标签:img mit mode 随机 text war array with class
SVM(Support Vector Machine)是一个类分类器,能够将不同类的样本在样本空间中进行分隔,分隔使用的面叫做分隔超平面。
比如对于二维样本,分布在二维平面上,此时超平面实际上是一条直线,直线上面是一类,下面是另一类。定义超平面为:
f(x)=w0+wTx
可以想象出,这样的直线可以有很多条,到底哪一条是超平面呢?规定超平面应该是距离两类的最近距离之和最大,因为只有这样才是最优的分类。
假设超平面是w0+wTx=0,那么经过上面这一类距离超平面最近点的直线是w0+wTx=1,下面的直线是w0+wTx=-1。其中一类到超平面的距离是
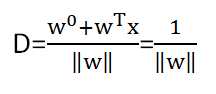
然后采用拉格朗日函数,经过一系列运算以后,得到
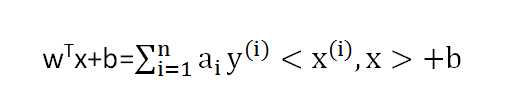
这也意味着,只用计算新点x与训练数据点的内积就可以对新点进行预测。
MLlib只实现了线性SVM,采用分布式随机梯度下降算法。将SVM二分类的1和-1转化为1和0,因此y变成了(2y-1),梯度为g=-(2y-1)x,梯度更新公式
![]()
直接上代码:
import org.apache.log4j.{ Level, Logger } import org.apache.spark.{ SparkConf, SparkContext } import org.apache.spark.mllib.classification.SVMWithSGD import org.apache.spark.mllib.util.MLUtils object SVMTest { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { // 设置运行环境 val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("SVM Test") .setMaster("spark://master:7077").setJars(Seq("E:\\Intellij\\Projects\\MachineLearning\\MachineLearning.jar")) val sc = new SparkContext(conf) Logger.getRootLogger.setLevel(Level.WARN) // 读取样本数据并解析 val dataRDD = MLUtils.loadLibSVMFile(sc, "hdfs://master:9000/ml/data/sample_svm_data.txt") // 样本数据划分,训练样本占0.8,测试样本占0.2 val dataParts = dataRDD.randomSplit(Array(0.8, 0.2)) val trainRDD = dataParts(0) val testRDD = dataParts(1) // 建立模型并训练 val numIterations = 100 val model = SVMWithSGD.train(trainRDD, numIterations) // 对测试样本进行测试 val predictionAndLabel = testRDD.map { point => val score = model.predict(point.features) (score, point.label, point.features) } val showPredict = predictionAndLabel.take(50) println("Prediction" + "\t" + "Label" + "\t" + "Data") for (i <- 0 to showPredict.length - 1) { println(showPredict(i)._1 + "\t" + showPredict(i)._2 + "\t" + showPredict(i)._3) } // 误差计算 val accuracy = 1.0 * predictionAndLabel.filter(x => x._1 == x._2).count() / testRDD.count() println("Accuracy = " + accuracy) } }
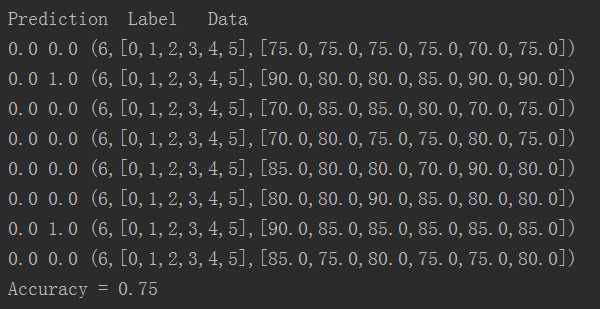
运行结果:
标签:img mit mode 随机 text war array with class
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mstk/p/7124148.html