标签:signed nts 开始 ges slave nec 用户权限 sla 协议
数据库(Database)是按照数据结构来组织、存储和管理数据的仓库,每个数据库都有一个或多个不同的API用于创建,访问,管理,搜索和复制所保存的数据。
我们使用关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS)来存储和管理的大数据量。所谓的关系型数据库,是建立在关系模型基础上的数据库,借助于集合代数等数学概念和方法来处理数据库中的数据。
RDBMS即关系数据库管理系统(Relational Database Management System)的特点:
RDBMS的一些术语:
一个关系型数据库由一个或数个表格组成, 如图所示的一个表格:
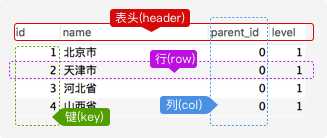
表头(header): 每一列的名称;
列(col): 具有相同数据类型的数据的集合;
行(row): 每一行用来描述某个人/物的具体信息;
值(value): 行的具体信息, 每个值必须与该列的数据类型相同;
键(key): 表中用来识别某个特定的人物的方法, 键的值在当前列中具有唯一性。
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB公司开发,目前属于Oracle公司。MySQL是一种关联数据库管理系统,关联数据库将数据保存在不同的表中,而不是将所有数据放在一个大仓库内,这样就增加了速度并提高了灵活性。
关于mysql的安装请参考链接:http://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-install.html
语法如下:

1 mysql -D 所选择的数据库名 -h 主机名 -u 用户名 -p 密码 2 3 例:mysql -u root -p

1 mysql> exit # 退出 使用 “quit;” 或 “\q;” 一样的效果 2 mysql> status; # 显示当前mysql的version的各种信息 3 mysql> select version(); # 显示当前mysql的version信息 4 mysql> show global variables like ‘port‘; # 查看MySQL端口号
注意:分号结束命令。
SHOW DATABASES;
默认数据库:
mysql - 用户权限相关数据
test - 用于用户测试数据
information_schema - MySQL本身架构相关数据

1 # utf-8 2 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名称 DEFAULT CHARSET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; 3 4 # gbk 5 CREATE DATABASE 数据库名称 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET gbk COLLATE gbk_chinese_ci; 6 7 例: 8 9 MySQL [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE JJ; 10 Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)

1 USE db_name;

1 SHOW TABLES;

1 创建用户 2 create user ‘用户名‘@‘IP地址‘ identified by ‘密码‘; 3 删除用户 4 drop user ‘用户名‘@‘IP地址‘; 5 修改用户 6 rename user ‘用户名‘@‘IP地址‘; to ‘新用户名‘@‘IP地址‘;; 7 修改密码 8 set password for ‘用户名‘@‘IP地址‘ = Password(‘新密码‘)
注:用户权限相关数据保存在mysql数据库的user表中,所以也可以直接对其进行操作(不建议)

1 show grants for ‘用户‘@‘IP地址‘; -- 查看权限 2 grant 权限 on 数据库.表 to ‘用户‘@‘IP地址‘; -- 授权 3 revoke 权限 on 数据库.表 from ‘用户‘@‘IP地址‘; -- 取消权限 4 5 6 all privileges 除grant外的所有权限 7 select 仅查权限 8 select,insert 查和插入权限 9 ... 10 usage 无访问权限 11 alter 使用alter table 12 alter routine 使用alter procedure和drop procedure 13 create 使用create table 14 create routine 使用create procedure 15 create temporary tables 使用create temporary tables 16 create user 使用create user、drop user、rename user和revoke all privileges 17 create view 使用create view 18 delete 使用delete 19 drop 使用drop table 20 execute 使用call和存储过程 21 file 使用select into outfile 和 load data infile 22 grant option 使用grant 和 revoke 23 index 使用index 24 insert 使用insert 25 lock tables 使用lock table 26 process 使用show full processlist 27 select 使用select 28 show databases 使用show databases 29 show view 使用show view 30 update 使用update 31 reload 使用flush 32 shutdown 使用mysqladmin shutdown(关闭MySQL) 33 super ????使用change master、kill、logs、purge、master和set global。还允许mysqladmin????????调试登陆 34 replication client 服务器位置的访问 35 replication slave 由复制从属使用 36 37 对于权限 38 39 权限参数 40 41 对于目标数据库以及内部其他: 42 数据库名.* 数据库中的所有 43 数据库名.表 指定数据库中的某张表 44 数据库名.存储过程 指定数据库中的存储过程 45 *.* 所有数据库 46 47 用户名@IP地址 用户只能在改IP下才能访问 48 用户名@192.168.1.% 用户只能在改IP段下才能访问(通配符%表示任意) 49 用户名@% 用户可以再任意IP下访问(默认IP地址为%) 50 51 52 grant all privileges on db1.tb1 TO ‘用户名‘@‘IP‘; 53 54 grant select on db1.* TO ‘用户名‘@‘IP‘; 55 56 grant select,insert on *.* TO ‘用户名‘@‘IP‘; 57 58 revoke select on db1.tb1 from ‘用户名‘@‘IP‘; 59 60 刷新权限 61 62 flush privileges,将数据读取到内存中,从而立即生效。 63 64 65 忘记密码的操作 66 # 启动免授权服务端 67 mysqld --skip-grant-tables 68 69 # 客户端 70 mysql -u root -p 71 72 # 修改用户名密码 73 update mysql.user set authentication_string=password(‘666‘) where user=‘root‘; 74 flush privileges; 75 76 忘记密码

1 create table 表名( 2 列名 类型 是否可以为空, 3 列名 类型 是否可以为空 4 )ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 5 6 7 是否可空,null表示空,非字符串 8 not null - 不可空 9 null - 可空 10 11 12 13 默认值,创建列时可以指定默认值,当插入数据时如果未主动设置,则自动添加默认值 14 create table tb1( 15 nid int not null defalut 2, 16 num int not null 17 ) 18 19 20 21 自增,如果为某列设置自增列,插入数据时无需设置此列,默认将自增(表中只能有一个自增列) 22 create table tb1( 23 nid int not null auto_increment primary key, 24 num int null 25 ) 26 或 27 create table tb1( 28 nid int not null auto_increment, 29 num int null, 30 index(nid) 31 ) 32 注意:1、对于自增列,必须是索引(含主键)。 33 2、对于自增可以设置步长和起始值 34 show session variables like ‘auto_inc%‘; 35 set session auto_increment_increment=2; 36 set session auto_increment_offset=10; 37 38 shwo global variables like ‘auto_inc%‘; 39 set global auto_increment_increment=2; 40 set global auto_increment_offset=10; 41 42 自增 43 44 主键,一种特殊的唯一索引,不允许有空值,如果主键使用单个列,则它的值必须唯一,如果是多列,则其组合必须唯一。 45 create table tb1( 46 nid int not null auto_increment primary key, 47 num int null 48 ) 49 或 50 create table tb1( 51 nid int not null, 52 num int not null, 53 primary key(nid,num) 54 ) 55 56 主键
外键
在MySQL 3.23.44版本后,InnoDB引擎类型的表支持了外键约束。
外键的使用条件:
1.两个表必须是InnoDB表,MyISAM表暂时不支持外键(据说以后的版本有可能支持,但至少目前不支持);
2.外键列必须建立了索引,MySQL 4.1.2以后的版本在建立外键时会自动创建索引,但如果在较早的版本则需要显示建立;
3.外键关系的两个表的列必须是数据类型相似,也就是可以相互转换类型的列,比如int和tinyint可以,而int和char则不可以;
外键的好处:可以使得两张表关联,保证数据的一致性和实现一些级联操作;
外键的定义语法:

1 [CONSTRAINT symbol] FOREIGN KEY [id] (index_col_name, ...) 2 REFERENCES tbl_name (index_col_name, ...) 3 [ON DELETE {RESTRICT | CASCADE | SET NULL | NO ACTION | SET DEFAULT}] 4 [ON UPDATE {RESTRICT | CASCADE | SET NULL | NO ACTION | SET DEFAULT}] 5 该语法可以在 CREATE TABLE 和 ALTER TABLE 时使用,如果不指定CONSTRAINT symbol,MYSQL会自动生成一个名字。 6 ON DELETE、ON UPDATE表示事件触发限制,可设参数: 7 RESTRICT(限制外表中的外键改动) 8 CASCADE(跟随外键改动) 9 SET NULL(设空值) 10 SET DEFAULT(设默认值) 11 NO ACTION(无动作,默认的) 12 13 14 15 creat table color( 16 nid int not null primary key, 17 name char(16) not null 18 ) 19 20 create table fruit( 21 nid int not null primary key, 22 smt char(32) null , 23 color_id int not null, 24 constraint fk_cc foreign key (color_id) references color(nid) 25 ) 26 27 28 create table student( 29 sid int not null auto_increment primary key, 30 sname char(32), 31 gender char(3), 32 class_id int, 33 constraint fk1 foreign key (class_id) references class(cid) 34 )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; 35 36 37 38 39 2.删除表 40 41 drop table 表名 42 43 3.清空表 44 45 delete from 表名 46 truncate table 表名 47 48 49 4.修改表 50 51 52 添加列:alter table 表名 add 列名 类型 53 删除列:alter table 表名 drop column 列名 54 修改列: 55 alter table 表名 modify column 列名 类型; -- 类型 56 alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 类型; -- 列名,类型 57 58 添加主键: 59 alter table 表名 add primary key(列名); 60 删除主键: 61 alter table 表名 drop primary key; 62 alter table 表名 modify 列名 int, drop primary key; 63 64 添加外键:alter table 从表 add constraint 外键名称(形如:FK_从表_主表) foreign key 从表(外键字段) references 主表(主键字段); 65 删除外键:alter table 表名 drop foreign key 外键名称 66 67 修改默认值:ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i SET DEFAULT 1000; 68 删除默认值:ALTER TABLE testalter_tbl ALTER i DROP DEFAULT; 69 70 71 5.基本数据类型 72 73 MySQL的数据类型大致分为:数值、时间和字符串 74 75 二进制 76 77 78 79 bit[(M)] 80 二进制位(101001),m表示二进制位的长度(1-64),默认m=1 81 82 83 整型 84 tinyint[(m)] [unsigned] [zerofill] 85 86 小整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围: 87 有符号: 88 -128 ~ 127. 89 无符号: 90 ~ 255 91 92 特别的: MySQL中无布尔值,使用tinyint(1)构造。 93 94 int[(m)][unsigned][zerofill] 95 96 整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围: 97 有符号: 98 -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 99 无符号: 100 ~ 4294967295 101 102 特别的:整数类型中的m仅用于显示,对存储范围无限制。例如: int(5),当插入数据2时,select 时数据显示为: 00002 103 104 bigint[(m)][unsigned][zerofill] 105 大整数,数据类型用于保存一些范围的整数数值范围: 106 有符号: 107 -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 108 无符号: 109 ~ 18446744073709551615 110 111 112 小数 113 114 decimal[(m[,d])] [unsigned] [zerofill] 115 准确的小数值,m是数字总个数(负号不算),d是小数点后个数。 m最大值为65,d最大值为30。 116 117 特别的:对于精确数值计算时需要用此类型 118 decaimal能够存储精确值的原因在于其内部按照字符串存储。 119 120 FLOAT[(M,D)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] 121 单精度浮点数(非准确小数值),m是数字总个数,d是小数点后个数。 122 无符号: 123 -3.402823466E+38 to -1.175494351E-38, 124 1.175494351E-38 to 3.402823466E+38 125 有符号: 126 1.175494351E-38 to 3.402823466E+38 127 128 **** 数值越大,越不准确 **** 129 130 DOUBLE[(M,D)] [UNSIGNED] [ZEROFILL] 131 双精度浮点数(非准确小数值),m是数字总个数,d是小数点后个数。 132 133 无符号: 134 -1.7976931348623157E+308 to -2.2250738585072014E-308 135 2.2250738585072014E-308 to 1.7976931348623157E+308 136 有符号: 137 2.2250738585072014E-308 to 1.7976931348623157E+308 138 **** 数值越大,越不准确 ****‘‘ 139 140 141 字符串 142 143 144 char (m) 145 char数据类型用于表示固定长度的字符串,可以包含最多达255个字符。其中m代表字符串的长度。 146 PS: 即使数据小于m长度,也会占用m长度 147 varchar(m) 148 varchars数据类型用于变长的字符串,可以包含最多达255个字符。其中m代表该数据类型所允许保存的字符串的最大长度,只要长度小于该最大值的字符串都可以被保存在该数据类型中。 149 150 注:虽然varchar使用起来较为灵活,但是从整个系统的性能角度来说,char数据类型的处理速度更快,有时甚至可以超出varchar处理速度的50%。因此,用户在设计数据库时应当综合考虑各方面的因素,以求达到最佳的平衡 151 152 text 153 text数据类型用于保存变长的大字符串,可以组多到65535 (2**16 ? 1)个字符。 154 155 mediumtext 156 A TEXT column with a maximum length of 16,777,215 (2**24 ? 1) characters. 157 158 longtext 159 A TEXT column with a maximum length of 4,294,967,295 or 4GB (2**32 ? 1) characters. 160 161 162 枚举类型 163 164 enum 165 枚举类型, 166 An ENUM column can have a maximum of 65,535 distinct elements. (The practical limit is less than 3000.) 167 示例: 168 CREATE TABLE shirts ( 169 name VARCHAR(40), 170 size ENUM(‘x-small‘, ‘small‘, ‘medium‘, ‘large‘, ‘x-large‘) 171 ); 172 INSERT INTO shirts (name, size) VALUES (‘dress shirt‘,‘large‘), (‘t-shirt‘,‘medium‘),(‘polo shirt‘,‘small‘); 173 174 集合类型 175 176 set 177 集合类型 178 A SET column can have a maximum of 64 distinct members. 179 示例: 180 CREATE TABLE myset (col SET(‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘, ‘d‘)); 181 INSERT INTO myset (col) VALUES (‘a,d‘), (‘d,a‘), (‘a,d,a‘), (‘a,d,d‘), (‘d,a,d‘); 182 183 184 时间 185 DATE 186 YYYY-MM-DD(1000-01-01/9999-12-31) 187 188 TIME 189 HH:MM:SS(‘-838:59:59‘/‘838:59:59‘) 190 191 YEAR 192 YYYY(1901/2155) 193 194 DATETIME 195 196 YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS(1000-01-01 00:00:00/9999-12-31 23:59:59 Y) 197 198 TIMESTAMP 199 200 YYYYMMDD HHMMSS(1970-01-01 00:00:00/2037 年某时)

1 insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...) 2 insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...),(值,值,值...) 3 insert into 表 (列名,列名...) select (列名,列名...) from 表 4 5 2.删 delete 6 7 8 delete from 表 9 delete from 表 where id=1 and name=‘123‘ 10 11 12 3.改 update 13 14 update 表 set name = ‘a‘ where id>1 15 16 17 4.查 select 18 19 select * from 表 20 select * from 表 where id > 1 21 select nid,name,gender as gg from 表 where id > 1 22 23 24 5.扩展参数及用法 25 26 条件 where 27 28 WHERE 子句用于规定选择的标准。 29 30 语法:SELECT 列名称 FROM 表名称 WHERE 列 运算符 值 31 32 select * from 表 where id > 1 and name != ‘alex‘ and num = 12; 33 34 select * from 表 where id between 5 and 16; 35 36 select * from 表 where id in (11,22,33) 37 select * from 表 where id not in (11,22,33) 38 select * from 表 where id in (select nid from 表) 39 40 41 42 AND 和 OR 43 44 AND - 如果第一个条件和第二个条件都成立; OR - 如果第一个条件和第二个条件中只要有一个成立; 45 46 47 48 IN 49 50 IN - 操作符允许我们在 WHERE 子句中规定多个值。 51 IN - 操作符用来指定范围,范围中的每一条,都进行匹配。IN取值规律,由逗号分割,全部放置括号中。 52 53 54 NOT 55 56 NOT - 操作符总是与其他操作符一起使用,用在要过滤的前面。 57 58 59 60 通配符 like 61 62 select * from 表 where name like ‘ale%‘ #ale开头的所有(多个字符串) 63 select * from 表 where name like ‘ale_‘ #ale开头的所有(一个字符) 64 65 66 限制 limit 67 68 select * from 表 limit 5; #前5行 69 select * from 表 limit 4,5; #从第4行开始的5行 70 select * from 表 limit 5 offset 4 #从第4行开始的5行 71 72 73 74 排序 ORDER BY 75 76 语句默认按照升序对记录进行排序。 77 ORDER BY - 语句用于根据指定的列对结果集进行排序。 78 DESC - 按照降序对记录进行排序。 79 ASC - 按照顺序对记录进行排序。 80 81 select * from 表 order by 列 asc - 根据 “列” 从小到大排列 82 select * from 表 order by 列 desc - 根据 “列” 从大到小排列 83 select * from 表 order by 列1 desc,列2 asc - 根据 “列1” 从大到小排列,如果相同则按列2从小到大排序 84 85 86 87 分组 group by 88 select num from 表 group by num 89 select num,nid from 表 group by num,nid 90 select num,nid from 表 where nid > 10 group by num,nid order nid desc 91 select num,nid,count(*),sum(score),max(score),min(score) from 表 group by num,nid 92 93 select num from 表 group by num having max(id) > 10 94 95 特别的:group by 必须在where之后,order by之前 96 97 例 98 99 mysql> SELECT * FROM employee_tbl; 100 +----+--------+---------------------+--------+ 101 | id | name | date | singin | 102 +----+--------+---------------------+--------+ 103 | 1 | 小明 | 2016-04-22 15:25:33 | 1 | 104 | 2 | 小王 | 2016-04-20 15:25:47 | 3 | 105 | 3 | 小丽 | 2016-04-19 15:26:02 | 2 | 106 | 4 | 小王 | 2016-04-07 15:26:14 | 4 | 107 | 5 | 小明 | 2016-04-11 15:26:40 | 4 | 108 | 6 | 小明 | 2016-04-04 15:26:54 | 2 | 109 +----+--------+---------------------+--------+ 110 6 rows in set (0.00 sec) 111 112 接下来我们使用 GROUP BY 语句 将数据表按名字进行分组,并统计每个人有多少条记录: 113 mysql> SELECT name, COUNT(*) FROM employee_tbl GROUP BY name; 114 +--------+----------+ 115 | name | COUNT(*) | 116 +--------+----------+ 117 | 小丽 | 1 | 118 | 小明 | 3 | 119 | 小王 | 2 | 120 +--------+----------+ 121 3 rows in set (0.01 sec) 122 123 124 AS 125 126 as - 可理解为:用作、当成,作为;别名 127 一般是重命名列名或者表名。 128 129 130 131 语法:select column_1 as 列1,column_2 as 列2 from table as 表 132 133 SELECT * FROM Employee AS emp 134 -- 这句意思是查找所有Employee 表里面的数据,并把Employee表格命名为 emp。 135 -- 当你命名一个表之后,你可以在下面用 emp 代替 Employee. 136 -- 例如 SELECT * FROM emp.
使用 MySQL 的 JOIN 在两个或多个表中查询数据。
JOIN: 如果表中有至少一个匹配,则返回行
FULL JOIN: 只要其中一个表中存在匹配,就返回行
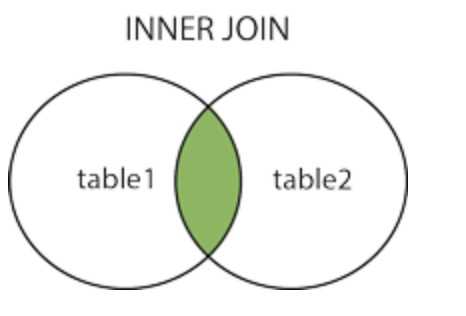
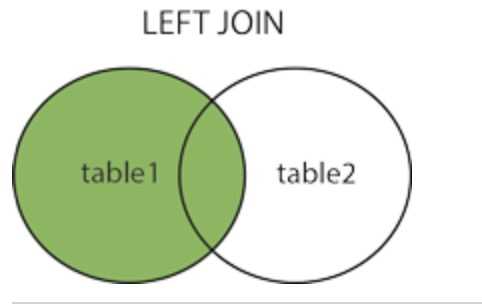
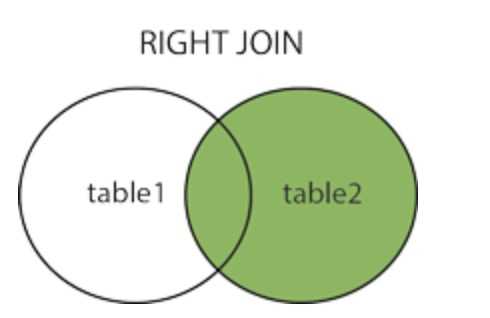

1 无对应关系则不显示 2 select A.num, A.name, B.name 3 from A,B 4 Where A.nid = B.nid 5 6 无对应关系则不显示 7 select A.num, A.name, B.name 8 from A inner join B 9 on A.nid = B.nid 10 11 A表所有显示,如果B中无对应关系,则值为null 12 select A.num, A.name, B.name 13 from A left join B 14 on A.nid = B.nid 15 16 B表所有显示,如果B中无对应关系,则值为null 17 select A.num, A.name, B.name 18 from A right join B 19 on A.nid = B.nid
组合 UNION
UNION - 操作符用于合并两个或多个 SELECT 语句的结果集。

1 组合,自动处理重合数据 2 select nickname 3 from A 4 union 5 select name 6 from B 7 8 组合,不处理重合数据 9 select nickname 10 from A 11 union all 12 select name 13 from B
补充:
COUNT 函数的用法很简单,就是为了统计记录数。SELECT 语句所返回的

1 mysql> SELECT * FROM employee_tbl; 2 +------+------+------------+--------------------+ 3 | id | name | work_date | daily_typing_pages | 4 +------+------+------------+--------------------+ 5 | 1 | John | 2007-01-24 | 250 | 6 | 2 | Ram | 2007-05-27 | 220 | 7 | 3 | Jack | 2007-05-06 | 170 | 8 | 3 | Jack | 2007-04-06 | 100 | 9 | 4 | Jill | 2007-04-06 | 220 | 10 | 5 | Zara | 2007-06-06 | 300 | 11 | 5 | Zara | 2007-02-06 | 350 | 12 +------+------+------------+--------------------+ 13 rows in set (0.00 sec)

mysql> SELECT * FROM employee_tbl; +------+------+------------+--------------------+ | id | name | work_date | daily_typing_pages | +------+------+------------+--------------------+ | 1 | John | 2007-01-24 | 250 | | 2 | Ram | 2007-05-27 | 220 | | 3 | Jack | 2007-05-06 | 170 | | 3 | Jack | 2007-04-06 | 100 | | 4 | Jill | 2007-04-06 | 220 | | 5 | Zara | 2007-06-06 | 300 | | 5 | Zara | 2007-02-06 | 350 | +------+------+------------+--------------------+ rows in set (0.00 sec)
假设要根据上表统计行的总数,当然可以这样做:

1 复制代码 2 3 mysql>SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee_tbl ; 4 +----------+ 5 | COUNT(*) | 6 +----------+ 7 | 7 | 8 +----------+ 9 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
同样,如果希望计算 Zara 的记录数,可以这样实现:

1 mysql>SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee_tbl 2 -> WHERE name="Zara"; 3 +----------+ 4 | COUNT(*) | 5 +----------+ 6 | 2 | 7 +----------+ 8 1 row in set (0.04 sec)
注意:由于 SQL 查询对大小写不敏感,所以在 WHERE 条件中,无论是写成 ZARA 还是 Zara,结果都是一样的。
PyMySQL 是在 Python3.x 版本中用于连接 MySQL 服务器的一个库,Python2中则使用mysqldb。
PyMySQL 遵循 Python 数据库 API v2.0 规范,并包含了 pure-Python MySQL 客户端库。

1 pip3 install PyMySQL

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 # 创建连接 6 conn = pymysql.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘, port=3306, user=‘root‘, passwd=‘123‘, db=‘t1‘) 7 # 创建游标 8 cursor = conn.cursor() 9 10 # 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数 11 effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = ‘1.1.1.2‘") 12 13 # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数 14 #effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = ‘1.1.1.2‘ where nid > %s", (1,)) 15 16 # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数 17 #effect_row = cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",1),("1.1.1.11",2)]) 18 19 20 # 提交,不然无法保存新建或者修改的数据 21 conn.commit() 22 23 # 关闭游标 24 cursor.close() 25 # 关闭连接 26 conn.close()
注:当使用字符串格式化时容易引起sql注入

1 sql = ‘select * from userinfo where username="%s" and password="%s" ‘ %(user,pwd,) #不推荐使用 2 3 sql = ‘select * from userinfo where username=%s and password=%s‘,[user,pwd] #推荐使用,mysql会自动格式化,避免SQL注入 4 5 import pymysql 6 7 user = input(‘请输入用户名:‘) 8 pwd = input(‘请输入密码:‘) 9 10 # 获取数据 11 conn = pymysql.Connect(host=‘192.168.12.89‘,port=3306,user=‘root‘,password="123",database="s17day11db",charset=‘utf8‘) 12 cursor = conn.cursor() 13 14 v = cursor.execute(‘select * from userinfo where username=%s and password=%s‘,[user,pwd]) 15 result = cursor.fetchone() 16 cursor.close() 17 conn.close() 18 19 print(result)
new_class_id = cursor.lastrowid # 获取新增数据自增ID

1 import pymysql 2 3 # 获取数据 4 conn = pymysql.Connect(host=‘192.168.12.89‘,port=3306,user=‘root‘,password="123",database="s17day11db",charset=‘utf8‘) 5 cursor = conn.cursor() 6 7 cursor.execute(‘insert into class(caption) values(%s)‘,[‘新班级‘]) 8 conn.commit() 9 new_class_id = cursor.lastrowid # 获取新增数据自增ID 10 11 cursor.execute(‘insert into student(sname,gender,class_id) values(%s,%s,%s)‘,[‘李杰‘,‘男‘,new_class_id]) 12 conn.commit() 13 14 cursor.close() 15 conn.close()
查询语句

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 conn = pymysql.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘, port=3306, user=‘root‘, passwd=‘123‘, db=‘t1‘) 6 cursor = conn.cursor() 7 cursor.execute("select * from hosts") 8 9 # 获取第一行数据 10 row_1 = cursor.fetchone() 11 12 # 获取前n行数据 13 # row_2 = cursor.fetchmany(3) 14 # 获取所有数据 15 # row_3 = cursor.fetchall() 16 17 conn.commit() 18 cursor.close() 19 conn.close()
注:在fetch数据时按照顺序进行,可以使用cursor.scroll(num,mode)来移动游标位置,如:
默认获取的数据是元祖类型,如果想要或者字典类型的数据
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 3 import pymysql 4 5 conn = pymysql.connect(host=‘127.0.0.1‘, port=3306, user=‘root‘, passwd=‘123‘, db=‘t1‘) 6 7 # 游标设置为字典类型 8 9 cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 10 v = cursor.execute(‘SELECT * FROM score‘) 11 result = cursor.fetchall() 12 # result = cursor.fetchone() 13 # result = cursor.fetchmany() 14 print(result) 15 16 17 18 cursor.close() 19 conn.close()
标签:signed nts 开始 ges slave nec 用户权限 sla 协议
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/you0329/p/7162251.html