标签:tac imp one 匿名 name 函数 art setdaemon str
1.1进程:每个进程都有独立的代码和数据空间(进程上下文),进程间的切换会有较大的开销,一个进程包含1~n个线程。(进程是资源分配的最小单位)
1.2线程:同一类线程共享代码和数据空间,每个线程有独立的运行栈和程序计数器(PC),线程切换开销小。(线程是cpu调度的最小单位)
继承Thread类 extends Thread
实现Runnable接口 implements Runnable
内部匿名类
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
});
推荐使用Runnable接口:原因有二:1 Java中的类仅仅只支持单继承,而接口支持多继承
2 使用Runnable接口可以轻松的实现多个线程间的资源共享
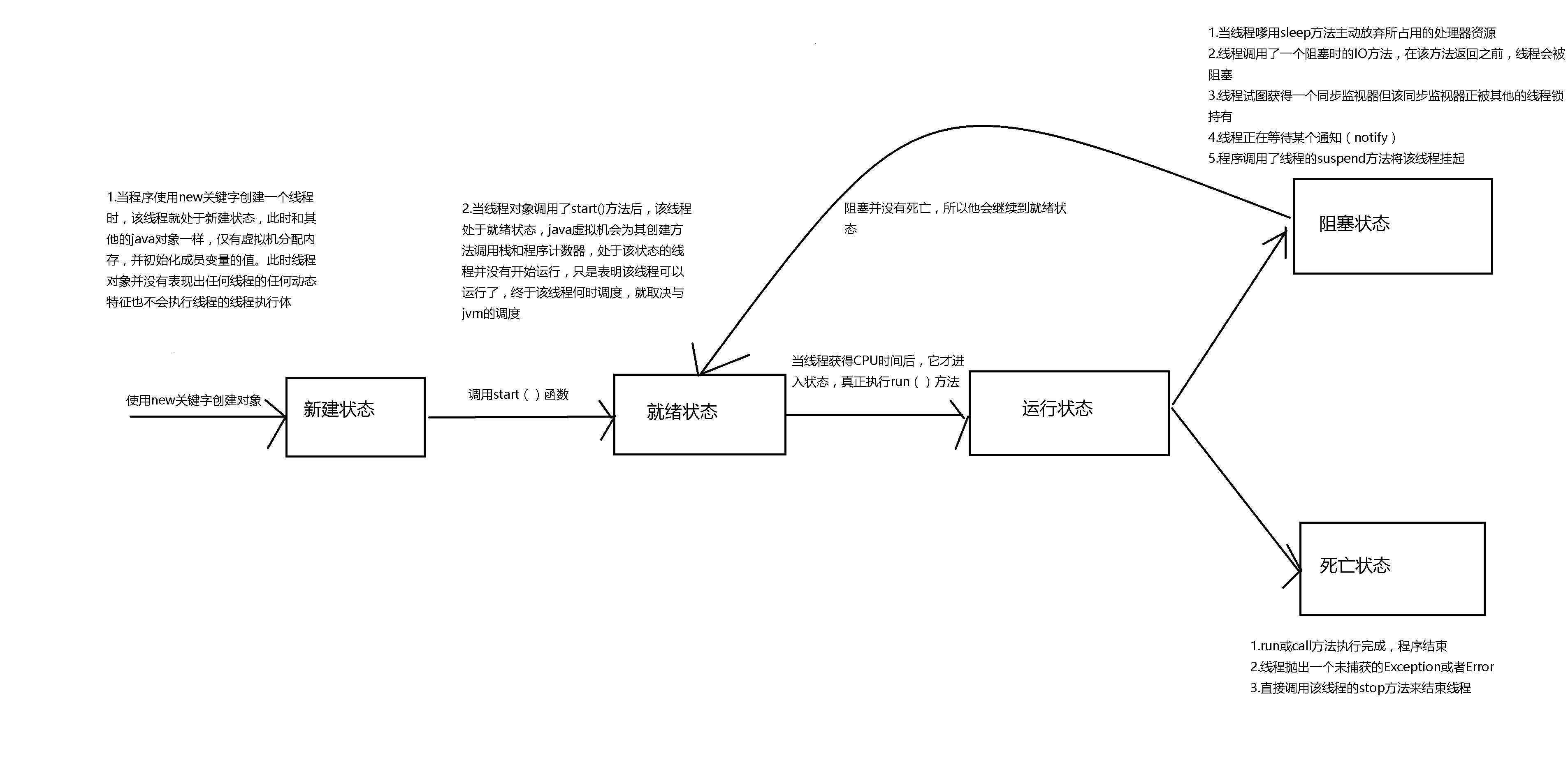
列子:

1 /** 2 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 3 */ 4 public class TestJoin { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 6 new JoinThread("新线程").start(); 7 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 8 if (i==5){ 9 JoinThread j1=new JoinThread("被join的线程"); 10 j1.start(); 11 j1.join(); 12 } 13 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i); 14 } 15 } 16 }

1 /** 2 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 3 */ 4 public class JoinThread extends Thread { 5 public JoinThread(String name) { 6 super(name); 7 } 8 9 public void run(){ 10 for (int i=1;i<=10;i++){ 11 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i); 12 } 13 } 14 }

1 import javax.naming.Name; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 5 */ 6 public class ThreadYeild extends Thread { 7 String name; 8 9 public ThreadYeild(String name) { 10 super(name); 11 this.name = name; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 17 System.out.println(this.getName()+" "+i); 18 if (i==30){ 19 Thread.yield(); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }

1 import javax.naming.Name; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 5 */ 6 public class ThreadYeild extends Thread { 7 String name; 8 9 public ThreadYeild(String name) { 10 super(name); 11 this.name = name; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) { 17 System.out.println(this.getName()+" "+i); 18 if (i==30){ 19 Thread.yield(); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }

1 /** 2 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 3 */ 4 public class BackGroundThread implements Runnable { 5 public void run() { 6 for (int i=1;i<100000000;i++){ 7 System.out.println("后台线程执行第"+i+"次"); 8 try { 9 Thread.sleep(7); 10 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 }

1 /** 2 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 3 */ 4 public class MyThreads extends Thread { 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) { 8 System.out.println("线程1第" + i + "次执行"); 9 try { 10 Thread.sleep(7); 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 }

1 /** 2 * Created by 123 on 2017/07/02. 3 * 守护线程 4 */ 5 public class TestThread { 6 //如果前台线程执行i次,后台线程执行i+1次,因为还有main线程 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Thread t1 = new MyThreads(); 9 Thread t2 = new Thread(new BackGroundThread()); 10 t2.setDaemon(true); //设置为守护线程 11 t1.start(); 12 t2.start(); 13 } 14 }
结论就是:如果前台线程执行i次,那么后台线程就会执行i+1次,因为还有一个main线程。
标签:tac imp one 匿名 name 函数 art setdaemon str
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bdqnquliang/p/7118066.html