标签:and tip 就会 启动 种类型 不同 倒序 包装 getname
@Before public void init() { random = new Random(); stuList = new ArrayList<Student>() { { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { add(new Student("student" + i, random.nextInt(50) + 50)); } } }; } public class Student { private String name; private Integer score; //-----getters and setters----- } //1列出班上超过85分的学生姓名,并按照分数降序输出用户名字 @Test public void test1() { List<String> studentList = stuList.stream() .filter(x->x.getScore()>85) .sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getScore).reversed()) .map(Student::getName) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(studentList); }
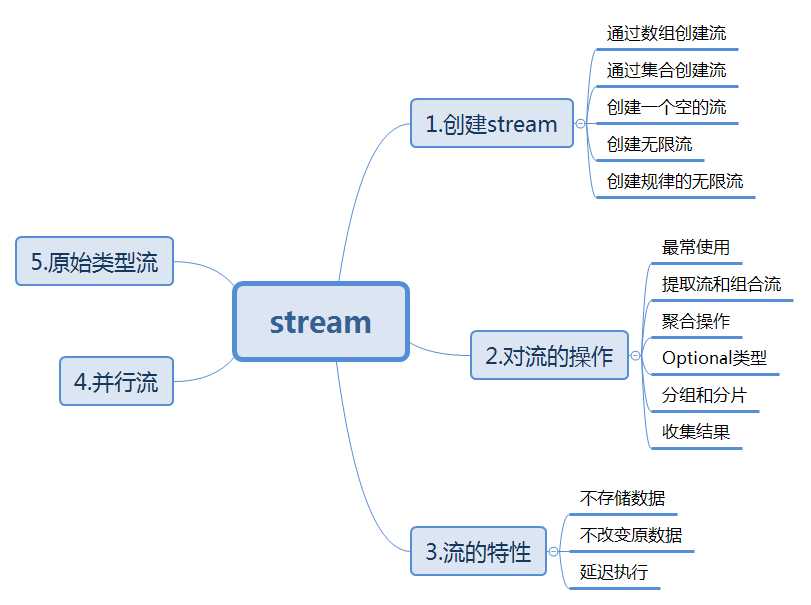
@Test public void test1(){ Stream<String> stream = Stream.generate(()->"user").limit(20); stream.forEach(System.out::println); stream.forEach(System.out::println); }
public boolean filter(Student s) { System.out.println("begin compare"); return s.getScore() > 85; } @Test public void test() { Stream<Student> stream = Stream.of(stuArr).filter(this::filter); System.out.println("split-------------------------------------"); List<Student> studentList = stream.collect(toList()); }

List<String> wordList; @Before public void init() { wordList = new ArrayList<String>() { { add("a"); add("b"); add("c"); add("d"); add("e"); add("f"); add("g"); } }; } /** * 延迟执行特性,在聚合操作之前都可以添加相应元素 */ @Test public void test() { Stream<String> words = wordList.stream(); wordList.add("END"); long n = words.distinct().count(); System.out.println(n); }
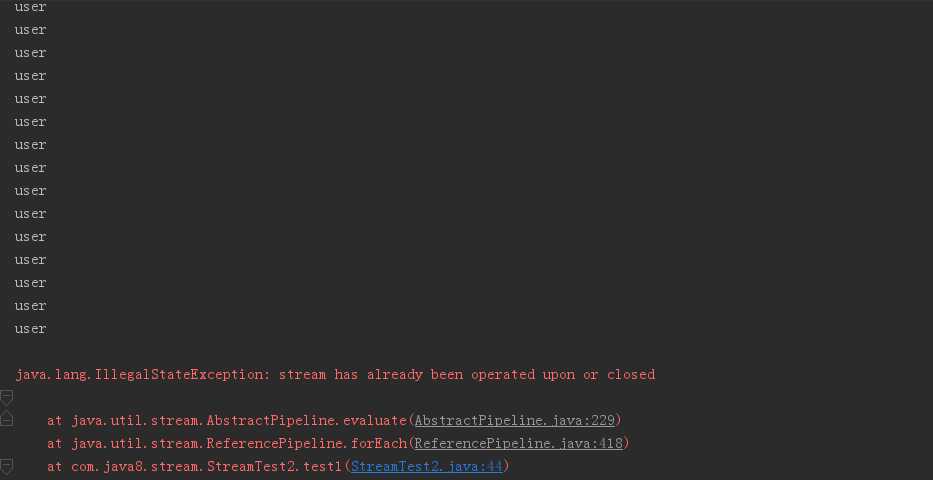
/** * 延迟执行特性,会产生干扰 * nullPointException */ @Test public void test2(){ Stream<String> words1 = wordList.stream(); words1.forEach(s -> { System.out.println("s->"+s); if (s.length() < 4) { System.out.println("select->"+s); wordList.remove(s); System.out.println(wordList); } }); }
/** * 通过数组创建流 */ @Test public void testArrayStream(){ //1.通过Arrays.stream //1.1基本类型 int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,34,5}; IntStream intStream = Arrays.stream(arr); //1.2引用类型 Student[] studentArr = new Student[]{new Student("s1",29),new Student("s2",27)}; Stream<Student> studentStream = Arrays.stream(studentArr); //2.通过Stream.of Stream<Integer> stream1 = Stream.of(1,2,34,5,65); //注意生成的是int[]的流 Stream<int[]> stream2 = Stream.of(arr,arr); stream2.forEach(System.out::println); }
/** * 通过集合创建流 */ @Test public void testCollectionStream(){ List<String> strs = Arrays.asList("11212","dfd","2323","dfhgf"); //创建普通流 Stream<String> stream = strs.stream(); //创建并行流 Stream<String> stream1 = strs.parallelStream(); }
@Test public void testEmptyStream(){ //创建一个空的stream Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.empty(); }
@Test public void testUnlimitStream(){ //创建无限流,通过limit提取指定大小 Stream.generate(()->"number"+new Random().nextInt()).limit(100).forEach(System.out::println); Stream.generate(()->new Student("name",10)).limit(20).forEach(System.out::println); }
/** * 产生规律的数据 */ @Test public void testUnlimitStream1(){ Stream.iterate(0,x->x+1).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); Stream.iterate(0,x->x).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); //Stream.iterate(0,x->x).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);与如下代码意思是一样的 Stream.iterate(0, UnaryOperator.identity()).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); }
/** * map把一种类型的流转换为另外一种类型的流 * 将String数组中字母转换为大写 */ @Test public void testMap() { String[] arr = new String[]{"yes", "YES", "no", "NO"}; Arrays.stream(arr).map(x -> x.toLowerCase()).forEach(System.out::println); }
@Test public void testFilter(){ Integer[] arr = new Integer[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; Arrays.stream(arr).filter(x->x>3&&x<8).forEach(System.out::println); }
/** * flapMap:拆解流 */ @Test public void testFlapMap1() { String[] arr1 = {"a", "b", "c", "d"}; String[] arr2 = {"e", "f", "c", "d"}; String[] arr3 = {"h", "j", "c", "d"}; // Stream.of(arr1, arr2, arr3).flatMap(x -> Arrays.stream(x)).forEach(System.out::println); Stream.of(arr1, arr2, arr3).flatMap(Arrays::stream).forEach(System.out::println); }
String[] arr1 = {"abc","a","bc","abcd"};
/**
* Comparator.comparing是一个键提取的功能
* 以下两个语句表示相同意义
*/
@Test
public void testSorted1_(){
/**
* 按照字符长度排序
*/
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted((x,y)->{
if (x.length()>y.length())
return 1;
else if (x.length()<y.length())
return -1;
else
return 0;
}).forEach(System.out::println);
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* 倒序
* reversed(),java8泛型推导的问题,所以如果comparing里面是非方法引用的lambda表达式就没办法直接使用reversed()
* Comparator.reverseOrder():也是用于翻转顺序,用于比较对象(Stream里面的类型必须是可比较的)
* Comparator. naturalOrder():返回一个自然排序比较器,用于比较对象(Stream里面的类型必须是可比较的)
*/
@Test
public void testSorted2_(){
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(String::length).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println);
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).forEach(System.out::println);
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.naturalOrder()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* thenComparing
* 先按照首字母排序
* 之后按照String的长度排序
*/
@Test
public void testSorted3_(){
Arrays.stream(arr1).sorted(Comparator.comparing(this::com1).thenComparing(String::length)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
public char com1(String x){
return x.charAt(0);
}
@Before public void init(){ arr1 = new String[]{"a","b","c","d"}; arr2 = new String[]{"d","e","f","g"}; arr3 = new String[]{"i","j","k","l"}; } /** * limit,限制从流中获得前n个数据 */ @Test public void testLimit(){ Stream.iterate(1,x->x+2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); } /** * skip,跳过前n个数据 */ @Test public void testSkip(){ // Stream.of(arr1).skip(2).limit(2).forEach(System.out::println); Stream.iterate(1,x->x+2).skip(1).limit(5).forEach(System.out::println); } /** * 可以把两个stream合并成一个stream(合并的stream类型必须相同) * 只能两两合并 */ @Test public void testConcat(){ Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of(arr1); Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of(arr2); Stream.concat(stream1,stream2).distinct().forEach(System.out::println); }
@Before public void init(){ arr = new String[]{"b","ab","abc","abcd","abcde"}; } /** * max、min * 最大最小值 */ @Test public void testMaxAndMin(){ Stream.of(arr).max(Comparator.comparing(String::length)).ifPresent(System.out::println); Stream.of(arr).min(Comparator.comparing(String::length)).ifPresent(System.out::println); } /** * count * 计算数量 */ @Test public void testCount(){ long count = Stream.of(arr).count(); System.out.println(count); } /** * findFirst * 查找第一个 */ @Test public void testFindFirst(){ String str = Stream.of(arr).parallel().filter(x->x.length()>3).findFirst().orElse("noghing"); System.out.println(str); } /** * findAny * 找到所有匹配的元素 * 对并行流十分有效 * 只要在任何片段发现了第一个匹配元素就会结束整个运算 */ @Test public void testFindAny(){ Optional<String> optional = Stream.of(arr).parallel().filter(x->x.length()>3).findAny(); optional.ifPresent(System.out::println); } /** * anyMatch * 是否含有匹配元素 */ @Test public void testAnyMatch(){ Boolean aBoolean = Stream.of(arr).anyMatch(x->x.startsWith("a")); System.out.println(aBoolean); } @Test public void testStream1() { Optional<Integer> optional = Stream.of(1,2,3).filter(x->x>1).reduce((x,y)->x+y); System.out.println(optional.get()); }
@Test public void testOptional() { List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>() { { add("user1"); add("user2"); } }; Optional<String> opt = Optional.of("andy with u"); opt.ifPresent(list::add); list.forEach(System.out::println); }
@Test public void testOptional2() { Integer[] arr = new Integer[]{4,5,6,7,8,9}; Integer result = Stream.of(arr).filter(x->x>9).max(Comparator.naturalOrder()).orElse(-1); System.out.println(result); Integer result1 = Stream.of(arr).filter(x->x>9).max(Comparator.naturalOrder()).orElseGet(()->-1); System.out.println(result1); Integer result2 = Stream.of(arr).filter(x->x>9).max(Comparator.naturalOrder()).orElseThrow(RuntimeException::new); System.out.println(result2); }
@Test public void testStream1() { Optional<Student> studentOptional = Optional.of(new Student("user1",21)); Optional<String> optionalStr = studentOptional.map(Student::getName); System.out.println(optionalStr.get()); } public static Optional<Double> inverse(Double x) { return x == 0 ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(1 / x); } public static Optional<Double> squareRoot(Double x) { return x < 0 ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(Math.sqrt(x)); } /** * Optional的迭代 */ @Test public void testStream2() { double x = 4d; Optional<Double> result1 = inverse(x).flatMap(StreamTest7::squareRoot); result1.ifPresent(System.out::println); Optional<Double> result2 = Optional.of(4.0).flatMap(StreamTest7::inverse).flatMap(StreamTest7::squareRoot); result2.ifPresent(System.out::println); }
Student[] students; @Before public void init(){ students = new Student[100]; for (int i=0;i<30;i++){ Student student = new Student("user",i); students[i] = student; } for (int i=30;i<60;i++){ Student student = new Student("user"+i,i); students[i] = student; } for (int i=60;i<100;i++){ Student student = new Student("user"+i,i); students[i] = student; } } @Test public void testCollect1(){ /** * 生成List */ List<Student> list = Arrays.stream(students).collect(toList()); list.forEach((x)-> System.out.println(x)); /** * 生成Set */ Set<Student> set = Arrays.stream(students).collect(toSet()); set.forEach((x)-> System.out.println(x)); /** * 如果包含相同的key,则需要提供第三个参数,否则报错 */ Map<String,Integer> map = Arrays.stream(students).collect(toMap(Student::getName,Student::getScore,(s,a)->s+a)); map.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); } /** * 生成数组 */ @Test public void testCollect2(){ Student[] s = Arrays.stream(students).toArray(Student[]::new); for (int i=0;i<s.length;i++) System.out.println(s[i]); } /** * 指定生成的类型 */ @Test public void testCollect3(){ HashSet<Student> s = Arrays.stream(students).collect(toCollection(HashSet::new)); s.forEach(System.out::println); } /** * 统计 */ @Test public void testCollect4(){ IntSummaryStatistics summaryStatistics = Arrays.stream(students).collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Student::getScore)); System.out.println("getAverage->"+summaryStatistics.getAverage()); System.out.println("getMax->"+summaryStatistics.getMax()); System.out.println("getMin->"+summaryStatistics.getMin()); System.out.println("getCount->"+summaryStatistics.getCount()); System.out.println("getSum->"+summaryStatistics.getSum()); }
Student[] students; @Before public void init(){ students = new Student[100]; for (int i=0;i<30;i++){ Student student = new Student("user1",i); students[i] = student; } for (int i=30;i<60;i++){ Student student = new Student("user2",i); students[i] = student; } for (int i=60;i<100;i++){ Student student = new Student("user3",i); students[i] = student; } } @Test public void testGroupBy1(){ Map<String,List<Student>> map = Arrays.stream(students).collect(groupingBy(Student::getName)); map.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); } /** * 如果只有两类,使用partitioningBy会比groupingBy更有效率 */ @Test public void testPartitioningBy(){ Map<Boolean,List<Student>> map = Arrays.stream(students).collect(partitioningBy(x->x.getScore()>50)); map.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); } /** * downstream指定类型 */ @Test public void testGroupBy2(){ Map<String,Set<Student>> map = Arrays.stream(students).collect(groupingBy(Student::getName,toSet())); map.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); } /** * downstream 聚合操作 */ @Test public void testGroupBy3(){ /** * counting */ Map<String,Long> map1 = Arrays.stream(students).collect(groupingBy(Student::getName,counting())); map1.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); /** * summingInt */ Map<String,Integer> map2 = Arrays.stream(students).collect(groupingBy(Student::getName,summingInt(Student::getScore))); map2.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); /** * maxBy */ Map<String,Optional<Student>> map3 = Arrays.stream(students).collect(groupingBy(Student::getName,maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getScore)))); map3.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); /** * mapping */ Map<String,Set<Integer>> map4 = Arrays.stream(students).collect(groupingBy(Student::getName,mapping(Student::getScore,toSet()))); map4.forEach((x,y)-> System.out.println(x+"->"+y)); }
DoubleStream doubleStream; IntStream intStream; /** * 原始类型流的初始化 */ @Before public void testStream1(){ doubleStream = DoubleStream.of(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.8); intStream = IntStream.of(1,3,5,7,9); IntStream stream1 = IntStream.rangeClosed(0,100); IntStream stream2 = IntStream.range(0,100); } /** * 流与原始类型流的转换 */ @Test public void testStream2(){ Stream<Double> stream = doubleStream.boxed(); doubleStream = stream.mapToDouble(Double::new); }
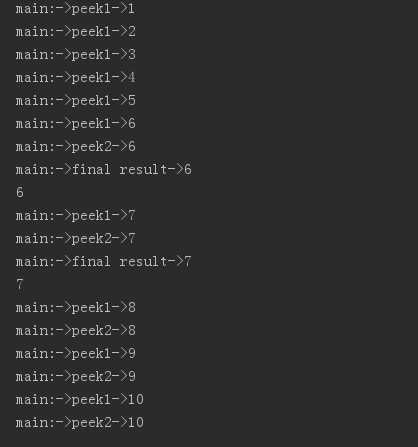
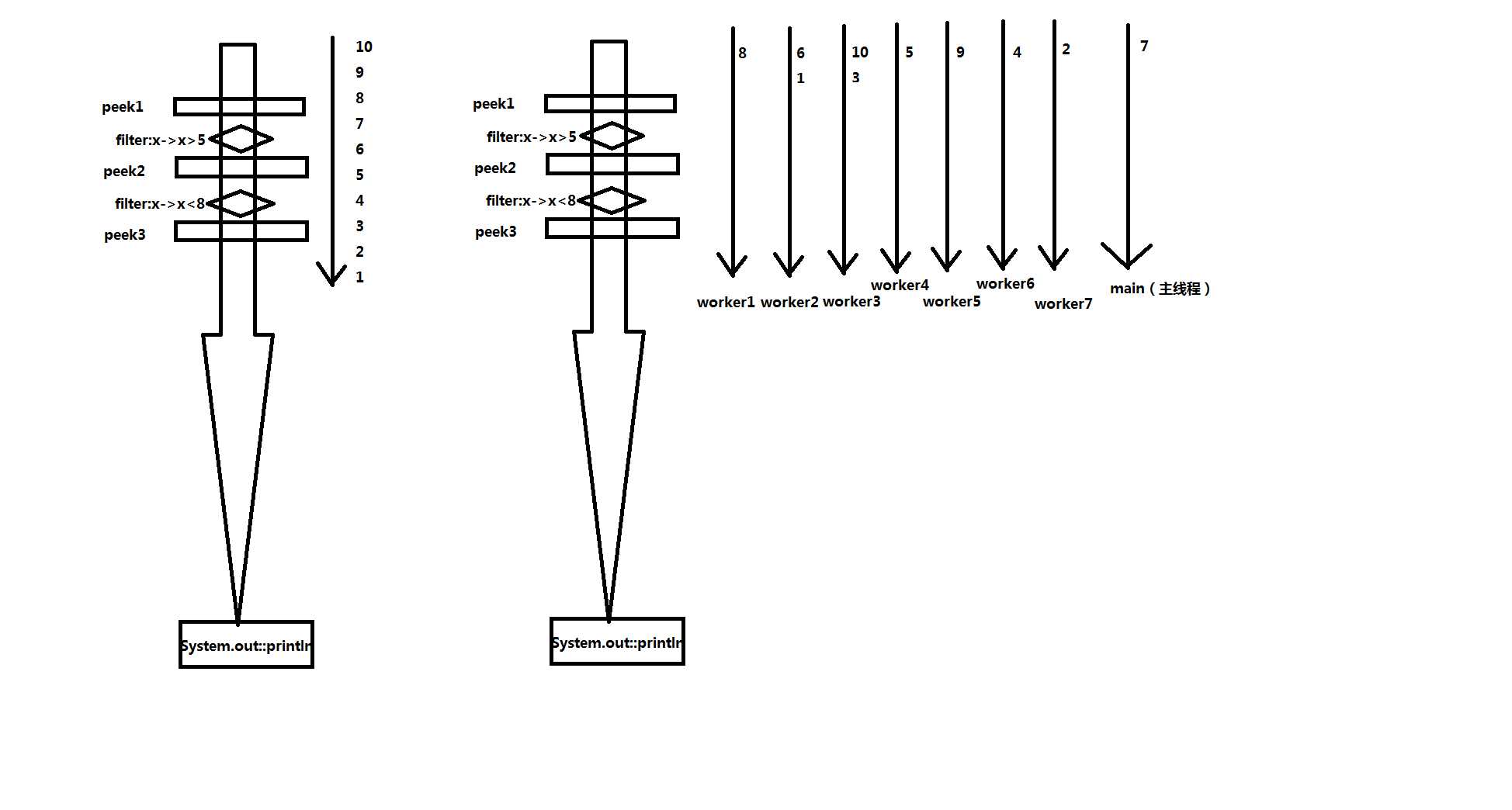
public void peek1(int x) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->peek1->" + x); } public void peek2(int x) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->peek2->" + x); } public void peek3(int x) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":->final result->" + x); } /** * peek,监控方法 * 串行流和并行流的执行顺序 */ @org.junit.Test public void testPeek() { Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 1).limit(10); stream.peek(this::peek1).filter(x -> x > 5) .peek(this::peek2).filter(x -> x < 8) .peek(this::peek3) .forEach(System.out::println); } @Test public void testPeekPal() { Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.iterate(1, x -> x + 1).limit(10).parallel(); stream.peek(this::peek1).filter(x -> x > 5) .peek(this::peek2).filter(x -> x < 8) .peek(this::peek3) .forEach(System.out::println); }
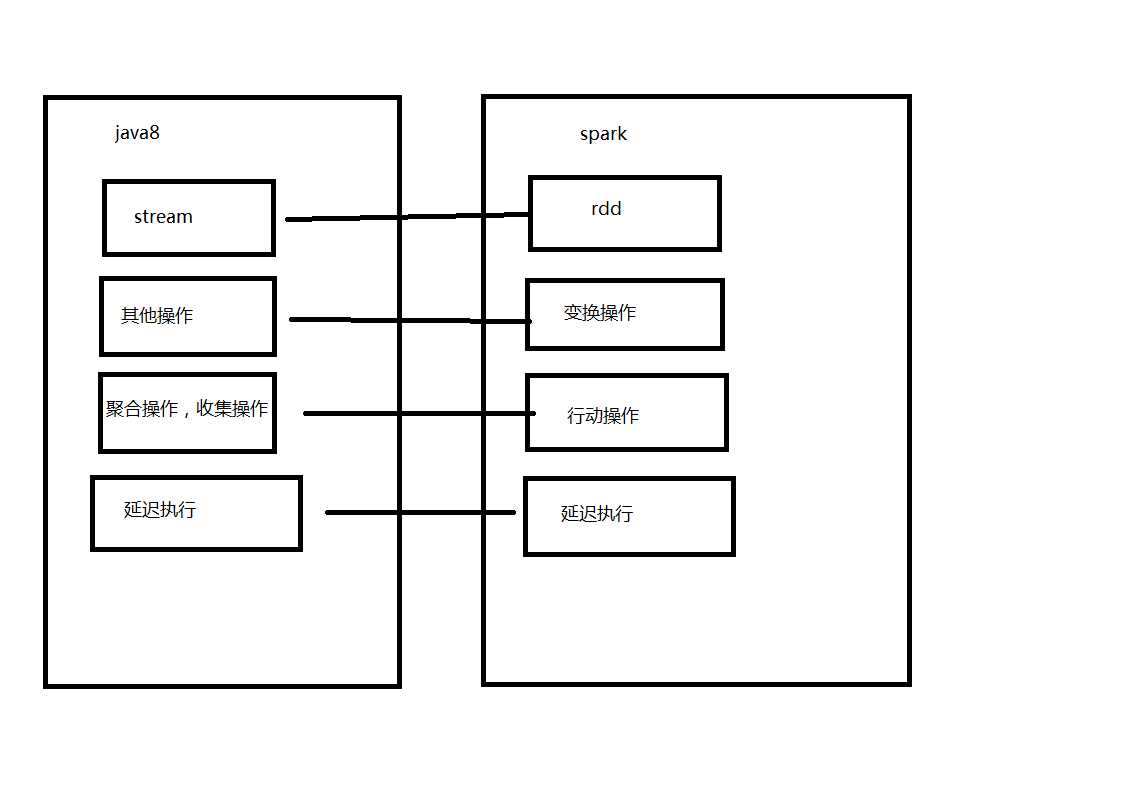
/** * 生成一亿条0-100之间的记录 */ @Before public void init() { Random random = new Random(); list = Stream.generate(() -> random.nextInt(100)).limit(100000000).collect(toList()); } /** * tip */ @org.junit.Test public void test1() { long begin1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); list.stream().filter(x->(x > 10)).filter(x->x<80).count(); long end1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end1-begin1); list.stream().parallel().filter(x->(x > 10)).filter(x->x<80).count(); long end2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end2-end1); long begin1_ = System.currentTimeMillis(); list.stream().filter(x->(x > 10)).filter(x->x<80).distinct().sorted().count(); long end1_ = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end1-begin1); list.stream().parallel().filter(x->(x > 10)).filter(x->x<80).distinct().sorted().count(); long end2_ = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end2_-end1_); }

val count = sc.parallelize(1 to NUM_SAMPLES).filter { _ =>
val x = math.random
val y = math.random
x*x + y*y < 1}.count()println(s"Pi is roughly ${4.0 * count / NUM_SAMPLES}")
标签:and tip 就会 启动 种类型 不同 倒序 包装 getname
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/andywithu/p/7404101.html