标签:mapping load 提示 保存 build servlet bsp 部署 end
HttpSession是通过Servlet容器创建和管理的,像Tomcat/Jetty都是保存在内存中的。但是我们把应用搭建成分布式的集群,然后利用LVS或Nginx做负载均衡,那么来自同一用户的Http请求将有可能被分发到多个不同的应用中。那问题来了,如何保证不同的应用能够共享同一份session数据呢?最简单的想法,就是把session数据保存到内存以外的一个统一的地方,例如Memcached/Redis等数据库中。那问题又来了,如何替换掉Servlet容器创建和管理的HttpSession的实现呢?
1、利用Servlet容器提供的插件功能,自定义HttpSession的创建和管理策略,并通过配置的方式替换掉默认的策略。这方面其实早就有开源项目了,例如memcached-session-manager(可以参考负载均衡+session共享(memcached-session-manager实现),以及tomcat-redis-session-manager。不过这种方式有个缺点,就是需要耦合Tomcat/Jetty等Servlet容器的代码。
2、设计一个Filter,利用HttpServletRequestWrapper,实现自己的 getSession()方法,接管创建和管理Session数据的工作。spring-session就是通过这样的思路实现的。
参考 spring-session之一 初探 spring-session
本博客不涉及session解释,关于session大家自行去查资料;关于spring-session的相关概念大家可以去spring官网查阅(http://projects.spring.io/spring-session/)。
我们先来看下单机应用,应用很简单,就是在session中设置变量,然后获取这些设置的变量进行展示 ,具体代码如下
pom.xml:

<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.yzb.lee</groupId> <artifactId>spring-session</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>spring-session Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>spring-session</finalName> </build> </project>
web.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>session</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.yzb.lee.servlet.SessionServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>session</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/session</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
SessionServlet.java

package com.yzb.lee.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class SessionServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String attributeName = req.getParameter("attributeName"); String attributeValue = req.getParameter("attributeValue"); req.getSession().setAttribute(attributeName, attributeValue); resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath() + "/"); } }
index.jsp

<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Session Attributes</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Description</h1>
<p>This application demonstrates how to use a Redis instance to back your session. Notice that there is no JSESSIONID cookie. We are also able to customize the way of identifying what the requested session id is.</p>
<h1>Try it</h1>
<form class="form-inline" role="form" action="./session" method="post">
<label for="attributeName">Attribute Name</label>
<input id="attributeName" type="text" name="attributeName"/>
<label for="attributeValue">Attribute Value</label>
<input id="attributeValue" type="text" name="attributeValue"/>
<input type="submit" value="Set Attribute"/>
</form>
<hr/>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Attribute Name</th>
<th>Attribute Value</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<c:forEach items="${sessionScope}" var="attr">
<tr>
<td><c:out value="${attr.key}"/></td>
<td><c:out value="${attr.value}"/></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</body>
</html>
整个项目结构非常简单,如下如
本地运行起来,效果如下
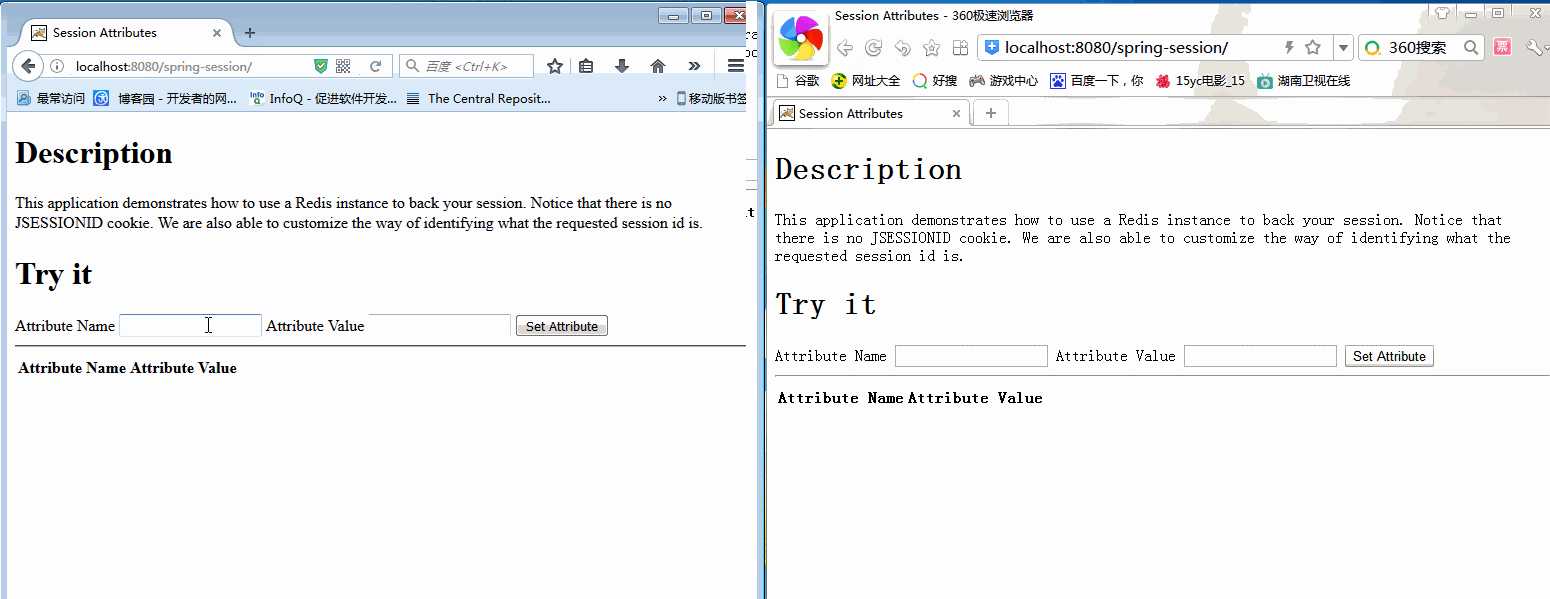
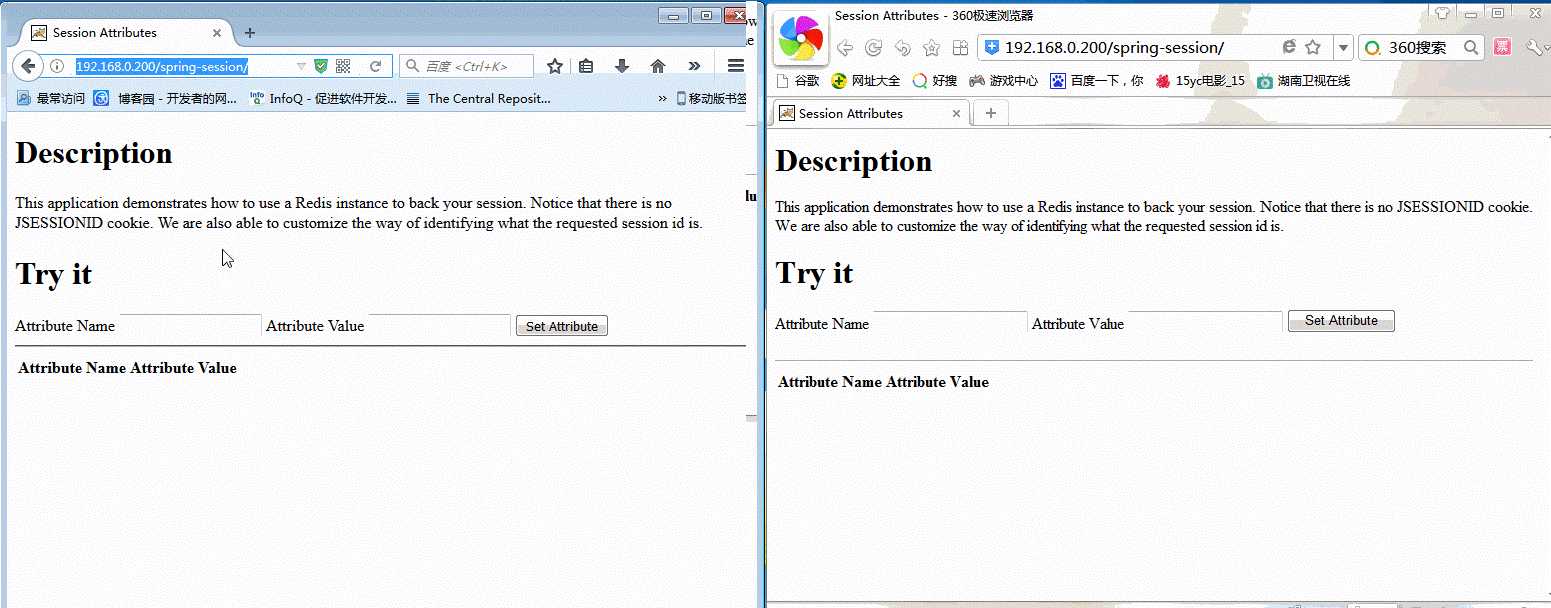
火狐浏览器与360浏览器代表不同的用户,各自都能获取各自session中的设置的全部变量,很正常,没毛病。
单机应用中,session肯定没问题,就存在本地的servlet容器中,那么在分布式集群中会像单机一样正常吗?我们接着往下看
搭建高可用的、实现负载均衡的分布式集群环境可参考nginx实现请求的负载均衡 + keepalived实现nginx的高可用,没搭建的需要先把分布式环境搭建起来
应用不变,代码与单机中的完全一致,将代码部署到分布式集群中去
全部运行起来,效果如下
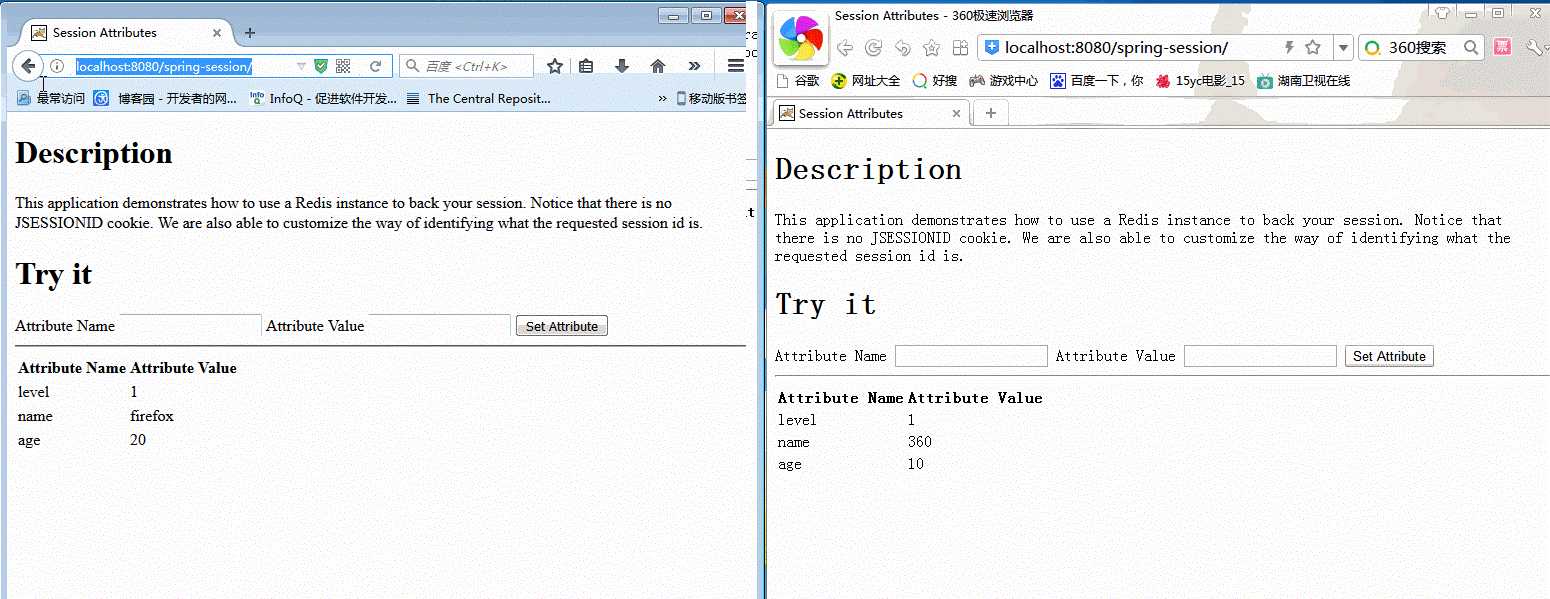
结果是:无论给session设置多少个值,session中的值都获取不到(离我的预期还是有差距,具体什么差距请看我的问题)
应用有所变化,代码与之前有所不同,具体区别如下(SessionServlet与index.jsp不变)
pom.xml

<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.yzb.lee</groupId> <artifactId>spring-session</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>spring-session Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>1.7</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.7</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId> <artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId> <version>1.3.1.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>biz.paluch.redis</groupId> <artifactId>lettuce</artifactId> <version>3.5.0.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>4.3.4.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>spring-session</finalName> </build> </project>
web.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<!-- spring-session config -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:spring-session.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 这个filter 要放在第一个 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>springSessionRepositoryFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSessionRepositoryFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
<dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher>
<dispatcher>ERROR</dispatcher>
</filter-mapping>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>session</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.yzb.lee.servlet.SessionServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>session</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/session</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
spring-session.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:annotation-config /> <!-- 加载properties文件 --> <bean id="configProperties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:session-redis.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- RedisHttpSessionConfiguration --> <bean class="org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.RedisHttpSessionConfiguration"> <property name="maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds" value="${redis.session.timeout}" /> <!-- session过期时间,单位是秒 --> </bean> <!--LettuceConnectionFactory --> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory" p:host-name="${redis.host}" p:port="${redis.port}" p:password="${redis.pass}" /> </beans>
session-redis.properties
redis.host=192.168.0.221 redis.pass=myredis redis.port=6379 redis.session.timeout=600
整个项目结构如下如
将代码部署到分布式集群中去,重新运行起来,效果如下
效果与单机应用的效果一样,这也就说明了session共享实现了,我们来看下redis中是否有session数据,如下图,redis中是存有session信息的
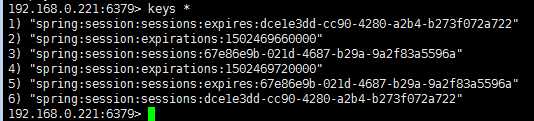
前面是用的一台redis服务器:192.168.0.221做的session服务器,只有一台的话一旦出现单点故障,那么整个session服务就没了,影响太大。为了避免出现单点故障问题,需要搭建一个session集群。搭建集群的时候,登录认证就不要打开了(requirepass注释不要打开,具体原因后续会有说明)
redis集群环境
192.168.0.221:3个节点(7000,7001,7002)
192.168.0.223:3个节点(7003,7004,7005)
redis集群搭建的过程具体可参考Redis集群搭建与简单使用
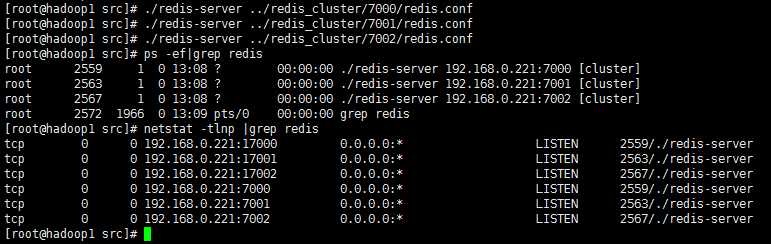
redis各个节点搭建成功之后,启动情况如下
192.168.0.221
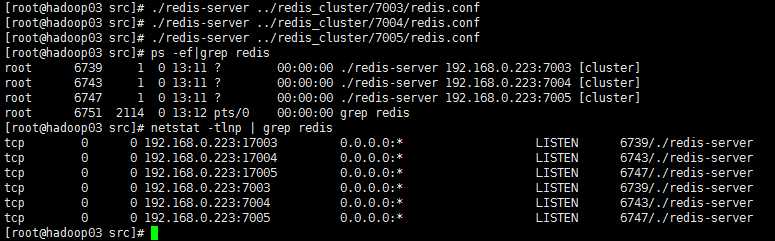
192.168.0.223
# ./redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.0.221:7000 192.168.0.221:7001 192.168.0.221:7002 192.168.0.223:7003 192.168.0.223:7004 192.168.0.223:7005
随便在哪一台(192.168.0.221、192.168.0.223中任意一台)执行如上命令即可,若出现下图信息,则表示集群搭建成功
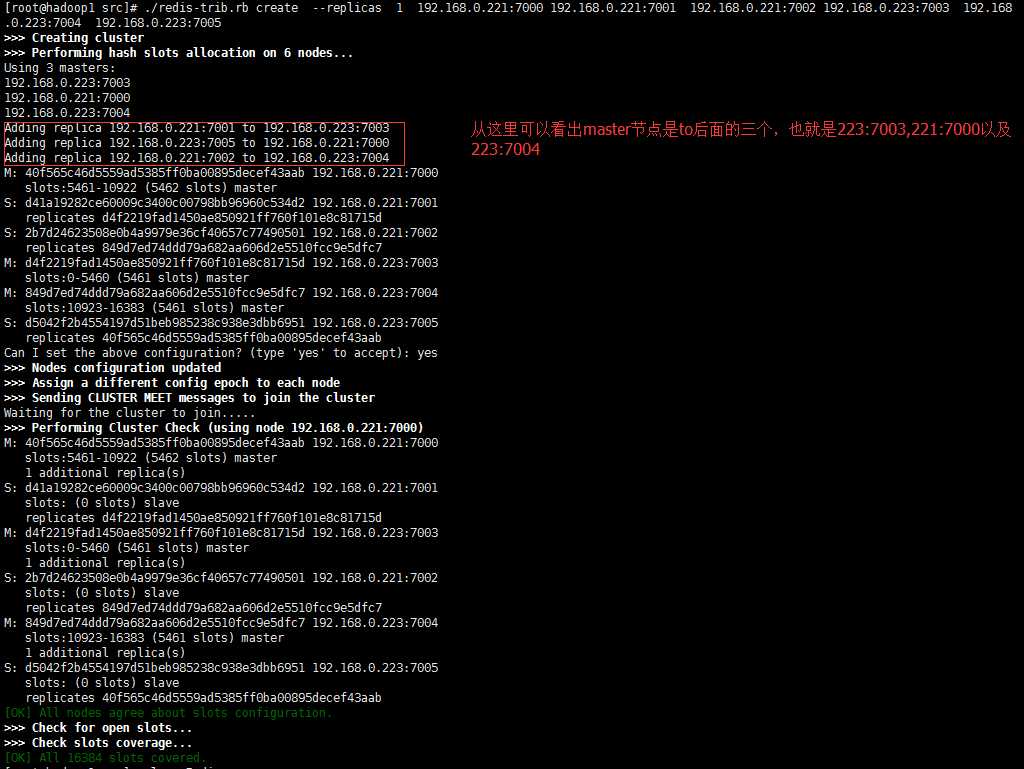
redis集群已经搭建好,接下来就是将redis集群应用到我们的工程中,代码是在spring-sesson实现session共享的基础上进行的,有差别的文件就只有spring-session.xml和session-redis.properties
spring-session.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:annotation-config /> <!-- 加载properties文件 --> <bean id="configProperties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:session-redis.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- RedisHttpSessionConfiguration --> <bean class="org.springframework.session.data.redis.config.annotation.web.http.RedisHttpSessionConfiguration"> <property name="maxInactiveIntervalInSeconds" value="${redis.session.timeout}" /> <!-- session过期时间,单位是秒 --> </bean> <!--JedisConnectionFactory --> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"> <constructor-arg> <!--redisCluster配置--> <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisClusterConfiguration"> <constructor-arg> <list> <value>${redis.master1}</value> <value>${redis.master2}</value> <value>${redis.master3}</value> </list> </constructor-arg> </bean> </constructor-arg> </bean> <!--LettuceConnectionFactory --> <!-- 单节点redis --> <!-- <bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory" p:host-name="${redis.host}" p:port="${redis.port}" p:password="${redis.pass}" /> --> </beans>
session-redis.properties

#redis.host=192.168.0.221 #redis.pass=myredis #redis.port=6379 redis.master1=192.168.0.221:7000 redis.master2=192.168.0.223:7003 redis.master3=192.168.0.223:7004 redis.session.timeout=600
据我亲测,效果与单节点redis的效果是一样的,我就不放效果图了,但是大家最好还是去亲测一下。
工程地址:spring-session
1、单机应用中,HttpSession是通过Servlet容器创建和管理的,servlet容器一旦停止服务,那么session也随之消失;但如果session被保存到redis中,只要redis服务没停且session在有效期间内,那么servlet容器停止服务了,session还是存在的,这有什么好处了,好处就是servlet容器出现闪停闪修复的情况,用户就不用重新登录了。
2、spring中的ContextLoaderListener与DispatcherServlet不知道大家了解不,严格的来讲这两者负责加载的bean是有区别的,也最好设置成加载不同的bean,不然可能会发生一些你意想不到的情况。不知道区别的可以去阅读浅谈ContextLoaderListener及其上下文与DispatcherServlet的区别。
3、测试的时候可以从底往高进行测试,也就是说先测试tomcat,再测试nginx,最后测试VIP。
4、redis中可以手动删除session,不一定非要等到session过期。
5、分布式测试的时候,最好在index.jsp加一些标记(例如ip,就写死成index.jsp所在服务器的ip),用来区分不同的服务器,那样测试起来更加明显。
6、spring-session官网提供的例子中,用注解的方式进行配置的,可我压根就没看到web.xml中有spring的配置,但实际上spring容器启动了,并且实例化了需要的bean,应用也能跑起来,这让我很是费解,spring容器是什么时候初始化的? 这其实是servlet3.0的新特性,servlet3.0开始支持无web.xml的注解配置方式,而AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer(AbstractHttpSessionApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer)就是接入点(就如在web.xml中配置spring一样),更多的详细信息需要大家去查阅资料了。
7、设置redis集群的时候,若设置了密码登录(将redis.conf中requirepass打开并设置了自己的密码),那么执行# ./redis-trib.rb create --replicas 1 192.168.0.221:7000 192.168.0.221:7001 192.168.0.221:7002 192.168.0.223:7003 192.168.0.223:7004 192.168.0.223:7005的时候会提示[ERR] Sorry, can‘t connect to node 192.168.0.221:7000,那么需要将/usr/lib/ruby/gems/1.8/gems/redis-3.3.0/lib/redis/client.rb中的password改成自己的密码即可,当然了,redis的所有实例的密码要一致,或者说全部的redis.conf中密码设置的值要一样,修改/usr/lib/ruby/gems/1.8/gems/redis-3.3.0/lib/redis/client.rb如下
vim /usr/lib/ruby/gems/1.8/gems/redis-3.3.0/lib/redis/client.rb 将client.rb中的password改成自己设置的redis密码 class Redis class Client DEFAULTS = { :url => lambda { ENV["REDIS_URL"] }, :scheme => "redis", :host => "127.0.0.1", :port => 6379, :path => nil, :timeout => 5.0, :password => "myredis", #改成自己的密码 :db => 0, :driver => nil, :id => nil, :tcp_keepalive => 0, :reconnect_attempts => 1, :inherit_socket => false }
之前说过,利用redis集群来存储session的时候,登录认证不要打开,因为jedis好像还不支持redis的集群密码设置。
1、分布式集群的没设置session共享的情况中,为什么设置进去的值一个都获取不到,按我的理解应该是每次返回回来的数据应该是某个tomcat上的session中的数据,当设置的值多了后,每次都应该有值返回,而测试得到的结果却是无论你设置多少值,没有任何值返回回来,这里没搞清楚原因。
2、jedis这么设置集群密码,目前还不知道,知道的请留个言; 或者知道lettuce怎么设置redis集群和集群密码的也可以留个言;再或者有其他方式的也可以留个言; 在此表示感谢了!
spring-session之一 初探 spring-session
【Spring】浅谈ContextLoaderListener及其上下文与DispatcherServlet的区别
探 Spring 3.1之无web.xml式 基于代码配置的servlet3.0应用
spring-session实现分布式集群session的共享
标签:mapping load 提示 保存 build servlet bsp 部署 end
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/youzhibing/p/7348337.html