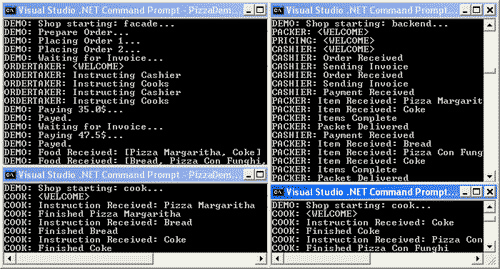
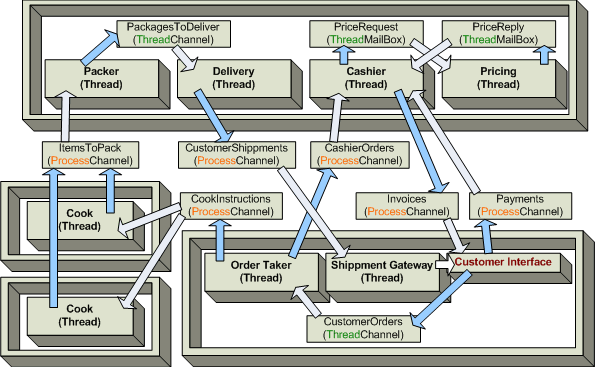
3. 跨进程共享内存:内存映射文件
我们已经实现了跨线程和跨进程的共享资源访问同步。但是传递/接收消息还需要共享资源。对于线程来说,只需要声明一个类成员变量就可以了。但是对于跨进程来说,我们需要使用到 win32 API 提供的内存映射文件(Memory Mapped Files,简称MMF)。使用 MMF和使用 win32 信号量差不多。我们需要先调用 CreateFileMapping 方法来创建一个内存映射文件的句柄:
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll",EntryPoint="CreateFileMapping",
SetLastError=true,CharSet=CharSet.Unicode)]
internal static extern IntPtr CreateFileMapping(uint hFile,
SecurityAttributes lpAttributes, uint flProtect,
uint dwMaximumSizeHigh, uint dwMaximumSizeLow, string lpName);
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll",EntryPoint="MapViewOfFile",
SetLastError=true,CharSet=CharSet.Unicode)]
internal static extern IntPtr MapViewOfFile(IntPtr hFileMappingObject,
uint dwDesiredAccess, uint dwFileOffsetHigh,
uint dwFileOffsetLow, uint dwNumberOfBytesToMap);
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll",EntryPoint="UnmapViewOfFile",
SetLastError=true,CharSet=CharSet.Unicode)]
[return : MarshalAs( UnmanagedType.VariantBool )]
internal static extern bool UnmapViewOfFile(IntPtr lpBaseAddress);
public static MemoryMappedFile CreateFile(string name,
FileAccess access, int size)
{
if(size < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Size must not be negative","size");
IntPtr fileMapping = NTKernel.CreateFileMapping(0xFFFFFFFFu,null,
(uint)access,0,(uint)size,name);
if(fileMapping == IntPtr.Zero)
throw new MemoryMappingFailedException();
return new MemoryMappedFile(fileMapping,size,access);
}
我们希望直接使用 pagefile 中的虚拟文件,所以我们用 -1(0xFFFFFFFF) 来作为文件句柄来创建我们的内存映射文件句柄。我们也指定了必填的文件大小,以及相应的名称。这样其他进程就可以通过这个名称来同时访问该映射文件。创建了内存映射文件后,我们就可以映射这个文件不同的部分(通过偏移量和字节大小来指定)到我们的进程地址空间。我们通过 MapViewOfFile 系统方法来指定:
public MemoryMappedFileView CreateView(int offset, int size,
MemoryMappedFileView.ViewAccess access)
{
if(this.access == FileAccess.ReadOnly && access ==
MemoryMappedFileView.ViewAccess.ReadWrite)
throw new ArgumentException(
"Only read access to views allowed on files without write access",
"access");
if(offset < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Offset must not be negative","size");
if(size < 0)
throw new ArgumentException("Size must not be negative","size");
IntPtr mappedView = NTKernel.MapViewOfFile(fileMapping,
(uint)access,0,(uint)offset,(uint)size);
return new MemoryMappedFileView(mappedView,size,access);
}
在不安全的代码中,我们可以将返回的指针强制转换成我们指定的类型。尽管如此,我们不希望有不安全的代码存在,所以我们使用 Marshal 类来从中读写我们的数据。偏移量参数是用来从哪里开始读写数据,相对于指定的映射视图的地址。
public byte ReadByte(int offset)
{
return Marshal.ReadByte(mappedView,offset);
}
public void WriteByte(byte data, int offset)
{
Marshal.WriteByte(mappedView,offset,data);
}
public int ReadInt32(int offset)
{
return Marshal.ReadInt32(mappedView,offset);
}
public void WriteInt32(int data, int offset)
{
Marshal.WriteInt32(mappedView,offset,data);
}
public void ReadBytes(byte[] data, int offset)
{
for(int i=0;i<data.Length;i++)
data[i] = Marshal.ReadByte(mappedView,offset+i);
}
public void WriteBytes(byte[] data, int offset)
{
for(int i=0;i<data.Length;i++)
Marshal.WriteByte(mappedView,offset+i,data[i]);
}
但是,我们希望读写整个对象树到文件中,所以我们需要支持自动进行序列化和反序列化的方法。
public object ReadDeserialize(int offset, int length)
{
byte[] binaryData = new byte[length];
ReadBytes(binaryData,offset);
System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary.BinaryFormatter formatter
= new System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary.BinaryFormatter();
System.IO.MemoryStream ms = new System.IO.MemoryStream(
binaryData,0,length,true,true);
object data = formatter.Deserialize(ms);
ms.Close();
return data;
}
public void WriteSerialize(object data, int offset, int length)
{
System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary.BinaryFormatter formatter
= new System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary.BinaryFormatter();
byte[] binaryData = new byte[length];
System.IO.MemoryStream ms = new System.IO.MemoryStream(
binaryData,0,length,true,true);
formatter.Serialize(ms,data);
ms.Flush();
ms.Close();
WriteBytes(binaryData,offset);
}
请注意:对象序列化之后的大小不应该超过映射视图的大小。序列化之后的大小总是比对象本身占用的内存要大的。我没有试过直接将对象内存流绑定到映射视图,那样做应该也可以,甚至可能带来少量的性能提升。