标签:bug [] length bytes actor通信 数组 细节 过程 平滑
· 文件描述符
· 阻塞IO模型
· 非阻塞IO模型
· IO复用模型
· 信号驱动IO模型
· 异步IO模型
· BIO编程
· 伪异步IO编程
· NIO编程
· 深入Buffer
· Selector
· AIO编程
· Netty入门
· 开发与部署
· 粘包/拆包问题
· 问题及其解决
· 问题描述及其解决
· HTTP协议开发
· 文件服务器
· 问题及其解决
· 原理(过程)
· 开发
· Netty架构
· 逻辑架构
· 高性能
· 可靠性
· 可定制性
· 可扩展性
· 私有协议栈开发
1. Linux内核将所有外部设备视为文件来操作。
2. 对一个文件的读写操作会调用内核提供的系统命令,返回一个file descripter(fd,文件描述符)。
3. 对一个socket的读写也会有相应的描述符,称为socketfd(socket描述符)。
1. 最常用的IO模型。
2. 默认的IO模型。
3. 以socket接口为例说明阻塞IO模型。
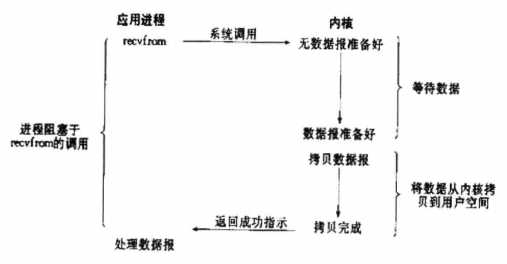
1. 一般轮训检查内核数据是否就绪。
2. 如果内核数据未就绪,则直接返回一个EWOULDBLOCK错误。
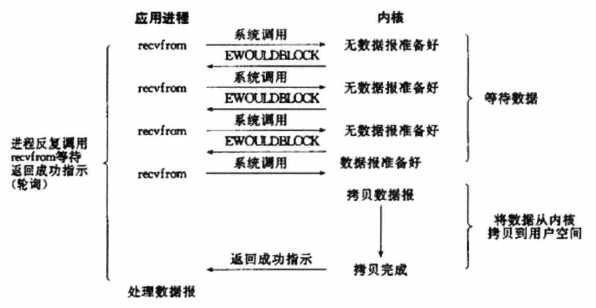
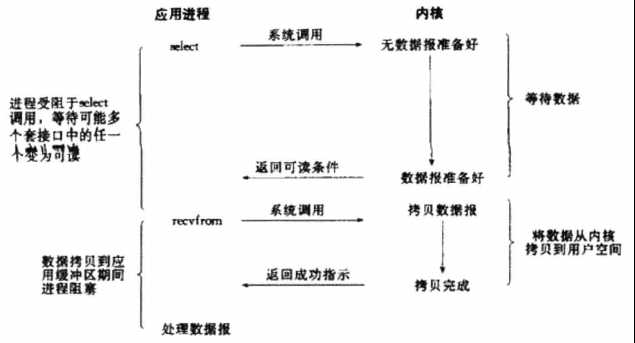
1. Linux提供select/poll,进程传递一个或多个fd给select或poll系统调用,阻塞在select操作上,这样select/poll可以帮助进程同时检测多个fd是否就绪。
2. select/poll存在支持fd数量有限、线性轮训等问题,应采用基于事件驱动方式的epoll代替(当有fd就绪时,立即回调函数)。
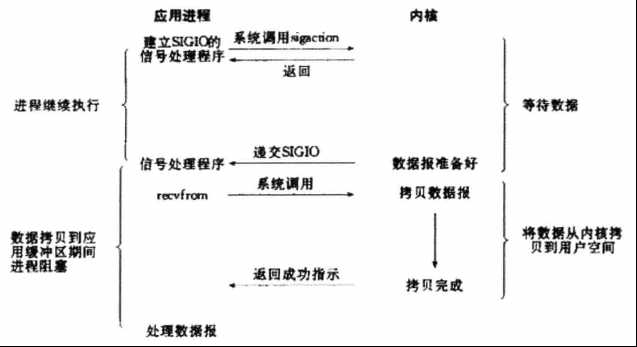
进程先系统调用sigaction执行一个非阻塞的信号处理函数,进程继续运行。当数据就绪时,为该进程生成一个SIGIO信号,通知进程调用recvfrom读取数据。
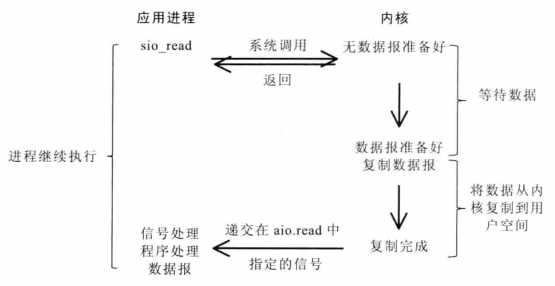
1. 进程告知内核启动某个操作,并在内核完成整个操作后再通知进程。
2. 与信号驱动IO模型区别:信号驱动IO模型只通知数据就绪;异步IO模型通知操作已完成。
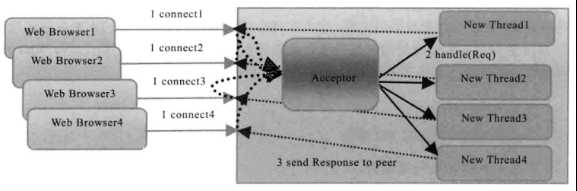
1. 有一个独立的Acceptor线程负责监听客户端连接,接收到连接后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理,处理完之后,通过输出流返回给客户端,线程销毁。
2. 问题:服务端线程个数与客户端并发访问数1:1关系。当客户端并发访问量越来越大时,系统会发生线程堆栈溢出、创建新线程失败等问题,最终导致进程宕机或僵死。
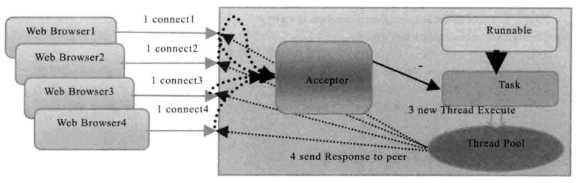
1. 当新客户端接入时,将客户端Socket封装成一个Task(实现Runnable接口)投递到线程池中进行处理。
2. 好处:由于可以设置线程池队列的大小和最大线程数,所以资源占用是可控的,客户端并发数量增加不会导致资源耗尽、宕机。
3. 问题:底层通信依然采用同步阻塞模型,无法从根本上解决应答消息缓慢或网络传输较慢时,长时间阻塞线程的问题。
1. BIO是面向流的,一次处理一个字节;NIO是面向块的,以块的形式处理数据。
2. BIO的java.io.*已经使用NIO重新实现过。
3. Buffer缓冲区存放着准备要写入或读出的数据。通常是一个字节数组,但也可以是其他类型的数组或不是数组。
4. Buffer类型:
a) ByteBuffer(常用)
b) CharBuffer
c) ShortBuffer
d) IntBuffer
e) LongBuffer
f) FloatBuffer
g) DoubleBuffer
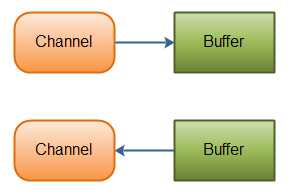
5. Channel通道是双向的,可通过它读取或写入数据。所有的数据都要通过Buffer来处理,永远不会将数据直接写入Channel。
6. 写文件示例。

1 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; 4 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 5 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 6 import java.util.Random; 7 import java.util.UUID; 8 9 public class Test { 10 11 private static byte[] getRandomData() { 12 int randomLength = new Random().nextInt(100); 13 StringBuilder data = new StringBuilder(); 14 for (int index = 0; index < randomLength; index++) { 15 data.append(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); 16 } 17 return data.toString().getBytes(); 18 } 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; 22 try { 23 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:/test.txt"); 24 FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); 25 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = null; 26 for (int index = 0; index < 1000; index++) { 27 byte[] data = getRandomData(); 28 if (byteBuffer == null) { 29 byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(data); 30 } else if (data.length > byteBuffer.capacity()) { 31 if (byteBuffer.position() > 0) { 32 byteBuffer.flip(); 33 fileChannel.write(byteBuffer); 34 byteBuffer.clear(); 35 } 36 byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(data); 37 } else if (data.length > byteBuffer.remaining()) { 38 byteBuffer.flip(); 39 fileChannel.write(byteBuffer); 40 byteBuffer.clear(); 41 } 42 43 byteBuffer.put(data); 44 } 45 byteBuffer.flip(); 46 fileChannel.write(byteBuffer); 47 byteBuffer.clear(); 48 49 } catch (IOException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } finally { 52 if (fileOutputStream != null) { 53 try { 54 fileOutputStream.close(); 55 } catch (IOException e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 62 }
7. 读文件示例。

1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 4 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 5 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; 10 try { 11 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:/test.txt"); 12 FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel(); 13 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64); 14 while (fileChannel.read(byteBuffer) > 0) { 15 byteBuffer.flip(); 16 while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) { 17 System.out.print((char) byteBuffer.get()); 18 } 19 byteBuffer.clear(); 20 } 21 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } finally { 25 if (fileInputStream != null) { 26 try { 27 fileInputStream.close(); 28 } catch (IOException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 35 }
8. 复制文件示例。

1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 3 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 4 import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; 5 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 RandomAccessFile sourceFile = null; 10 RandomAccessFile targetFile = null; 11 try { 12 sourceFile = new RandomAccessFile("D:/test.txt", "r"); 13 targetFile = new RandomAccessFile("D:/test.txt.bak", "rw"); 14 FileChannel sourceFileChannel = sourceFile.getChannel(); 15 FileChannel targetFileChannel = targetFile.getChannel(); 16 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64); 17 while (sourceFileChannel.read(byteBuffer) > 0) { 18 byteBuffer.flip(); 19 targetFileChannel.write(byteBuffer); 20 byteBuffer.clear(); 21 } 22 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 28 }
1. Buffer可以理解成数组,它通过以下3个值描述状态:
a) position:下一个元素的位置;
b) limit:可读取或写入的元素总数,position总是小于或者等于limit;
c) capacity:Buffer最大容量,limit总是小于或者等于capacity。
2. 以读、写举例说明Buffer。
a) 创建一个8字节的ByteBuffer。position=0,limit=8,capacity=8。
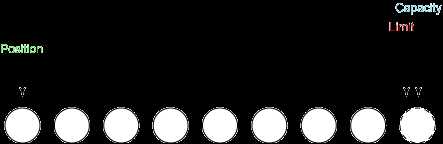
b) 读取3个字节。position=3,limit=8,capacity=8。

c) 读取2个字节。position=5,limit=8,capacity=8。
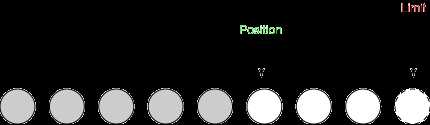
d) 执行flip()。position=0,limit=5,capacity=8。
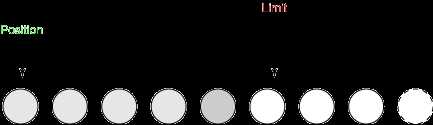
e) 写入4个字节。position=4,limit=5,capacity=8。
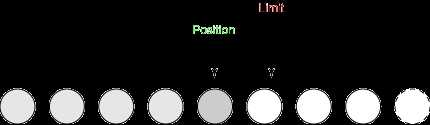
f) 写入1个字节。position=5,limit=5,capacity=8。
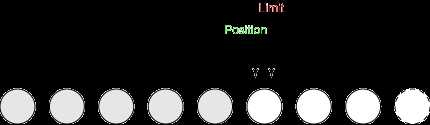
g) 执行clear()。position=0,limit=8,capacity=8。

3. 创建ByteBuffer的两种方法:
a) 创建固定大小的Buffer。
ByteBuffer.allocate(capacity)
b) 将数组及其内容包装成Buffer。
byte array[] = new byte[1024]; ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(array);
1. Selector即IO复用模型中的多路复用器。
2. JDK使用了epoll。
1. AIO也称NIO2.0,是异步IO模型。
2. JDK 7时在java.nio.channels包下新增了4个异步Channel。
a) AsynchronousSocketChannel
b) AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
c) AsynchronousFileChannel
d) AsynchronousDatagramChannel
3. 使用Future写文件:异步执行,阻塞Future.get(),直到取得结果。

1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 3 import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel; 4 import java.nio.file.Path; 5 import java.nio.file.Paths; 6 import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 import java.util.List; 9 import java.util.Random; 10 import java.util.UUID; 11 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 12 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 13 14 public class Test { 15 16 private static byte[] getRandomData() { 17 int randomLength = new Random().nextInt(100); 18 StringBuilder data = new StringBuilder(); 19 for (int index = 0; index < randomLength; index++) { 20 data.append(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); 21 } 22 return data.append(‘\n‘).toString().getBytes(); 23 } 24 25 public static void main (String [] args) { 26 Path file = Paths.get("D:/test.txt"); 27 AsynchronousFileChannel asynchronousFileChannel = null; 28 try { 29 asynchronousFileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(file, StandardOpenOption.WRITE); 30 List<Future<Integer>> futures = new ArrayList<>(); 31 for (int index = 0; index < 10; index++) { 32 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(getRandomData()); 33 Future<Integer> future = asynchronousFileChannel.write(byteBuffer, 0); 34 futures.add(future); 35 } 36 for (Future<Integer> future : futures) { 37 Integer length = null; 38 try { 39 length = future.get(); 40 } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { 41 e.printStackTrace(); 42 } 43 System.out.println("Bytes written: " + length); 44 } 45 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } finally { 49 if (asynchronousFileChannel != null) { 50 try { 51 asynchronousFileChannel.close(); 52 } catch (IOException e) { 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 }
4. 使用CompletionHandler写文件:异步执行,回调CompletionHandler。注意:示例中,由于不阻塞主线程,即异步任务是否结果主线程都会结束,有时会看不到结果,所以sleep 5秒。

1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 3 import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel; 4 import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler; 5 import java.nio.file.Path; 6 import java.nio.file.Paths; 7 import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; 8 import java.util.Random; 9 import java.util.UUID; 10 11 public class Test { 12 13 private static byte[] getRandomData() { 14 int randomLength = new Random().nextInt(100); 15 StringBuilder data = new StringBuilder(); 16 for (int index = 0; index < randomLength; index++) { 17 data.append(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); 18 } 19 return data.append(‘\n‘).toString().getBytes(); 20 } 21 22 public static void main (String [] args) { 23 Path file = Paths.get("D:/test.txt"); 24 AsynchronousFileChannel asynchronousFileChannel = null; 25 try { 26 asynchronousFileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(file, StandardOpenOption.WRITE); 27 CompletionHandler<Integer, Object> completionHandler = new CompletionHandler<Integer, Object>() { 28 @Override 29 public void completed(Integer result, Object attachment) { 30 System.out.println("Bytes written: " + result); 31 } 32 @Override 33 public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) { 34 } 35 }; 36 for (int index = 0; index < 10; index ++) { 37 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(getRandomData()); 38 asynchronousFileChannel.write(byteBuffer, 0, null, completionHandler); 39 } 40 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } finally { 44 if (asynchronousFileChannel != null) { 45 try { 46 asynchronousFileChannel.close(); 47 } catch (IOException e) { 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 try { 53 Thread.sleep(5000); 54 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 } 57 } 58 }
5. 使用Future读文件:异步执行,阻塞Future.get(),直到取得结果。

1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 3 import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel; 4 import java.nio.file.Path; 5 import java.nio.file.Paths; 6 import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; 7 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 8 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 9 10 public class Test { 11 12 public static void main (String [] args) { 13 Path file = Paths.get("D:/test.txt"); 14 AsynchronousFileChannel asynchronousFileChannel = null; 15 try { 16 asynchronousFileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(file, StandardOpenOption.READ); 17 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64); 18 int position = 0; 19 int length = 0; 20 do { 21 Future<Integer> future = asynchronousFileChannel.read(byteBuffer, position); 22 length = future.get(); 23 if (length > 0) { 24 byteBuffer.flip(); 25 System.out.print(new String(byteBuffer.array())); 26 byteBuffer.clear(); 27 } 28 position += length; 29 } while (length > 0); 30 31 } catch (IOException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } finally { 38 if (asynchronousFileChannel != null) { 39 try { 40 asynchronousFileChannel.close(); 41 } catch (IOException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }
6. 使用CompletionHandler读文件:异步执行,回调CompletionHandler。注意:示例中,由于不阻塞主线程,即异步任务是否结果主线程都会结束,有时会看不到结果,所以sleep 5秒。

1 import java.io.IOException; 2 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 3 import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel; 4 import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler; 5 import java.nio.file.Path; 6 import java.nio.file.Paths; 7 import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; 8 9 public class Test { 10 11 public static void main (String [] args) { 12 Path file = Paths.get("D:/test.txt"); 13 AsynchronousFileChannel asynchronousFileChannel = null; 14 try { 15 asynchronousFileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(file, StandardOpenOption.READ); 16 // 10个异步任务分别读取文件头64个字节,5秒后分别输出。 17 CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> completionHandler = new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() { 18 @Override 19 public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer byteBuffer) { 20 byteBuffer.flip(); 21 System.out.print(new String(byteBuffer.array())); 22 byteBuffer.clear(); 23 } 24 @Override 25 public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer byteBuffer) { 26 } 27 }; 28 for (int index = 0; index < 10; index++) { 29 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64); 30 asynchronousFileChannel.read(byteBuffer, byteBuffer.limit() * index, byteBuffer, completionHandler); 31 } 32 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } finally { 36 if (asynchronousFileChannel != null) { 37 try { 38 asynchronousFileChannel.close(); 39 } catch (IOException e) { 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 try { 45 Thread.sleep(5000); 46 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } 49 } 50 }
1. 对比。
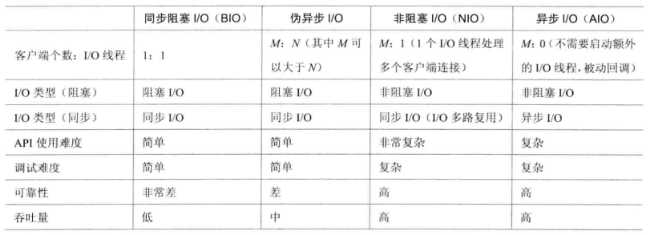
2. 选择NIO框架Netty,而不选择JDK的NIO类库的理由。
a) NIO类库和API繁杂。
b) 需另具备Java多线程编程等技能。
c) 可靠性不高,工作量和难度非常大。
d) 臭名昭著的epoll Bug导致Selector空轮训。
1. 开发环境:CLASSPATH中导入“netty-all-x.y.z.jar”即可。
2. 打包部署:由于是非Web应用,构建成jar包部署即可。
1. 配置Maven的pom.xml文件。

<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>5.0.0.Alpha1</version>
</dependency>
2. 时间服务器TimeServer

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 5 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 9 10 public class TimeServer { 11 12 public void bind(int port) throws Exception { 13 // 服务器NIO线程组线 14 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 15 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 16 try { 17 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); 18 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 19 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 20 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) 21 .childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 22 // 绑定端口,同步等待成功 23 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); 24 // 等待服务器监听端口关闭 25 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 26 } finally { 27 // 优雅退出,释放线程池资源 28 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 29 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 30 } 31 } 32 33 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 34 35 @Override 36 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 37 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler()); 38 } 39 40 } 41 42 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 43 new TimeServer().bind(8080); 44 } 45 46 }
3. 时间服务器TimeServerHandler

1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 4 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 5 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 6 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 7 8 public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 9 10 @Override 11 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 12 ByteBuf reqBuf = (ByteBuf) msg; 13 byte[] req = new byte[reqBuf.readableBytes()]; 14 reqBuf.readBytes(req); 15 String reqString = new String(req, "UTF-8"); 16 String respString = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(reqString) ? new Date().toString() : "BAD ORDER"; 17 ByteBuf respBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(respString.getBytes()); 18 ctx.write(respBuf); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 23 ctx.flush(); 24 } 25 26 @Override 27 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 28 ctx.close(); 29 } 30 31 }
4. 时间客户端TimeClient

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 5 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; 9 10 public class TimeClient { 11 12 public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception { 13 EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 14 try { 15 // 客户端NIO线程组 16 Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); 17 bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) 18 .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) 19 .handler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 20 // 发起异步连接操作 21 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync(); 22 // 等待客户端链路关闭 23 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 24 25 } finally { 26 // 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组 27 group.shutdownGracefully(); 28 } 29 } 30 31 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 32 33 @Override 34 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 35 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler()); 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 41 new TimeClient().connect("127.0.0.1", 8080); 42 } 43 44 }
5. 时间客户端TimeClientHandler

1 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 2 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 5 6 public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 7 8 private final ByteBuf reqBuf; 9 10 public TimeClientHandler() { 11 byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes(); 12 reqBuf = Unpooled.buffer(req.length); 13 reqBuf.writeBytes(req); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 18 ctx.writeAndFlush(reqBuf); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 23 ByteBuf respBuf = (ByteBuf) msg; 24 byte[] resp = new byte[respBuf.readableBytes()]; 25 respBuf.readBytes(resp); 26 String respString = new String(resp, "UTF-8"); 27 System.out.println(respString); 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 32 ctx.close(); 33 } 34 35 }
1. TCP是一个“流协议”,是没有界限的一串数据。
2. TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分。所以在业务上认为,一个完整的包可能会被TCP拆包发送,也可能封装多个
小包成大包发送。
3. 业界主流协议的解决方案归纳:
a) 消息定长。如每个报文的大小固定长度200字节,不足时空位补空格。
b) 在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割。如FTP协议。
c) 将消息分为消息头、消息体,消息头中包含消息总长度(或消息体长度)的字段。
d) 更复杂的应用层协议。
4. Netty提供了多种编码器用于解决粘包/拆包问题。
1. 原理:遍历ByteBuf中的可读字节,发现“\n”或“\r\n”时就结束。
2. 支持携带结束符或不携带结束符两种编码方式;支持配置单行的最大长度(超过最大长度未发现换行符则抛出异常,同时忽略掉之前读到的异常码流)。
3. StringDecoder功能:将接受到的对象转成字符串,然后继续调用后面的Handler。
4. 使用LineBasedFrameDecoder优化后的时间服务器。
a) 时间服务器TimeServer

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 5 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; 11 12 public class TimeServer { 13 14 public void bind(int port) throws Exception { 15 // 服务器NIO线程组线 16 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 17 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 18 try { 19 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); 20 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 21 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 22 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) 23 .childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 24 // 绑定端口,同步等待成功 25 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); 26 // 等待服务器监听端口关闭 27 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 28 } finally { 29 // 优雅退出,释放线程池资源 30 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 31 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 36 37 @Override 38 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 39 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024)); 40 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); 41 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler()); 42 } 43 44 } 45 46 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 47 new TimeServer().bind(8080); 48 } 49 50 }
b) 时间服务器TimeServerHandler

1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 4 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 5 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 6 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 7 8 public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 9 10 @Override 11 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 12 String reqString = (String) msg; 13 String respString = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(reqString) ? new Date().toString() : "BAD ORDER"; 14 respString += "\n"; 15 ByteBuf respBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(respString.getBytes()); 16 ctx.write(respBuf); 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 21 ctx.flush(); 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 26 ctx.close(); 27 } 28 29 }
c) 时间客户端TimeClient

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 5 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; 11 12 public class TimeClient { 13 14 public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception { 15 EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 16 try { 17 // 客户端NIO线程组 18 Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); 19 bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) 20 .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) 21 .handler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 22 // 发起异步连接操作 23 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync(); 24 // 等待客户端链路关闭 25 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 26 27 } finally { 28 // 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组 29 group.shutdownGracefully(); 30 } 31 } 32 33 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 34 35 @Override 36 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 37 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024)); 38 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); 39 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler()); 40 } 41 42 } 43 44 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 45 new TimeClient().connect("127.0.0.1", 8080); 46 } 47 48 }
d) 时间客户端TimeClientHandler

1 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 2 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 5 6 public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 7 8 private final ByteBuf reqBuf; 9 10 public TimeClientHandler() { 11 byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER\n".getBytes(); 12 reqBuf = Unpooled.buffer(req.length); 13 reqBuf.writeBytes(req); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 18 ctx.writeAndFlush(reqBuf); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 23 String respString = (String) msg; 24 System.out.println(respString); 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 29 ctx.close(); 30 } 31 32 }
1. 功能:以分隔符作为码流结束标识符的消息解码。
2. 时间服务器TimeServer

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 3 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 5 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 6 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 7 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 8 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 9 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 10 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 11 import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder; 12 import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; 13 14 public class TimeServer { 15 16 public void bind(int port) throws Exception { 17 // 服务器NIO线程组线 18 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 19 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 20 try { 21 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); 22 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 23 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 24 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) 25 .childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 26 // 绑定端口,同步等待成功 27 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); 28 // 等待服务器监听端口关闭 29 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 30 } finally { 31 // 优雅退出,释放线程池资源 32 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 33 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 34 } 35 } 36 37 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 38 39 @Override 40 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 41 ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("*&*".getBytes()); 42 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, delimiter)); 43 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); 44 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeServerHandler()); 45 } 46 47 } 48 49 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 50 new TimeServer().bind(8080); 51 } 52 53 }
3. 时间服务器TimeServerHandler

1 import java.util.Date; 2 3 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 4 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 5 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 6 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 7 8 public class TimeServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 9 10 @Override 11 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 12 String reqString = (String) msg; 13 String respString = "QUERY TIME ORDER".equalsIgnoreCase(reqString) ? new Date().toString() : "BAD ORDER"; 14 respString += "*&*"; 15 ByteBuf respBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(respString.getBytes()); 16 ctx.write(respBuf); 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 21 ctx.flush(); 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 26 ctx.close(); 27 } 28 29 }
4. 时间客户端TimeClient

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; 2 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 3 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 5 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 6 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 7 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 8 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 9 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 10 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; 11 import io.netty.handler.codec.DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder; 12 import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; 13 14 public class TimeClient { 15 16 public void connect(String host, int port) throws Exception { 17 EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 18 try { 19 // 客户端NIO线程组 20 Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); 21 bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) 22 .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) 23 .handler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 24 // 发起异步连接操作 25 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync(); 26 // 等待客户端链路关闭 27 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 28 29 } finally { 30 // 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组 31 group.shutdownGracefully(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 36 37 @Override 38 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 39 ByteBuf delimiter = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("*&*".getBytes()); 40 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(1024, delimiter)); 41 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); 42 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new TimeClientHandler()); 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 48 new TimeClient().connect("127.0.0.1", 8080); 49 } 50 51 }
5. 时间客户端TimeClientHandler

1 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 2 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 5 6 public class TimeClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 7 8 private final ByteBuf reqBuf; 9 10 public TimeClientHandler() { 11 byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER*&*".getBytes(); 12 reqBuf = Unpooled.buffer(req.length); 13 reqBuf.writeBytes(req); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 18 ctx.writeAndFlush(reqBuf); 19 } 20 21 @Override 22 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 23 String respString = (String) msg; 24 System.out.println(respString); 25 } 26 27 @Override 28 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 29 ctx.close(); 30 } 31 32 }
1. 原理:无论一次接受到多少数据包,它都会按照设置的固定长度解码,如果是半包消息,则缓存半包消息并等待下个包到达后进行拼包,直到读取到一个完整的包。
2. 回显服务器EchoServer

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; 5 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.FixedLengthFrameDecoder; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder; 11 12 public class EchoServer { 13 14 public void bind(int port) throws Exception { 15 // 服务器NIO线程组线 16 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 17 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 18 try { 19 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); 20 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 21 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 22 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024) 23 .childHandler(new ChildChannelHandler()); 24 // 绑定端口,同步等待成功 25 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); 26 // 等待服务器监听端口关闭 27 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 28 } finally { 29 // 优雅退出,释放线程池资源 30 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 31 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 private class ChildChannelHandler extends ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel> { 36 37 @Override 38 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 39 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(20)); 40 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder()); 41 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler()); 42 } 43 44 } 45 46 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 47 new EchoServer().bind(8080); 48 } 49 50 }
3. 回显服务器EchoServerHandler

1 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 3 4 public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter { 5 6 @Override 7 public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 8 System.out.println(msg); 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { 13 ctx.close(); 14 } 15 16 }
4. 使用telnet命令测试,当长度达到20个字符时,服务器打印。
1. 无法跨语言。Java序列化是Java语言内部的私有协议,其他语言并不支持。
2. 序列化后的码流太大。编码后的字节数组越大,存储的时候就越占空间,存储的硬件成本就越高,网络传输时更占带宽,导致系统的吞吐量降低。
3. 序列化性能太低。编解码耗时长。
4. 解决:编解码框架,如Google Protobuf、MessagePack。此处不深入展开。
1. 由于HTTP协议的通用性,很多异构系统间的通信交互采用HTTP协议,如非常流行的HTTP + XML或者RESTful + JSON。
2. 与Web容器相比,Netty开发HTTP的优势:轻量级;安全。
3. 这里以文件服务器举例,至于HTTP + XML,此处不深入展开。
1. 文件服务器HttpFileServer

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 5 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder; 11 import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler; 12 13 public class HttpFileServer { 14 15 public void run(int port, String folderPath) throws Exception { 16 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 17 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 18 try { 19 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); 20 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 21 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 22 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { 23 24 @Override 25 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 26 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder()); 27 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536)); 28 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder()); 29 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler()); 30 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpFileServerHandler(folderPath)); 31 } 32 33 }); 34 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); 35 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 36 } finally { 37 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 38 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 43 int port = 8080; 44 String folderPath = "E:/workspace"; 45 new HttpFileServer().run(port, folderPath); 46 } 47 48 }
2. 文件服务器HttpFileServerHandler

1 import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; 2 import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; 4 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 5 import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; 6 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpResponse; 7 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultHttpResponse; 8 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders; 11 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpMethod; 12 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponse; 13 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus; 14 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion; 15 import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedFile; 16 import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; 17 18 import java.io.File; 19 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 20 import java.io.RandomAccessFile; 21 import java.net.URLDecoder; 22 23 public class HttpFileServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> { 24 25 private String folderPath; 26 27 public HttpFileServerHandler(String folderPath) { 28 this.folderPath = folderPath; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest req) throws Exception { 33 if (!req.getDecoderResult().isSuccess()) { 34 sendStatus(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST); 35 return; 36 } 37 if (!HttpMethod.GET.equals(req.getMethod())) { 38 sendStatus(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED); 39 return; 40 } 41 String uri = req.getUri(); 42 File file = getFile(uri); 43 if (file == null || file.isHidden() || !file.exists()) { 44 sendStatus(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.NOT_FOUND); 45 return; 46 } 47 try { 48 if (file.isDirectory()) { 49 listFiles(ctx, file, uri); 50 } else { 51 returnFile(ctx, req, file); 52 } 53 } catch (Exception e) { 54 sendStatus(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); 55 } 56 } 57 58 private File getFile(String uri) throws Exception { 59 uri = URLDecoder.decode(uri, "UTF-8"); 60 return new File(folderPath + uri); 61 } 62 63 private void listFiles(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, File folder, String uri) throws Exception { 64 uri = uri.endsWith("/") ? uri : uri + "/"; 65 StringBuilder html = new StringBuilder("<h1>Index of ").append(URLDecoder.decode(uri, "UTF-8")).append("</h1><hr/><pre><a href=\"").append(uri).append("../\">../</a>\n"); 66 File[] subfiles = folder.listFiles(); 67 if (subfiles != null && subfiles.length > 0) { 68 for (File subfile : subfiles) { 69 String name = subfile.getName(); 70 html.append("<a href=\"").append(uri).append(name).append("\">").append(name).append("</a>\n"); 71 } 72 } 73 html.append("</pre><hr/>"); 74 FullHttpResponse resp = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK); 75 resp.headers().add(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html;charset=UTF-8"); 76 ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(html, CharsetUtil.UTF_8); 77 resp.content().writeBytes(content); 78 ctx.writeAndFlush(resp).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); 79 } 80 81 private void returnFile(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest req, File file) throws Exception { 82 83 RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null; 84 try { 85 randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r"); 86 HttpResponse resp = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK); 87 resp.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, randomAccessFile.length()) 88 .set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "application/octet-stream"); 89 if (HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(req.headers().get(HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION))) { 90 resp.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.KEEP_ALIVE); 91 } 92 ctx.write(resp); 93 ctx.writeAndFlush(new ChunkedFile(randomAccessFile, 0, randomAccessFile.length(), 8192)).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); 94 95 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 96 sendStatus(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.NOT_FOUND); 97 } finally { 98 if (randomAccessFile != null) { 99 randomAccessFile.close(); 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 104 private void sendStatus(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpResponseStatus status) throws Exception { 105 HttpResponse resp = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, status); 106 ctx.writeAndFlush(resp).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); 107 } 108 109 }
1. 轮训、Comet等服务器推送技术效率低下,大量消耗服务器带宽和资源。
2. WebSocket的特点:
a) 单一的TCP连接,全双工模式。
b) 对代理、防火墙和路由器透明。
c) 无头部信息、Cookie和身份验证。
d) 无安全开销。
e) 通过“ping/pong”帧保持链路激活。
f) 服务器可以主动传递消息给客户端,客户端不再轮训。
1. 浏览器向服务器发起一个HTTP请求(特别的头信息,Sec-WebSocket-Key是随机的),准备建立WebSocket连接。
GET /chat HTTP/1.1 Host: server.example.com Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Key: x3JJHMbDL1EzLkh9GBhXDw== Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat, superchat Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13 Origin: http://example.com
2. 服务器用Sec-WebSocket-Key加上魔幻字符串“258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11”,先SHA-1加密,再BASE-64编码,作为Sec-WebSocket-Accept返回浏览器。握手完成。
HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Accept: HSmrc0sMlYUkAGmm5OPpG2HaGWk= Sec-WebSocket-Protocol: chat
3. 服务器和浏览器可通过message方式进行通信。
4. 关闭消息带有一个状态码和一个可选的关闭原因,按协议要求发送一个Close控制帧,当对端接受到关闭控制帧指令时,主动关闭WebSocket连接。
1. 服务器WebSocketServer

1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 5 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder; 11 import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler; 12 13 public class WebSocketServer { 14 15 public void run(int port) throws Exception { 16 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 17 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 18 try { 19 ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); 20 serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 21 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 22 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { 23 24 @Override 25 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception { 26 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpRequestDecoder()); 27 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(65536)); 28 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new HttpResponseEncoder()); 29 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler()); 30 socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new WebSocketServerHandler()); 31 } 32 33 }); 34 ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync(); 35 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 36 } finally { 37 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 38 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 43 int port = 8080; 44 new WebSocketServer().run(port); 45 } 46 47 }
2. 服务器WebSocketServerHandler

1 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; 3 import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; 4 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultHttpResponse; 5 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest; 6 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders; 7 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponse; 8 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.CloseWebSocketFrame; 11 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.PingWebSocketFrame; 12 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.PongWebSocketFrame; 13 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.TextWebSocketFrame; 14 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketFrame; 15 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerHandshaker; 16 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.websocketx.WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory; 17 18 import java.util.Date; 19 20 public class WebSocketServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Object> { 21 22 private WebSocketServerHandshaker handshaker; 23 24 @Override 25 protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { 26 // 传统HTTP 27 if (msg instanceof FullHttpRequest) { 28 handleHttpRequest(ctx, (FullHttpRequest) msg); 29 } else if (msg instanceof WebSocketFrame) { 30 handleWebSocketFrame(ctx, (WebSocketFrame) msg); 31 } 32 } 33 34 @Override 35 public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { 36 ctx.flush(); 37 } 38 39 private void handleHttpRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest req) throws Exception { 40 if (!req.getDecoderResult().isSuccess() 41 || !HttpHeaders.Values.WEBSOCKET.toString().equalsIgnoreCase(req.headers().get(HttpHeaders.Names.UPGRADE))) { 42 sendStatus(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST); 43 return; 44 } 45 WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory wsFactory = new WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory("ws://localhost:8080/testws", null, false); 46 handshaker = wsFactory.newHandshaker(req); 47 if (handshaker == null) { 48 WebSocketServerHandshakerFactory.sendUnsupportedWebSocketVersionResponse(ctx.channel()); 49 } else { 50 handshaker.handshake(ctx.channel(), req); 51 } 52 } 53 54 private void handleWebSocketFrame(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, WebSocketFrame frame) throws Exception { 55 if (frame instanceof CloseWebSocketFrame) { 56 handshaker.close(ctx.channel(), (CloseWebSocketFrame) frame.retain()); 57 return; 58 } 59 if (frame instanceof PingWebSocketFrame) { 60 ctx.channel().write(new PongWebSocketFrame(frame.content().retain())); 61 return; 62 } 63 if (!(frame instanceof TextWebSocketFrame)) { 64 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 65 } 66 String req = ((TextWebSocketFrame) frame).text(); 67 ctx.channel().write(new TextWebSocketFrame("欢迎" + req + ",现在时刻" + new Date())); 68 } 69 70 private void sendStatus(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpResponseStatus status) throws Exception { 71 HttpResponse resp = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, status); 72 ctx.writeAndFlush(resp).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); 73 } 74 75 }
3. 浏览器websocketclient.html

1 <script type="text/javascript"> 2 var socket; 3 function initSocket() { 4 if (socket) return; 5 if (!window.WebSocket) window.WebSocket = window.MozWebSocket; 6 if (!window.WebSocket) { 7 alert(‘浏览器不支持WebSocket‘); 8 return; 9 } 10 socket = new WebSocket(‘ws://localhost:8080/testws‘); 11 socket.onmessage = function(event) { 12 alert(event.data); 13 }; 14 socket.onopen = function(event) { 15 alert(‘WebSocket连接建立成功‘); 16 }; 17 socket.onclose = function(event) { 18 alert(‘WebSocket连接已关闭‘); 19 }; 20 } 21 22 function sendMsg() { 23 initSocket(); 24 if (socket && WebSocket && socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) { 25 var msg = document.getElementById(‘msg‘).value; 26 socket.send(msg); 27 } 28 } 29 </script> 30 <input type="text" id="msg"/> 31 <input type="button" value="Send" onclick="sendMsg()"/>
1. Netty采用三层网络架构设计和开发。
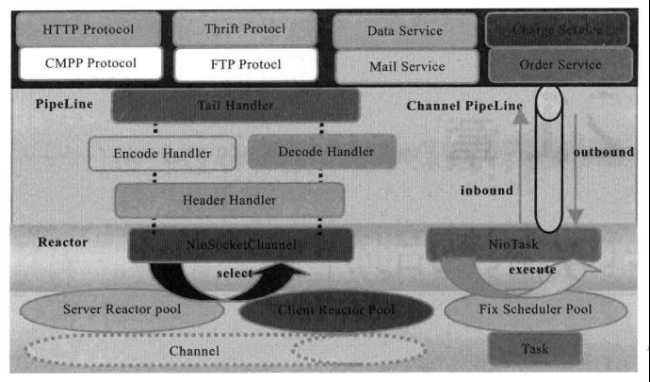
2. Reactor通信调度层(第1层)。负责监听网络的读写和连接操作。将网络层的数据读取到内存缓存区,然后触发各种网络事件,如连接创建、连接激活、读事件、写事件等,将这些事件触发到Pipeline中,有Pipeline管理的责任链进行后续处理。
3. 责任链ChannelPipleline(第2层)。负责事件在责任链中的有序传播,同时动态地编排责任链。通常,由编解码Handler将外部协议消息转换成内部POJO对象,这样上层业务只需关心业务逻辑处理。
4. 业务逻辑编排层Service ChannelHandler(第3层)。通常有两类:存储的业务逻辑编排和其他应用层协议插件,用于特定协议相关的会话和链路管理。
5. 通常,开发者值需关系责任链和业务逻辑编排层。
Netty的高性能是如何实现的?
1. 采用异步非阻塞IO类库,基于Reactor模式实现,解决了传统同步阻塞IO模式下一个服务端无法平滑处理线性增长的客户端的问题。
2. TCP接收和发送缓冲区使用直接内存代替堆内存,避免内存复制,提升了IO读写性能。俗称“零拷贝”(Zero-Copy)。
3. 通过内存池方式循环利用ByteBuf,避免了频繁创建和销毁ByteBuf带来的性能损耗。
4. 可配置IO线程数、TCP参数等,为不同场景提供定制化的调优参数,满足不同的性能场景。
5. 采用环形数组缓冲区实现无锁化并发编程,代替传统的线程安全容器和锁。
6. 合理使用线程安全容器、原子类等,提升系统的并发处理能力。
7. 关键资源的处理使用单线程串行化方式,避免了多线程并发访问带来的锁竞争和额外的CPU资源消耗问题。
8. 通过引用计数器及时申请释放不再被引用的对象,细粒度的内存管理降低了GC频繁,减少了频繁GC带来的延时和CPU损耗。
Netty的可靠性是如何实现的?
1. 链路有效性检测。
a) 长连接无需每次发送消息时创建链路,也无需在消息交互完成后关闭链路,因此相对短链接更高。
b) 为保证长连接有效性,需要周期性心跳检测。一旦发现问题,可以及时关闭链路,重建TCP链接。
2. 内存保护机制。
a) 通过对象引用计数器对ByteBuf等内置对象进行细粒度的内存申请和释放,对非法对象引用进行检测和保护。
b) 通过内存池方式循环利用ByteBuf,节省内存。
c) 可设置内存容量上限,包括ByteBuf、线程池线程数等。
3. 优雅停机。
a) 当系统退出时,JVM通过注册的Shutdown Hook拦截到退出信号量,然后执行退出操作,释放相关模块的资源,将缓冲区的消息处理完成或清空,将待刷新的数据持久化到磁盘或数据库,完成后再退出。
b) 需设置超时时间T,如果达到T后仍然没有退出,则通过“kill -9 pid”强杀进程。
Netty的可定制性是如何实现的?
1. 责任链模式:ChannelPipeline基于责任链模式,便于业务逻辑的拦截、定制和扩展。
2. 基于接口开发:关键类库都提供了接口或抽象类。
3. 提供大量工厂类,重载工厂类可创建用户实现的对象。
4. 提供大量系统参数供用户设置。
可定义私有协议栈。
1. 开发时编写的代码。
a) 数据结构NettyMessage;
b) 消息编解码器NettyMessageEncoder和NettyMessageDecoder;
c) 握手认证Handler LoginAuthReqHanlder和LoginAuthRespHanlder;
d) 心跳检测Handler HearBeatReqHanlder和HearBeatRespHanlder。
2. 私有协议栈细节待补充。
作者:netoxi
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/netoxi
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,未经同意须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。欢迎指正与交流。
标签:bug [] length bytes actor通信 数组 细节 过程 平滑
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/netoxi/p/7289381.html