标签:logs 父类 .net receive 解释 details generate either completed
首先我们不要在学习Spring的开始产生畏难情绪。Spring没有臆想的那么高深,相反,它帮我们再项目开发中制定项目框架,简化项目开发。它的主要功能是将项目开发中繁琐的过程流程化,模式化,使用户仅在固定文件中增加特定标签并实现特定逻辑层的代码就能完成项目开发。下面我们来分析web项目启动时bean的初始化过程。
我们遵循类的依赖,引用关系来理清spring在这一过程中的架构和细节实现。java web项目入口在web.xml,Spring在此配置入口servlet完成bean的加载。DispatcherServlet 作为前置控制器是web服务器的入口。
<servlet> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet>
我们知道load-on-startup元素标记容器是否在启动的时候就加载这个servlet(实例化并调用其init()方法)。进入DispatcherServlet寻找init方法,在其父类HttpServletBean中找到。
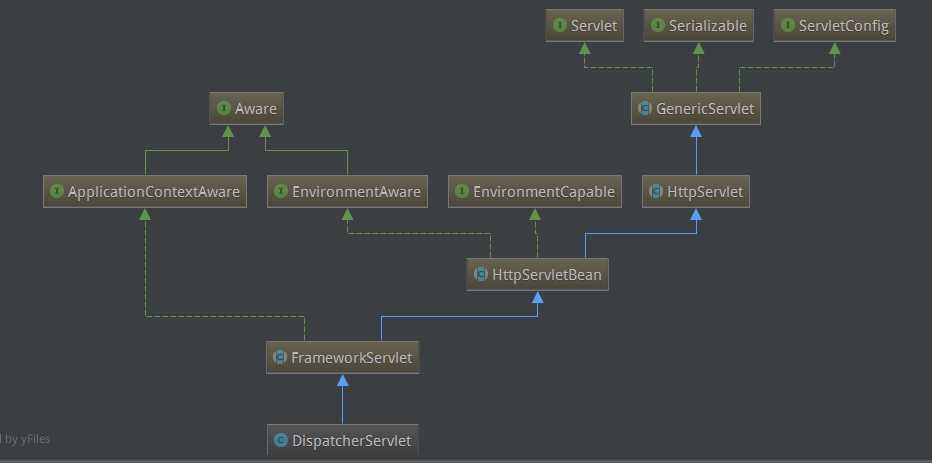
DispatcherServlet的继承关系如下图
init方法细节代码如下
/** * Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and * invoke subclass initialization. * @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required * properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails. */ @Override public final void init() throws ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); } // Set bean properties from init parameters. try { PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘", ex); } throw ex; } // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘ configured successfully"); } }
其中try catch 模块做对bean包装器的初始化相关的工作,initServletBean才是我们跟踪的主线调用方法,查看在其父类FrameworkServlet中的此方法
/** * Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties * have been set. Creates this servlet‘s WebApplicationContext. */ @Override protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException { getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘"); if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘: initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); throw ex; } if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } }
由方法注释可以了解到此方法主要功能为初始化WebApplicationContext。[Context也就是我们常说的spring容器,打个比方,context就像是一家公司,beans则是公司的工厂,除了工厂,公司还有翻译,仓库以及办公场所等等] .对于ApplicationContext,它提供了如下功能:
* Bean factory methods for accessing application components.[获取应用组件]
* Inherited from {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory}.
* The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion.[加载通用格式资源文件]
* Inherited from the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader} interface.
* The ability to publish events to registered listeners.[发布事件到监听器]
* Inherited from the {@link ApplicationEventPublisher} interface.
* The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization.[解析信息,支持国际化]
* Inherited from the {@link MessageSource} interface.
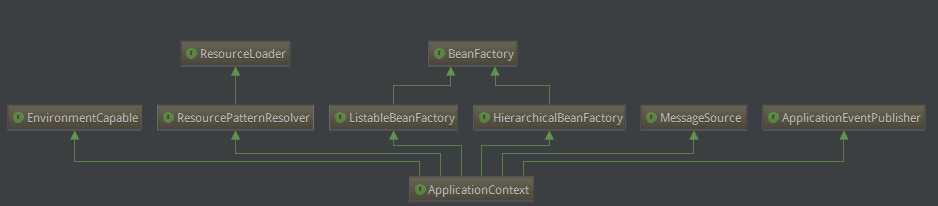
它的继承关系如下,[其实现在我们发现我们的目的最终是查看beanFactory中bean的加载过程]
WebApplicationContext又做了如下扩展
* This interface adds a {@code getServletContext()} method to the generic[增加getServletContext方法]
* ApplicationContext interface, and defines a well-known application attribute name
* that the root context must be bound to in the bootstrap process.
我们回到主线上,进入initWebApplicationContext的方法
/** * Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet. * <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation * of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses. * @return the WebApplicationContext instance * @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext) * @see #setContextClass * @see #setContextConfigLocation */ protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. onRefresh(wac); } if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet ‘" + getServletName() + "‘ as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]"); } } return wac; }
第一个if判断是否在在构造时注入了context实例,在我们的跟踪场景下不会走这一步;第二个if函数是查找是否在servlet context中注册了context,依然不会走这步;第三个if函数
会创建WebApplicationContext,我们跟进去看详细内容
/** * Instantiate the WebApplicationContext for this servlet, either a default * {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext} * or a {@link #setContextClass custom context class}, if set. * <p>This implementation expects custom contexts to implement the * {@link org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} * interface. Can be overridden in subclasses. * <p>Do not forget to register this servlet instance as application listener on the * created context (for triggering its {@link #onRefresh callback}, and to call * {@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()} * before returning the context instance. * @param parent the parent ApplicationContext to use, or {@code null} if none * @return the WebApplicationContext for this servlet * @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext */ protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) { Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug("Servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘ will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class ‘" + contextClass.getName() + "‘" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]"); } if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name ‘" + getServletName() + "‘: custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"); } ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); wac.setParent(parent); wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation()); configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; } protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) { if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) { // The application context id is still set to its original default value // -> assign a more useful id based on available information if (this.contextId != null) { wac.setId(this.contextId); } else { // Generate default id... wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX + ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + ‘/‘ + getServletName()); } } wac.setServletContext(getServletContext()); wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig()); wac.setNamespace(getNamespace()); wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener())); // The wac environment‘s #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context // is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for // use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig()); } postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac); applyInitializers(wac); wac.refresh(); } /** * Instantiate the WebApplicationContext for this servlet, either a default * {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext} * or a {@link #setContextClass custom context class}, if set. * Delegates to #createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext). * @param parent the parent WebApplicationContext to use, or {@code null} if none * @return the WebApplicationContext for this servlet * @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext * @see #createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext) */ protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(WebApplicationContext parent) { return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent); }
我们可以看到createWebApplicationContext方法设置了Environment、父context、配置文件位置ConfigLocation等操作,查看configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext逻辑,第一个
if判断是否可以根据可用信息为其分配一个更通用的id。接下来的逻辑设置一些属性,而这些属性正是我们上文中解释ApplicationContext时其应拥有的特性
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext()); wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig()); wac.setNamespace(getNamespace()); wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
接下来我们进入ConfigurableWebApplicationContext子类AbstractApplicationContext中找到refresh[它是context的核心方法,描述了整个容器构建的过程]的实现。
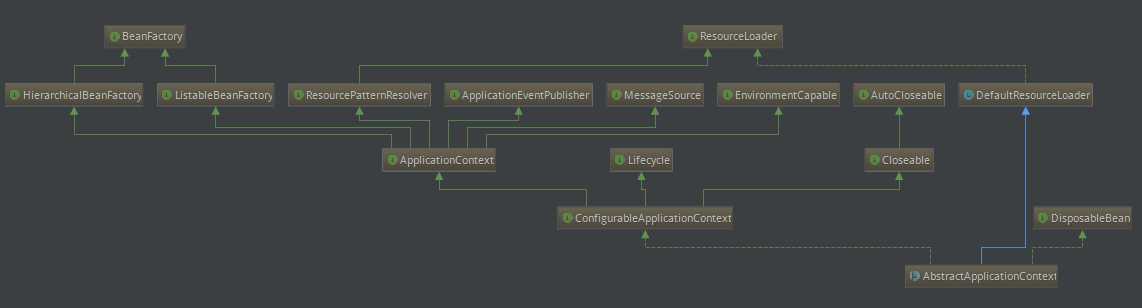
首先我们还是来看下AbstractApplicationContext的类继承关系图
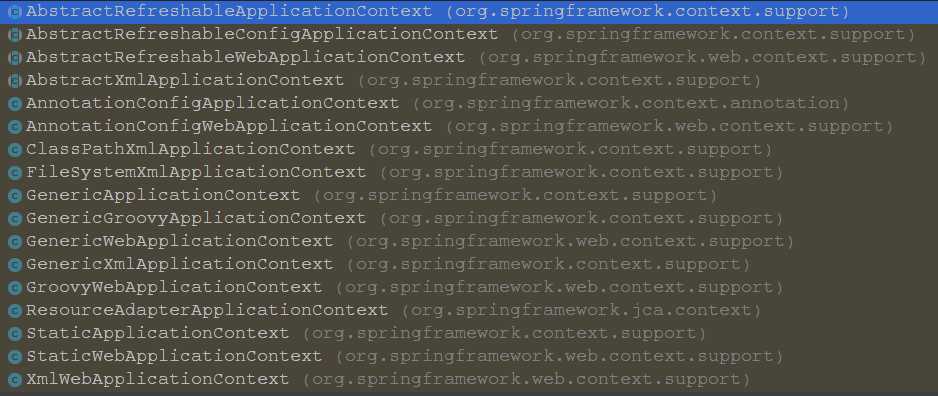
这个类实现了context的主要功能,同时他的子类如下
其中
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext定义了loadBeanDefinitions模板方法,它创建bean factory并load配置文件。它生成了我们熟悉的DefaultListableBeanFactory
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext增加了设置资源的路径的能力。
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext增加了针对web的一些特性提供一些context属性行为设置能力。
这些context分别会在不同场景下用到,接下来我们仍旧回到主线分析refresh方法
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset ‘active‘ flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring‘s core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
我们一眼发现代码中对beanFactory初始化设置过程及初始化监听器,设置message。进入初始化非懒加载bean的方法finishBeanFactoryInitialization
/** * Finish the initialization of this context‘s bean factory, * initializing all remaining singleton beans. */ protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { // Initialize conversion service for this context. if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) { beanFactory.setConversionService( beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)); } // Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor // (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before: // at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values. if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) { beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(new StringValueResolver() { @Override public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) { return getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal); } }); } // Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early. String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false); for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) { getBean(weaverAwareName); } // Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching. beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null); // Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes. beanFactory.freezeConfiguration(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(); }
这个方法负责了context的beanFactory中单例bean的初始化。
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/davidwang456/p/4090058.html
http://blog.csdn.net/szwandcj/article/details/50762990
http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/spring/ioc-container/spring-application-context-container.html
转载请注明出处http://www.cnblogs.com/shibit/p/7137139.html
标签:logs 父类 .net receive 解释 details generate either completed
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shibit/p/7137139.html