标签:遍历 选择 python 应该 ... 技术 src 9.png lis
对于图结构的实现来说,最直观的方式之一就是使用邻接列表。下面我们来实现一个最简单的:假设现在我们有n个节点,编号分别为0,...,n-1。
然后,每个邻接列表就是一个数字列表,我们可以将他们编入一个大小为n的主列表,并用节点编号对其进行索引。
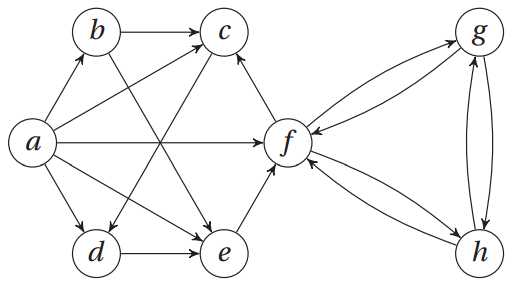
邻接集表示法:
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = range(8)
N = [
{b, c, d, e, f}, # a
{c, e}, # b
{d}, # c
{e}, # d
{f}, # e
{c, g, h}, # f
{f, h}, # g
{f, g} # h
]
邻接列表
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = range(8) N = [ [b, c, d, e, f], # a [c, e], # b [d], # c [e], # d [f], # e [c, g, h], # f [f, h], # g [f, g] # h ]
加权邻接字典
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = range(8)
N = [
{b:2, c:1, d:3, e:9, f:4}, # a
{c:4, e:3}, # b
{d:8}, # c
{e:7}, # d
{f:5}, # e
{c:2, g:2, h:2}, # f
{f:1, h:6}, # g
{f:9, g:8} # h
]
嵌套 list 实现的邻接矩阵
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = range(8)
# a b c d e f g h
N = [[0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0], # a
[0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0], # b
[0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0], # c
[0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0], # d
[0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0], # e
[0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1], # f
[0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1], # g
[0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0]] # h
由于图上没有自循环状态,其对角线上的值应该全为假。
无向图的邻接矩阵应该是一个对称矩阵。
我们通常会把不存在的边的权值设置为无穷大。
inf = float(‘inf‘)
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h = range(8) # a b c d e f g h N = [[inf, 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 ,inf,inf], # a [inf,inf, 1 ,inf, 1 ,inf,inf,inf], # b [inf,inf,inf, 1 ,inf,inf,inf,inf], # c [inf,inf,inf,inf, 1 ,inf,inf,inf], # d [inf,inf,inf,inf,inf, 1 ,inf,inf], # e [inf,inf, 1 ,inf,inf,inf, 1 , 1 ], # f [inf,inf,inf,inf,inf, 1 ,inf, 1 ], # g [inf,inf,inf,inf,inf, 1 , 1 ,inf]] # h
在邻接矩阵中,查询变(u,v)需要的时间为Θ(1),遍历v邻居的操作时间为Θ(n);
邻接列表中,两种操作所需的时间都为Θ(d(v))
我们应该根据图的具体用处来选择相关的表示法。
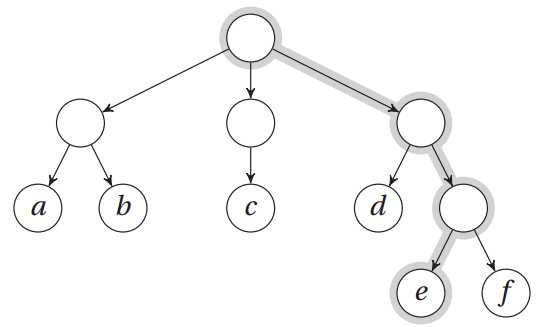
树表示成一个二维列表
>>> T = [["a", "b"], ["c"], ["d", ["e", "f"]]] >>> T[0][1] ‘b‘ >>> T[2][1][0] ‘e‘
二叉树类:
class Tree:
def __init__(self, left, right):
self.left = left
self.right = right
>>> t = Tree(Tree("a", "b"), Tree("c", "d"))
>>> t.right.left
‘c‘
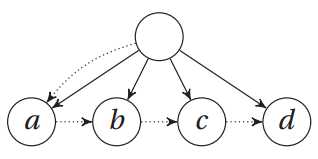
多路搜索树类:
class Tree:
def __init__(self, kids, next=None):
self.kids = self.val = kids
self.next = next
>>> t = Tree(Tree("a", Tree("b", Tree("c", Tree("d")))))
>>> t.kids.next.next.val
‘c‘
Bunch模式:
class Bunch(dict):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwds):
super(Bunch, self).__init__(*args, **kwds)
self.__dict__ = self
>>> T = Bunch
>>> t = T(left=T(left="a", right="b"), right=T(left="c"))
>>> t.left
{‘right‘: ‘b‘, ‘left‘: ‘a‘}
>>> t.left.right
‘b‘
>>> t[‘left‘][‘right‘]
‘b‘
>>> "left" in t.right
True
>>> "right" in t.right
False
标签:遍历 选择 python 应该 ... 技术 src 9.png lis
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/5poi/p/7271447.html