标签:自动化 illegal 加载类 uri integer not uil png efault
一.注解的基本
1.注解的通俗理解
注解(Annotation) 为我们在代码中添加信息提供了一种形式化的方法,是我们可以在稍后 某个时刻方便地使用这些数据(通过解析注解来使用这些数据)。
2.注解的作用
3.注解的状态
源码注解:只在源码中存在的注解。
编译时注解:注解在源码和.class文件中都存在。
运行时注解:运行阶段还起作用,甚至会影响运行逻辑的注解,如Spring, Mybatic中常用的注解。
4.注解的分类
a.jdk内置注解:
如下Override的例子,其他方法自测,child继承Person,并且覆盖了Person中的方法:
public class child extends Person { @Override//覆盖 public int age() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } @Override public String name() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public void sing() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
b.元注解
注解的注解,常见的有4个,在自定义注解中会用到,分别是
@Target,@Retention,@Documented,@Inherited

c.自定义注解
自己定义的注解。自定义注解由元注解和自己定义的注解(annotation)构成,格式,要求及实例如下:
//自定义注解 //下面4行是元注解 @Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)//元注解的作用域,生命周期 @Inherited //允许子继承 @Documented//生成javadoc文档时会包含次注解 //使用@interface关键字定义注解 public @interface Description{ /* * 成员类型是受限的,所有基本类型、String、Class、enum、Annotation、以上类型的数组形式。 * 如果注解只有一个成员时,则成员名必须取名为value(), * 在使用是可以忽略成员名和赋值名 * 注解类可以没有成员,没有成员的注解称为标识注解 */ String value();//成员以无参无异常方式声明 //String author(); //int age() default 18;//可以给成员指定默认的值 }
5.注解解析
注解解析其实是用了Java中的反射机制,不明白的可以看看我的上一篇博客,Java--反射的逐步理解
核心代码如下:
//1.使用类加载器加载类 try { Class class1 =Class.forName("cn.ann.test.child");
//2.找到类上面的注解 boolean isExist=class1.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class);//判断是否存在这个注解 Method[] ms = class1.getMethods(); for (Method method : ms) { boolean exist=method.isAnnotationPresent(Description.class); if(exist){ Description b=(Description)method.getAnnotation(Description.class); System.out.println(b.value()); } } if(isExist){ //3.得拿到注解实例 Description a=(Description)class1.getAnnotation(Description.class); System.out.println(a.value()); } //4.找到方法上的注解 for (Method method : ms) { Annotation[] s =method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation : s) { if(annotation instanceof Description){ System.out.println(((Description) annotation).value()); } } } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } }
二.注解应用的一个小场景
1.场景要求
a.有一张用户表,字段包括用户ID,用户名,昵称,年龄,所在城市
b.方便的对每个字段或着字段的组合条件进行检索,并打印出SQL
2.实现方法
具体代码如下(其中注释了代码的思路):
a.用户表Users.java
@Table("user")
public class Users {
@Column("id")
private int id;
@Column("user_name")
private String userName;
@Column("nick_name")
private String nickName;
@Column("age")
private int age;
@Column("city")
private String city;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
b.自定义注解Table.java
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited @Documented public @interface Table { String value(); }
c.自定义注解Column.java
@Target({ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited @Documented public @interface Column { String value(); }
d.测试类test.java
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Users f1 = new Users(); f1.setId(68);//表示查询id为68的用户 f1.setAge(35);
Users f2 = new Users(); f2.setUserName("huhu"); f2.setCity("lanzhou");
Users f3 = new Users(); f3.setAge(20);
String sql1 = query(f1); String sql2 = query(f2); String sql3 = query(f3);
System.out.println(sql1); System.out.println(sql2); System.out.println(sql3); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static String query(Object obj) { StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder(); //1.获取到class Class class1 = obj.getClass(); //2.获取到table的名字 boolean isExist = class1.isAnnotationPresent(Table.class); if(isExist){ Table hTable=(Table)class1.getAnnotation(Table.class); s.append("select * from ").append(hTable.value()).append(" where 1=1"); } //3.遍历所有的字段 Field[] fields =class1.getDeclaredFields(); for (Field field : fields) { boolean exist = field.isAnnotationPresent(Column.class); if(exist){ Column f =(Column)field.getAnnotation(Column.class); String columnName = f.value(); //System.out.println(columnName); String fieldName = field.getName(); Object fieldString=null; String getMethodName="get"+fieldName.substring(0,1).toUpperCase()+fieldName.substring(1); try { /* * 4.处理每个字段对应的sql * 4.1拿到字段名 * 4.2拿到字段的值 * 4.3拼装sql */ Method aMethod = class1.getMethod(getMethodName); fieldString=(Object)aMethod.invoke(obj,null); //System.out.println(fieldString); if(fieldString==null||(fieldString instanceof Integer &&(Integer)fieldString==0)){ continue; } s.append(" and "+columnName); if(fieldString instanceof String){ s.append(" = "+"‘"+fieldString+"‘"); } else{ s.append(" = "+fieldString); } } catch (SecurityException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } //Method[] msMethods = class1.getMethods(); //for (Method method : msMethods) { //method.invoke(class1, Object); //} return s.toString(); } }
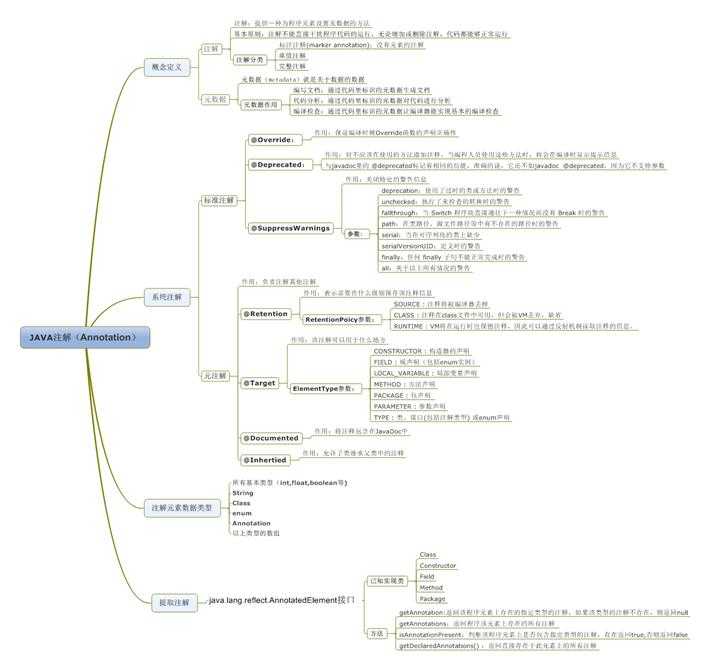
三.一张图描述注解
谢谢大家阅读。
标签:自动化 illegal 加载类 uri integer not uil png efault
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/huhu1203/p/7233713.html