标签:开源 dao injection ica close classpath 路径 不能 etag
Spring是一个开源框架,为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。主要优势之一就是其分层架构。Spring的核心是控制反转和面向切面。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的一站式轻量级开源框架。
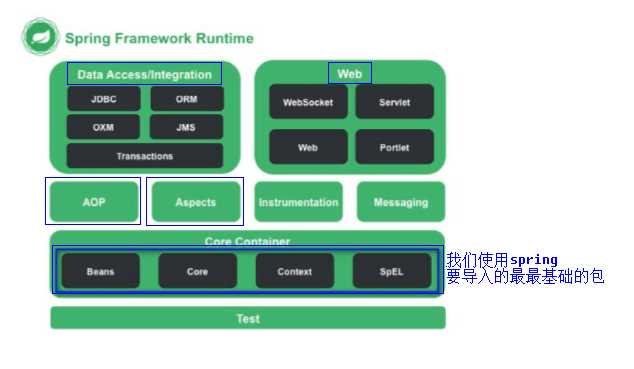

除了上面的4个包之外还需要日志包:

下面的包可选,老版本有需要:
com.springsource.org.apache.log4j-1.2.15.jar

package com.yyb.bean; public class User { public User() { System.out.println("User对象空参构造方法!!!!"); } private String name; private Integer age; private Car car; public User(String name, Car car) { System.out.println("User(String name, Car car)!!"); this.name = name; this.car = car; } public User(Car car,String name) { System.out.println("User(Car car,String name)!!"); this.name = name; this.car = car; } public User(Integer name, Car car) { System.out.println("User(Integer name, Car car)!!"); this.name = name+""; this.car = car; } public Car getCar() { return car; } public void setCar(Car car) { this.car = car; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public void init(){ System.out.println("我是初始化方法!"); } public void destory(){ System.out.println("我是销毁方法!"); } @Override public String toString() { return "User [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]"; } }

package com.yyb.bean; public class Car { private String name; private String color; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public String toString() { return "Car [name=" + name + ", color=" + color + "]"; } }
配置文件放的位置任意(建议放到src下);配置文件名任意(建议applicationContext.xml)。
在配置文件中添加如下代码:
package com.yyb.springTest; import com.yyb.bean.User; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by Administrator on 2017/8/8. */ public class SpringTest { @Test public void func1(){ ApplicationContext ac =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user = (User)ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user); } }
打印结果如下,可已发现User对象创建成功了:
User对象空参构造方法!!!! User [name=null, age=null, car=null]
IOC: Inverse Of Control ,即反转控制。指的是对象的创建权反转(交给)给Spring。作用是实现了程序的解耦合。
以前对象的创建是由我们自己创建,比如Service层中需要使用Dao层的类,则直接在Service层中使用new创建Dao层的对象。两层之间严重耦合。使用了Spring之后,对象的创建以及依赖关系可以由spring完成创建以及注入。
DI: Dependency Injection 即依赖注入。需要有IOC的环境,Spring创建这个类的过程中,将类的依赖属性设置进去。
注入方式:
注入类型:
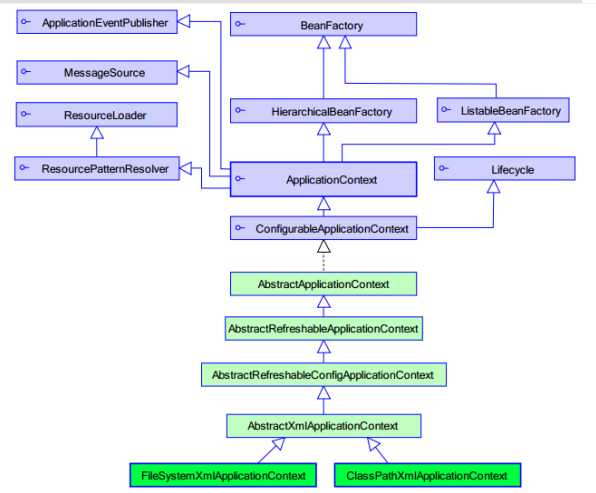
BeanFactory接口,是spring原始接口。针对原始接口的实现类功能较为单一。BeanFactory接口实现类的容器特点是每次在获得对象时才会创建对象。
每次容器启动时就会创建容器中配置的所有对象,并提供更多功能。
两个典型的实现类:
结论:web开发中,使用applicationContext。在资源匮乏的环境可以使用BeanFactory。
使用Bean元素描述需要spring容器管理的对象。
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ></bean>
scope属性
<bean name="user" class="com.yyb.bean.User" scope="singleton"></bean>
测试代码:
@Test //scope:singleton 单例 //scope:prototype 多例 public void fun4(){ //1 创建容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"); //2 向容器"要"user对象 User u = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u2 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u3 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); User u4 = (User) ac.getBean("user"); System.out.println(u2==u4);//单例:true //多例:false //3 打印user对象 System.out.println(u); }
生命周期属性
通过配置<bean>标签上的init-method作为Bean的初始化的时候执行的方法,配置destory-method作为Bean的销毁的时候执行的方法。销毁的方法想要执行,需要是单利创建的Bean,而且在工厂关闭的时候,Bean才会被销毁。
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" ></bean>
user类中代码:
public void init(){ System.out.println("我是初始化方法!"); } public void destory(){ System.out.println("我是销毁方法!"); }
测试代码:
@Test //测试生命周期方法 public void fun5(){ //1 创建容器对象 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"); //2 向容器"要"user对象 User u = (User) ac.getBean("user"); //3 打印user对象 System.out.println(u); //关闭容器,触发销毁方法 ac.close(); }
创建方式1:空参构造创建
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User"></bean>
测试代码:
@Test //创建方式1:空参构造 public void fun1(){ //1 创建容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"); //2 向容器"要"user对象 User u = (User) ac.getBean("user"); //3 打印user对象 System.out.println(u); }
创建方式2:静态工厂创建
<!-- 创建方式2:静态工厂创建 调用UserFactory的createUser方法创建名为user2的对象.放入容器 --> <bean name="user2" class="cn.itcast.b_create.UserFactory" factory-method="createUser" ></bean>
UserFactory类
package cn.itcast.b_create; import cn.itcast.bean.User; public class UserFactory { public static User createUser(){ System.out.println("静态工厂创建User"); return new User(); } }
测试代码:
//创建方式2:静态工厂 @Test public void fun2(){ //1 创建容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"); //2 向容器"要"user对象 User u = (User) ac.getBean("user2"); //3 打印user对象 System.out.println(u); }
创建方式3:实例工厂创建
<!-- 创建方式3:实例工厂创建 调用UserFactory对象的createUser2方法创建名为user3的对象.放入容器 --> <bean name="user3" factory-bean="userFactory" factory-method="createUser2" ></bean> <bean name="userFactory" class="cn.itcast.b_create.UserFactory" ></bean>
UserFactory类
package cn.itcast.b_create; import cn.itcast.bean.User; public class UserFactory { public User createUser2(){ System.out.println("实例工厂创建User"); return new User(); } }
测试代码:
@Test public void fun3(){ //1 创建容器对象 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"); //2 向容器"要"user对象 User u = (User) ac.getBean("user3"); //3 打印user对象 System.out.println(u); }
在主配置文件中导入其他路径的配置文件
<!-- 导入其他spring配置文件 --> <import resource="cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"/>
<!-- set方式注入: --> <bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" > <!--值类型注入: 为User对象中名为name的属性注入tom作为值 --> <property name="name" value="tom" ></property> <property name="age" value="18" ></property> <!-- 引用类型注入: 为car属性注入下方配置的car对象 --> <property name="car" ref="car" ></property> </bean>
<!-- 将car对象配置到容器中 --> <bean name="car" class="cn.itcast.bean.Car" > <property name="name" value="兰博基尼" ></property> <property name="color" value="黄色" ></property> </bean>
User类中必须存在SetXXX()方法。
<!-- 构造函数注入 --> <bean name="user2" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" > <!-- name属性: 构造函数的参数名 --> <!-- index属性: 构造函数的参数索引 --> <!-- type属性: 构造函数的参数类型--> <constructor-arg name="name" index="0" type="java.lang.Integer" value="999" ></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="car" ref="car" index="1" ></constructor-arg> </bean>
前提,必须有相应的构造函数
public User(Integer name, Car car) { System.out.println("User(Integer name, Car car)!!"); this.name = name+""; this.car = car; }
<!-- p名称空间注入, 走set方法 1.导入P名称空间 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 2.使用p:属性完成注入 |-值类型: p:属性名="值" |-对象类型: p:属性名-ref="bean名称" --> <bean name="user3" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" p:name="jack" p:age="20" p:car-ref="car" > </bean>
<!-- spel注入: spring Expression Language sping表达式语言 --> <bean name="user4" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" > <property name="name" value="#{user.name}" ></property> <!--取对象为user的name值--> <property name="age" value="#{user3.age}" ></property> <!--取对象为user3的age值--> <property name="car" ref="car" ></property> </bean>
<!-- 复杂类型注入 --> <bean name="cb" class="cn.itcast.c_injection.CollectionBean" > <!-- 如果数组中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可 <property name="arr" value="tom" ></property> --> <!-- array注入,多个元素注入 --> <property name="arr"> <array> <value>tom</value> <value>jerry</value> <ref bean="user4" /> </array> </property> <!-- 如果List中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可 <property name="list" value="jack" ></property>--> <property name="list" > <list> <value>jack</value> <value>rose</value> <ref bean="user3" /> </list> </property> <!-- map类型注入 --> <property name="map" > <map> <entry key="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///crm" ></entry> <entry key="user" value-ref="user4" ></entry> <entry key-ref="user3" value-ref="user2" ></entry> </map> </property> <!-- prperties 类型注入 --> <property name="prop" > <props> <prop key="driverClass">com.jdbc.mysql.Driver</prop> <prop key="userName">root</prop> <prop key="password">1234</prop> </props> </property> </bean>
CollectionBean类
package cn.itcast.c_injection; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; public class CollectionBean { private Object[] arr;//数组类型注入 private List list;//list/set 类型注入 private Map map;//map类型注入 private Properties prop;//properties类型注入 public Object[] getArr() { return arr; } public void setArr(Object[] arr) { this.arr = arr; } public List getList() { return list; } public void setList(List list) { this.list = list; } public Map getMap() { return map; } public void setMap(Map map) { this.map = map; } public Properties getProp() { return prop; } public void setProp(Properties prop) { this.prop = prop; } @Override public String toString() { return "CollectionBean [arr=" + Arrays.toString(arr) + ", list=" + list + ", map=" + map + ", prop=" + prop + "]"; } }
1、需要导包:spring-web-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
2、在Action中获得容器中的Service对象
<!-- 可以让spring容器随项目的启动而创建,随项目的关闭而销毁 --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
//获得spring容器=>从Application域获得即可 //1 获得servletContext对象 ServletContext sc = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); //2.从Sc中获得ac容器 WebApplicationContext ac = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(sc); //3.从容器中获得CustomerService CustomerService cs = (CustomerService) ac.getBean("customerService");
标签:开源 dao injection ica close classpath 路径 不能 etag
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ginb/p/7308088.html