标签:having 多列 ges 重复 返回 表达 常用 nbsp gen
第二部分 常用sql用法和注意事项
1. exists 和 in
2. union 和 union all
3. with as
4. order by
5. group by
6. where 和 having
7. case when 和 decode
1.exits和in用法
1)说明:
1. exists先对外表做循环,每次循环对内表查询;in将内表和外表做hash连接
2. 使用exists oracle会先检查主查询; 使用in,首先执行子查询,并将结果存储在临时表中
1. 使用exists和not exists
select name, classno from student where exists (select * from class where student.classno= class.classno);
select name, classno from student where not exists (select * from class where student.classno= class.classno);
2. 使用in 和not in
select name, classno from student where classno in (select classno from class);
select name, classno from student where classno not in (select classno from class);
2)比较
1. 如果两个表大小相当,in和exists差别不大
2. 如果两个表大小相差较大则子查询表大的用exists,子查询表小的用in
3.尽量不要使用not in
2.union和union all
1)说明:
1. 使用场景:需要将两个select语句结果整体显示时,可以使用union和union all
2. union对两个结果集取并集不包含重复结果同时进行默认规则的排序;而union all对两个结果集去并集,包括重复行,不进行排序
3. union需要进行重复值扫描,效率低,如果没有要删除重复行,应该使用union all
4. insersect和minus分别交集和差集,都不包括重复行,并且进行默认规则的排序
2)使用注意事项
1.可以将多个结果集合并
2. 必须保证select集合的结果有相同个数的列,并且每个列的类型是一样的(列名不一定要相同,会默认将第一个结果的列名作为结果集的列名)
3.with as
1)说明:
1. with table as 可以建立临时表,一次分析,多次使用
2. 对于复杂查询,使用with table as可以抽取公共查询部分,多次查询时可以提高效率
3. 增强了易读性
2)语法:
with tabName as (select ...)
4. order by
1)说明:
1. order by 决定oracle如何将查询结果排序
2. 不指定asc或者desc时默认asc
2)使用:
1. 单列升序(可以去掉asc)
select * from student order by score asc;
2. 多列升序
select * from student order by score,deptno;
3. 多列降序
select * from student order by score desc,deptno desc;
4. 混合
select * from student order by score asc,deptno desc;
3)对NULL的处理
1. oracle在order by 时认为null是最大值,asc时排在最后,desc时排在最前
2. 使用 nulls first (不管asc或者desc,null记录排在最前)或者nulls last 可以控制null的位置
4)将某行数据置顶(decode)
select * from student order by decode(score,100,1,2);
select * from student order by decode(score,100,1,2), score; //(某一行置顶,其他的升序)
5)注意事项
1. 任何在order by 语句的非索引项都将降低查询速度
2. 避免在order by 子句中使用表达式
5. group by
1)说明:
1.用于对where执行结果进行分组
eg1:select sum(score), deptno from student group by deptno;
eg2:select deptno,sum(score) from student where deptno>1 group by deptno;
6.where和having
1)说明:
1. where和having都是用来筛选数据,但是执行的顺序不同 where --group by--having(即分组计算前计算where语句,分组计算后计算having‘语句)
2. having一般用来对分组后的数据进行筛选
3. where中不能使用聚组函数如sum,count,max等
2)例子
eg1:
select deptno,sum(score) from student where deptno>1 group by deptno having sum(score)>100;
7. case when 和decode
1)说明:
1. decode更简洁
2. decode只能做等值的条件区分,case when可以使用区间的做判断
2)语法:
decode(条件,值1,返回值1,值2,返回值2,...值n,返回值n,缺省值)
--等价于:
IF 条件=值1 THEN
RETURN(翻译值1)
ELSIF 条件=值2 THEN
RETURN(翻译值2)
......
ELSIF 条件=值n THEN
RETURN(翻译值n)
ELSE
RETURN(缺省值)
END IF
CASE expr WHEN comparison_expr1 THEN return_expr1
[WHEN comparison_expr2 THEN return_expr2
WHEN comparison_exprn THEN return_exprn
ELSE else_expr]
END
CASE
WHEN comparison_expr1 THEN return_expr1
[WHEN comparison_expr2 THEN return_expr2
WHEN comparison_exprn THEN return_exprn
ELSE else_expr]
END
3)例子:
eg1:
方式一:
select name, score,gender,
case gender when ‘1‘ then ‘女‘
when ‘2‘ then ‘男‘
else ‘未说明‘
end gender_t
from student;
方式二:
select name, score,gender,
case when gender=‘1‘ then ‘女‘
when gender=‘2‘ then ‘男‘
else ‘未说明‘
end gender_t
from student;
方式三:
select name,gender,decode(gender,‘1‘,‘女‘,‘2‘,‘男‘,‘未说明‘)gender_t from student;
结果:
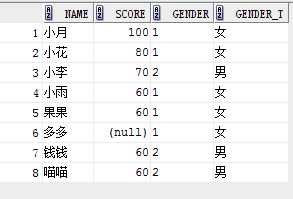
eg2:
select name,score,
case when score >80 then‘优秀‘
when score>=60 and score <=80 then ‘良好‘
when score<60 then ‘不及格‘
end evalution
from student;
结果:
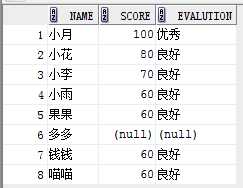
设置默认值,将null置为没成绩:
select name,score,
case when score >80 then‘优秀‘
when score>=60 and score <=80 then ‘良好‘
when score<60 then ‘不及格‘
else ‘没成绩‘
end evalution
from student;
结果:

4)注意:
1.case有两种形式,其中case 表达式 when then方式效率高于case when 表达式效率
2.使用decode函数可以避免重复扫描相同记录或者重复连接相同的表,因而某些情况可以减少处理时间
sql优化(oracle)- 第二部分 常用sql用法和注意事项
标签:having 多列 ges 重复 返回 表达 常用 nbsp gen
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sunziying/p/7187036.html