreadPoolMap;
public RpcThreadPool getThreadPool(String threadPoolName){
return this.rpcThreadPoolMap.get(threadPoolName);
}
}
将方法体包装成Task交给线程池去执行。
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, RpcRequest rpcRequest) {
this.executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
RpcInvoker rpcInvoker=RpcServerInvoker.this.buildInvokerChain(RpcServerInvoker.this);
RpcResponse response=(RpcResponse) rpcInvoker.invoke(RpcServerInvoker.this.buildRpcInvocation(rpcRequest));
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}
目前缺乏压测,所以暂时没有明确的数据对比。
https://github.com/jiangmin168168/jim-framework
标签:概念 var repr 工厂 out ber component display 方法
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ASPNET2008/p/7106820.html