标签:nbsp 顺序 代码 运行 条件 list start 作用 ima
python装饰器
装饰器本质上是一个函数,在不对其他函数源代码进行修改的情况下,为其他函数提供额外功能。
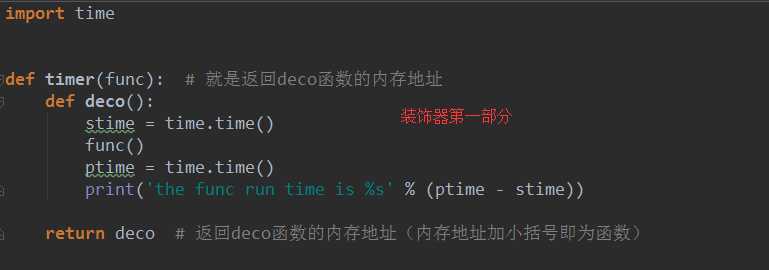
import time
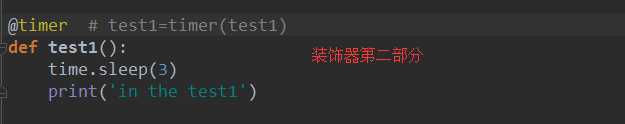
def test1():
time.sleep(3)
print(‘in the test1‘)
def test2():
time.sleep(3)
print(‘in the test2‘)
def timer(func): #就是返回deco函数的内存地址
def deco():
stime=time.time()
func()
ptime=time.time()
print(‘the func run time is %s‘%(ptime-stime))
return deco #返回deco函数的内存地址(内存地址加小括号即为函数)
test1=timer(test1)
test1()
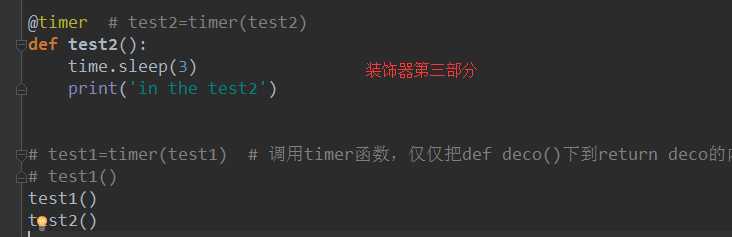
分析:test1的内存地址(只有函数名,没有小括号就是指其内存地址)赋值给func,func()就等价与test1()运行,deco记录test1()运行相关时间
二:高阶函数
满足下列条件之一就可成函数为高阶函数
某一函数名当做参数传入另一个函数中
函数的返回值包含n个函数,n>0
高阶函数示范:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
def bar(): print ‘in the bar‘def foo(func): res=func() return resfoo(bar) |
高阶函数的牛逼之处
|
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
def foo(func): return funcprint ‘Function body is %s‘ %(foo(bar))print ‘Function name is %s‘ %(foo(bar).func_name)foo(bar)()#foo(bar)() 等同于bar=foo(bar)然后bar()bar=foo(bar)bar() |
三:内嵌函数和变量作用域:
定义:在一个函数体内创建另外一个函数,这种函数就叫内嵌函数(基于python支持静态嵌套域)
函数嵌套示范:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
def foo(): def bar(): print ‘in the bar‘ bar()foo()# bar() |
局部作用域和全局作用域的访问顺序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
x=0def grandpa(): # x=1 def dad(): x=2 def son(): x=3 print x son() dad()grandpa() |
局部变量修改对全局变量的影响
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
y=10# def test():# y+=1# print ydef test(): # global y y=2 print ytest()print ydef dad(): m=1 def son(): n=2 print ‘--->‘,m + n print ‘-->‘,m son()dad() |
四:闭包:
如果在一个内部函数里,对在外部作用域(但不是在全局作用域)的变量进行引用,那么内部函数就被认为是 closure
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
def counter(start_num=0): count=[start_num] def incr(): count[0]+=1 return count[0] return incrprint counter()print counter()()print counter()()c=counter()print c()print c() |
标签:nbsp 顺序 代码 运行 条件 list start 作用 ima
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/gilgamesh-hjb/p/7226090.html